Abstract
Exosomes are special extracellular vesicles secreted by cells, which are of great significance in the basic research of life science and clinical application and has become a hot research field with rapid development in recent 10 years. Therefore, the isolation and separation of exosomes is particularly important for the research and application of exosomes. This paper aims to review the research progress of exosome isolation and separation methods in recent years, including ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, size‑exclusion chromatography, precipitation, immunomagnetic bead capture method, aptamer-based isolation, and isolation methods based on microfluidic technology. It is generally accepted that most of the existing methods have limitations, for example, ultracentrifugation is time-consuming and laborious, and immunomagnetic bead capture method and aptamer-based separation method have small sample processing capacity and high cost. As a result, we also introduce some common situations in which two or more methods are combined for use. Finally, the separation and isolation methods including all those presented in this review were compared and summarized.
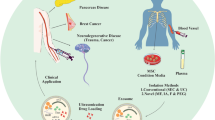
Graphical Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Anderson NG (1966) An introduction to particle separations in zonal centrifuges. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 21:9–39 (PMID: 5926674)
Bang C, Thum T (2012) Exosomes: new players in cell-cell communication. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(11):2060–2064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2012.08.007 (Epub 2012 Aug 10 PMID: 22903023)
Benedikter BJ, Bouwman FG, Vajen T, Heinzmann ACA, Grauls G, Mariman EC, Wouters EFM, Savelkoul PH, Lopez-Iglesias C, Koenen RR, Rohde GGU, Stassen FRM (2017) Ultrafiltration combined with size exclusion chromatography efficiently isolates extracellular vesicles from cell culture media for compositional and functional studies. Sci Rep 7(1):15297. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15717-7
Bobrie A, Colombo M, Krumeich S, Raposo G, Théry C (2012) Diverse subpopulations of vesicles secreted by different intracellular mechanisms are present in exosome preparations obtained by differential ultracentrifugation. J Extracell Vesicles 16:1. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v1i0.18397.PMID:24009879;PMCID:PMC3760636
Chen C, Skog J, Hsu CH, Lessard RT, Balaj L, Wurdinger T, Carter BS, Breakefield XO, Toner M, Irimia D (2010) Microfluidic isolation and transcriptome analysis of serum microvesicles. Lab Chip 10(4):505–511. https://doi.org/10.1039/b916199f
Chen W, Cao R, Su W, Zhang X, Xu Y, Wang P, Gan Z, Xie Y, Li H, Qin J (2021) Simple and fast isolation of circulating exosomes with a chitosan modified shuttle flow microchip for breast cancer diagnosis. Lab Chip 21(9):1759–1770. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0lc01311k (PMID: 33710183)
Contreras-Naranjo JC, Wu HJ, Ugaz VM (2017) Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab Chip 17(21):3558–3577. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7lc00592j
Cvjetkovic A, Lötvall J, Lässer C (2014) The influence of rotor type and centrifugation time on the yield and purity of extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 25:3. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v3.23111 (PMID:24678386;PMCID:PMC3967015)
Doyle LM, Wang MZ (2019) Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells 8(7):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8070727
Gardiner C, Di Vizio D, Sahoo S, Théry C, Witwer KW, Wauben M, Hill AF (2016) Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: results of a worldwide survey. J Extracell Vesicles 31(5):32945. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v5.32945
Guan S, Yu H, Yan G, Gao M, Sun W, Zhang X (2020) Characterization of urinary exosomes purified with size exclusion chromatography and ultracentrifugation. J Proteome Res 19(6):2217–2225. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00693 (Epub 2020 Apr 28 PMID: 32248692)
Hassanpour Tamrin S, Sanati Nezhad A, Sen A (2021) Label-free isolation of exosomes using microfluidic technologies. ACS Nano. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c03469 (PMID: 34723478)
He M, Crow J, Roth M, Zeng Y, Godwin AK (2014) Integrated immunoisolation and protein analysis of circulating exosomes using microfluidic technology. Lab Chip 14(19):3773–3780. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4lc00662c
Hendrix A (2021) The nature of blood(y) extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(4):243. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00348-8 (PMID: 33568799)
