Abstract
Purpose
The aim of our study is to identify radiological patterns of cortical gray matter atrophy (CGMA) that correlate with disease duration in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS).
Methods
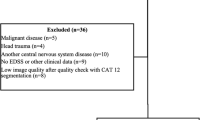
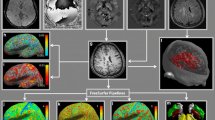
RRMS patients were randomly selected from the Sheba Multiple Sclerosis (MS) center computerized data registry based on stratification of disease duration up to 10 years. Patients were scanned by 3.0 T (Signa, GE) MRI, using a T1 weighted 3D high resolution, FSPGR, MS protocol. Neurological disability was assessed by the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). FreeSurfer was used to obtain brain volumetric segmentation and to perform cortical thickness surface-based analysis. Clusters of change in cortical thickness with correlation to disease duration were produced.
Results
Two hundred seventy-one RRMS patients, mean ± SD age 33.0 ± 7.0 years, EDSS 1.6 ± 1.2, disease duration 5.0 ± 3.4 years. Cortical thickness analysis demonstrated focal areas of cerebral thinning that correlated with disease duration. Seven clusters accounting for 11.7% of the left hemisphere surface and eight clusters accounting for 10.6% of the right hemisphere surface were identified, with cluster-wise probability of p < 0.002 and p < 0.02, respectively.The clusters included bilateral involvement of areas within the cingulate, precentral, postcentral, paracentral, superior-parietal, superior-frontal gyri and insular cortex. Mean and cluster-wise cortical thickness negatively correlated with EDSS score, p < 0.001, with stronger Spearman rho for cluster-wise measurements.
Conclusions
We identified CGMA patterns in sensitive brain regions which give insight and better understanding of the progression of cortical gray matter loss in relation to dissemination in space and time. These patterns may serve as markers to modulate therapeutic interventions to improve the management of MS patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudick RA, Trapp BD (2009) Gray-matter injury in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 361(15):1505–1506. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcibr0905482
Calabrese M, Rinaldi F, Grossi P, Mattisi I, Bernardi V, Favaretto A, Perini P, Gallo P (2010) Basal ganglia and frontal/parietal cortical atrophy is associated with fatigue in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 16(10):1220–1228. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458510376405
Houtchens MK, Benedict RH, Killiany R, Sharma J, Jaisani Z, Singh B, Weinstock-Guttman B, Guttmann CR, Bakshi R (2007) Thalamic atrophy and cognition in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 69(12):1213–1223. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000276992.17011.b5
Pellicano C, Gallo A, Li X, Ikonomidou VN, Evangelou IE, Ohayon JM, Stern SK, Ehrmantraut M, Cantor F, McFarland HF, Bagnato F (2010) Relationship of cortical atrophy to fatigue in patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 67(4):447–453. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2010.48
Nygaard GO, Walhovd KB, Sowa P, Chepkoech JL, Bjornerud A, Due-Tonnessen P, Landro NI, Damangir S, Spulber G, Storsve AB, Beyer MK, Fjell AM, Celius EG, Harbo HF (2015) Cortical thickness and surface area relate to specific symptoms in early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 21(4):402–414. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458514543811
Charil A, Dagher A, Lerch JP, Zijdenbos AP, Worsley KJ, Evans AC (2007) Focal cortical atrophy in multiple sclerosis: relation to lesion load and disability. NeuroImage 34(2):509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.10.006
Calabrese M, Atzori M, Bernardi V, Morra A, Romualdi C, Rinaldi L, McAuliffe MJ, Barachino L, Perini P, Fischl B, Battistin L, Gallo P (2007) Cortical atrophy is relevant in multiple sclerosis at clinical onset. J Neurol 254(9):1212–1220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0503-6
Pirko I, Lucchinetti CF, Sriram S, Bakshi R (2007) Gray matter involvement in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 68(9):634–642. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000250267.85698.7a
Fisniku LK, Chard DT, Jackson JS, Anderson VM, Altmann DR, Miszkiel KA, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2008) Gray matter atrophy is related to long-term disability in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 64(3):247–254. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21423
Roosendaal SD, Bendfeldt K, Vrenken H, Polman CH, Borgwardt S, Radue EW, Kappos L, Pelletier D, Hauser SL, Matthews PM, Barkhof F, Geurts JJ (2011) Grey matter volume in a large cohort of MS patients: relation to MRI parameters and disability. Mult Scler (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 17(9):1098–1106. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458511404916
Calabrese M, Favaretto A, Poretto V, Romualdi C, Rinaldi F, Mattisi I, Morra A, Perini P, Gallo P (2013) Low degree of cortical pathology is associated with benign course of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 19(7):904–911. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458512463767
Chen JT, Narayanan S, Collins DL, Smith SM, Matthews PM, Arnold DL (2004) Relating neocortical pathology to disability progression in multiple sclerosis using MRI. NeuroImage 23(3):1168–1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.046
Achiron A, Chapman J, Magalashvili D, Dolev M, Lavie M, Bercovich E, Polliack M, Doniger GM, Stern Y, Khilkevich O, Menascu S, Hararai G, Gurevich M, Barak Y (2013) Modeling of cognitive impairment by disease duration in multiple sclerosis: a cross-sectional study. PLoS One 8(8):e71058. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071058
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O'Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thompson AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69(2):292–302. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22366