Huang LR, Cox EC, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2004) Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304(5673):987–990. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094567 (PMID: 15143275)
Iliescu FS, Vrtačnik D, Neuzil P, Iliescu C (2019) Microfluidic technology for clinical applications of exosomes. Micromachines (basel) 10(6):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060392.PMID:31212754;PMCID:PMC6631586
Jin-ge QIU, De-wu LIU, Bao-li SUN, Yao-kun LI, Yong-qing GUO, Ming DENG, Guang-bin LIU (2020) Research progress on animal exosome isolation methods. China Biotechnology 40(9):36–42. https://doi.org/10.13523/j.cb.2004051
Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C (1987) Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem 262(19):9412–9420
Koh YQ, Almughlliq FB, Vaswani K, Peiris HN, Mitchell MD (2018) Exosome enrichment by ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography. Front Biosci (landmark Ed) 23(5):865–874. https://doi.org/10.2741/4621 (PMID: 28930577)
Le MN, Fan ZH (2021) Exosome isolation using nanostructures and microfluidic devices. Biomed Mater 16(2):022005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/abde70.PMID:33477118;PMCID:PMC8082697
Lee K, Shao H, Weissleder R, Lee H (2015) Acoustic purification of extracellular microvesicles. ACS Nano 9(3):2321–2327. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn506538f
Liang L-G et al (2017) An integrated double-filtration microfluidic device for isolation, enrichment and quantification of urinary extracellular vesicles for detection of bladder cancer. Sci Rep 7:46224. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46224
Liao Z, Li Y, Gu L, Lei R, Miao Y, Lan H, Deng Y, Geng L (2019) Advances in microfluidic chip-based extracellular vesicle separation. Se Pu. 37(4):343–347. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1123.2018.11045
Liu C, Guo J, Tian F, Yang N, Yan F, Ding Y, Wei J, Hu G, Nie G, Sun J (2017) Field-free isolation of exosomes from extracellular vesicles by microfluidic viscoelastic flows. ACS Nano 11(7):6968–6976. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b02277 (Epub 2017 Jul 7 PMID: 28679045)
Liu C, Zhao J, Tian F, Chang J, Zhang W, Sun J (2019) λ-DNA- and aptamer-mediated sorting and analysis of extracellular vesicles. J Am Chem Soc 141(9):3817–3821. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b00007 (Epub 2019 Feb 22 PMID: 30789261)
Livshits MA, Khomyakova E, Evtushenko EG, Lazarev VN, Kulemin NA, Semina SE, Generozov EV, Govorun VM (2015) Isolation of exosomes by differential centrifugation: theoretical analysis of a commonly used protocol. Sci Rep 30(5):17319. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17319
Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW, Wong CS, Wiegmans AP, Leimgruber A, Möller A (2015) Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles 17(4):27031. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.27031
Mathieu M, Névo N, Jouve M, Valenzuela JI, Maurin M, Verweij FJ, Palmulli R, Lankar D, Dingli F, Loew D, Rubinstein E, Boncompain G, Perez F, Théry C (2021) Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9. Nat Commun 12(1):4389. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24384-2.PMID:34282141;PMCID:PMC8289845
Mousavi SM, Amin Mahdian SM, Ebrahimi MS, Taghizadieh M, Vosough M, Sadri Nahand J, Hosseindoost S, Vousooghi N, Javar HA, Larijani B, Hadjighassem MR, Rahimian N, Hamblin MR, Mirzaei H (2022) Microfluidics for detection of exosomes and microRNAs in cancer: State of the art. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 27(28):758–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2022.04.011
Na LIU, Pan-pan DU, Yang YANG, Xiao-mao LI (2019) Research progress on exosomes isolation methods based on microfluidics technology[J]. Biotechnol Bull 35(1):207–213. https://doi.org/10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2018-0571
Pan BT, Johnstone RM (1983) Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 33(3):967–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(83)90040-5 (PMID: 6307529)
Raju D, Bathini S, Badilescu S, Ghosh A, Packirisamy M (2022) Microfluidic platforms for the isolation and detection of exosomes: a brief review. Micromachines 13(5):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050730
Rashed MH, Bayraktar E, Helal KG, Abd-Ellah MF, Amero P, Chavez-Reyes A, Rodriguez-Aguayo C (2017) Exosomes: From Garbage Bins to Promising Therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 18(3): 538 doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030538. PMID: 28257101; PMCID: PMC5372554.
Shirejini SZ, Inci F (2022) The Yin and Yang of exosome isolation methods: conventional practice, microfluidics, and commercial kits. Biotechnol Adv 54:107814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107814
Sidhom K, Obi PO, Saleem A (2020) A review of exosomal isolation methods: is size exclusion chromatography the best option? Int J Mol Sci 21(18):6466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186466
Smith JT, Wunsch BH, Dogra N, Ahsen ME, Lee K, Yadav KK, Weil R, Pereira MA, Patel JV, Duch EA, Papalia JM, Lofaro MF, Gupta M, Tewari AK, Cordon-Cardo C, Stolovitzky G, Gifford SM (2018) Integrated nanoscale deterministic lateral displacement arrays for separation of extracellular vesicles from clinically-relevant volumes of biological samples. Lab Chip 18(24):3913–3925. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8lc01017j (PMID: 30468237)
Su W, Li H, Chen W, Qin J (2019) Microfluidic strategies for label-free exosomes isolation and analysis Trac Trends Anal. Chem 118:686–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.06.037
Tian Y, Gong M, Hu Y, Liu H, Zhang W, Zhang M, Hu X, Aubert D, Zhu S, Wu L, Yan X (2019) Quality and efficiency assessment of six extracellular vesicle isolation methods by nano-flow cytometry. J Extracell Vesicles 9(1):1697028. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2019.1697028
Tulkens J, De Wever O, Hendrix A (2020) Analyzing bacterial extracellular vesicles in human body fluids by orthogonal biophysical separation and biochemical characterization. Nat Protoc 15(1):40–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0236-5 (Epub 2019 Nov 27 PMID: 31776460)
Vergauwen G, Dhondt B, Van Deun J, De Smedt E, Berx G, Timmerman E, Gevaert K, Miinalainen I, Cocquyt V, Braems G, Van den Broecke R, Denys H, De Wever O, Hendrix A (2017) Confounding factors of ultrafiltration and protein analysis in extracellular vesicle research. Sci Rep 7(1):2704. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02599-y
Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, Bora A, Lässer C, Lötvall J, Nolte-’t Hoen EN, Piper MG, Sivaraman S, Skog J, Théry C, Wauben MH, Hochberg F (2013) Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles 27:2. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v2i0.20360
Wu M, Ouyang Y, Wang Z, Zhang R, Huang PH, Chen C, Li H, Li P, Quinn D, Dao M, Suresh S, Sadovsky Y, Huang TJ (2017) Isolation of exosomes from whole blood by integrating acoustics and microfluidics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(40):10584–10589. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1709210114
Xu H, Liao C, Zuo P, Liu Z, Ye BC (2018) Magnetic-based microfluidic device for on-chip isolation and detection of tumor-derived exosomes. Anal Chem 90(22):13451–13458. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03272 (Epub 2018 Oct 3 PMID: 30234974)
Yu-Xing Z, Xiang Z, Wen-Jie C, Li-Guo Z (2018) Research progress on the methods of exosome isolation [J]. E-Journal of Translational Medicine 5(04):42–46
Zarovni N, Corrado A, Guazzi P, Zocco D, Lari E, Radano G, Muhhina J, Fondelli C, Gavrilova J, Chiesi A (2015) Integrated isolation and quantitative analysis of exosome shuttled proteins and nucleic acids using immunocapture approaches. Methods 1(87):46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.05.028 (Epub 2015 Jun 2 PMID: 26044649)
Zhang K, Yue Y, Wu S, Liu W, Shi J, Zhang Z (2019) Rapid capture and nondestructive release of extracellular vesicles using aptamer-based magnetic isolation. ACS Sens 4(5):1245–1251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00060 (Epub 2019 Apr 29 PMID: 30915846)
Zhang H, Zhang Q, Deng Y, Chen M, Yang C (2021) Improving isolation of extracellular vesicles by utilizing nanomaterials. Membranes (basel) 12(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12010055.PMID:35054584;PMCID:PMC8780510
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the laboratory and the research group for their consistent research on new methods for exosome separation. The authors also thank the foundation for its support.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China international (Regional) Cooperation and exchange project “Research on Bio-inspired New Material Additive Manufacturing (Number 5181101987) “.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ES performed the conceptualization; WX, JC, LA wrote the main manuscript text; ES was in charge of review and supervise. WX prepared Fig. 1 and Table 1 and was responsible for the edit. All authors have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, WM., Li, A., Chen, JJ. et al. Research Development on Exosome Separation Technology. J Membrane Biol 256, 25–34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-022-00260-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-022-00260-y