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(20):11050–11055. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.200033797
Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C, van der Kouwe A, Killiany R, Kennedy D, Klaveness S, Montillo A, Makris N, Rosen B, Dale AM (2002) Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron 33(3):341–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00569-X
Fischl B, Salat DH, van der Kouwe AJ, Makris N, Segonne F, Quinn BT, Dale AM (2004) Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage 23(Suppl 1):S69–S84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.016
Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Buckner RL, Dale AM, Maguire RP, Hyman BT, Albert MS, Killiany RJ (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 31(3):968–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021
Fischl B, van der Kouwe A, Destrieux C, Halgren E, Segonne F, Salat DH, Busa E, Seidman LJ, Goldstein J, Kennedy D, Caviness V, Makris N, Rosen B, Dale AM (2004) Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 14(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhg087
Rosas HD, Liu AK, Hersch S, Glessner M, Ferrante RJ, Salat DH, van der Kouwe A, Jenkins BG, Dale AM, Fischl B (2002) Regional and progressive thinning of the cortical ribbon in Huntington's disease. Neurology 58(5):695–701. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.58.5.695
Kuperberg GR, Broome MR, McGuire PK, David AS, Eddy M, Ozawa F, Goff D, West WC, Williams SC, van der Kouwe AJ, Salat DH, Dale AM, Fischl B (2003) Regionally localized thinning of the cerebral cortex in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60(9):878–888. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.60.9.878
Salat DH, Buckner RL, Snyder AZ, Greve DN, Desikan RS, Busa E, Morris JC, Dale AM, Fischl B (2004) Thinning of the cerebral cortex in aging. Cereb Cortex 14(7):721–730. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhh032
Han X, Jovicich J, Salat D, van der Kouwe A, Quinn B, Czanner S, Busa E, Pacheco J, Albert M, Killiany R, Maguire P, Rosas D, Makris N, Dale A, Dickerson B, Fischl B (2006) Reliability of MRI-derived measurements of human cerebral cortical thickness: the effects of field strength, scanner upgrade and manufacturer. NeuroImage 32(1):180–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.051
Hagler DJ Jr, Saygin AP, Sereno MI (2006) Smoothing and cluster thresholding for cortical surface-based group analysis of fMRI data. NeuroImage 33(4):1093–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.07.036
Abe O, Yamasue H, Aoki S, Suga M, Yamada H, Kasai K, Masutani Y, Kato N, Kato N, Ohtomo K (2008) Aging in the CNS: comparison of gray/white matter volume and diffusion tensor data. Neurobiol Aging 29(1):102–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.09.003
Dickerson BC, Feczko E, Augustinack JC, Pacheco J, Morris JC, Fischl B, Buckner RL (2009) Differential effects of aging and Alzheimer's disease on medial temporal lobe cortical thickness and surface area. Neurobiol Aging 30(3):432–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.07.022
Fjell AM, Westlye LT, Amlien I, Espeseth T, Reinvang I, Raz N, Agartz I, Salat DH, Greve DN, Fischl B, Dale AM, Walhovd KB (2009) High consistency of regional cortical thinning in aging across multiple samples. Cereb Cortex 19(9):2001–2012. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhn232
De Stefano N, Airas L, Grigoriadis N, Mattle HP, O'Riordan J, Oreja-Guevara C, Sellebjerg F, Stankoff B, Walczak A, Wiendl H, Kieseier BC (2014) Clinical relevance of brain volume measures in multiple sclerosis. CNS drugs 28(2):147–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-014-0140-z
Achiron A, Chapman J, Tal S, Bercovich E, Gil H, Achiron A (2012) Superior temporal gyrus thickness correlates with cognitive performance in multiple sclerosis. Brain Struct Funct 218(4):943–950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0440-3
Narayana PA, Govindarajan KA, Goel P, Datta S, Lincoln JA, Cofield SS, Cutter GR, Lublin FD, Wolinsky JS, Houston MRIACa, The CombiRx Investigators G (2012) Regional cortical thickness in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis: a multi-center study. Neuroimage Clin 2:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2012.11.009
Sailer M, Fischl B, Salat D, Tempelmann C, Schonfeld MA, Busa E, Bodammer N, Heinze HJ, Dale A (2003) Focal thinning of the cerebral cortex in multiple sclerosis. Brain J Neurol 126(Pt 8):1734–1744. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awg175
Bergsland N, Horakova D, Dwyer MG, Uher T, Vaneckova M, Tyblova M, Seidl Z, Krasensky J, Havrdova E, Zivadinov R (2018) Gray matter atrophy patterns in multiple sclerosis: a 10-year source-based morphometry study. Neuroimage Clin 17(supplement C):444–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.11.002
Merkel B, Butzkueven H, Traboulsee AL, Havrdova E, Kalincik T (2017) Timing of high-efficacy therapy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev 16(6):658–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2017.04.010
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. Yael Nissan for data assessment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest disclosure
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Sheba Medical Center IRB Committee and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
For this type of retrospective study formal consent is not required; however, patient confidentiality was observed by removing any identifying information from the study database.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orbach, L., Menascu, S., Hoffmann, C. et al. Focal cortical thinning in patients with stable relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: cross-sectional-based novel estimation of gray matter kinetics. Neuroradiology 60, 179–187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1964-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1964-2