Abstract
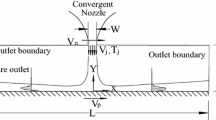
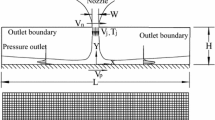
Numerical simulation of the flow field and conjugate heat transfer in an impinging jet with moving impingement plate is one of the important problems as it mimics closely with practical applications in industries. The Yang–Shih version of low Reynolds number k–\(\epsilon\) model has been used to resolve the flow field and the temperature field in a two-dimensional, steady, incompressible, confined, turbulent slot jet impinging normally on a moving flat plate of finite thickness. The turbulence intensity and the Reynolds number considered at the inlet are \(2\,\%\) and 15,000, respectively. The bottom face of the impingement plate has been maintained at a constant temperature higher than the nozzle exit temperature. The confinement plate has been considered to be adiabatic. The nozzle-to-surface spacing for the above study has been taken to be 6 and the surface-to-jet velocity ratios have been taken over a range of 0.25–1. The effects of impingement plate motion on the flow field and temperature field have been discussed elaborately with reference to stationary impingement plate. The dependence of flow field and fluid temperature field on impingement plate motion has been analyzed by plotting streamlines, isotherms for different plate speeds. A thorough study of flow characteristics for different surface-to-jet velocity ratios has been carried out by plotting profiles of mean vertical and horizontal components of velocity, pressure distribution, local shear stress distribution. The isotherms in the impingement plate of finite thickness, the distributions of solid–fluid interface temperature, the local Nusselt number, and the local heat flux for different surface-to-jet velocity ratios added to the understanding of conjugate heat transfer phenomenon.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(G_{n}\) :
-
Production by shear (Eq. 5)
- h, H :
-
Dimensional and nondimensional nozzle-to-plate spacings, respectively
- \(k, k_{n}\) :
-
Dimensional and nondimensional turbulent kinetic energies, respectively
- \(k_{f}, k_{s}\) :
-
Thermal conductivities of fluid and solid, respectively
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity ratio of solid-to-fluid, \(\frac{k_{s}}{k_{f}}\)
- p :
-
Static pressure
- \(p_{\infty }\) :
-
Ambient pressure
- P :
-
Nondimensional pressure
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- \(\text {Pr}_{t}\) :
-
Turbulent Prandtl number
- \(\text {Re}_{t}\) :
-
Turbulent Reynolds number, \(\frac{k^{2}}{\nu \tilde{\epsilon }}\)
- \(\text {Re}_{Y}\) :
-
Nondimensional distance, \(\sqrt{k}y/ \nu\)
- Re:
-
Reynolds number, \(\frac{U_{0}w}{\nu }\)
- s, S :
-
Dimensional and nondimensional solid plate thicknesses, respectively
- \(T, \theta\) :
-
Dimensional and nondimensional temperatures, respectively
- \(U_{1}, U_{2}\) :
-
Nondimensional mean velocities, \(U_{1}=U\) and \(U_{2}=V\) in X and Y directions respectively
- \(u_{1}, u_{2}\) :
-
Dimensional mean velocities, \(u_{1}=u\) and \(u_{2}= v\) in x and y directions respectively
- \(U_{0}\) :
-
Average inlet jet velocity
- \(U_{s}\) :
-
Surface-to-jet velocity ratio
- w :
-
Jet width
- \(x_{i}, X_{i}\) :
-
Dimensional and nondimensional Cartesian coordinates, respectively
- \(\tilde{\epsilon }, \tilde{\epsilon }_{n}\) :
-
Dimensional and nondimensional modified dissipation rates of turbulent kinetic energy, respectively
- \(\alpha , \alpha _{t}, \alpha _{t,n}\) :
-
Laminar, turbulent and nondimensional turbulent thermal diffusivities, respectively
- \(\nu , \nu _{t}, \nu _{t,n}\) :
-
Laminar, turbulent and nondimensional turbulent kinematic viscosities, respectively
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of fluid
References
Achari AM, Das MK (2015) Application of various RANS based models towards predicting turbulent slot jet impingement. Int J Therm Sci 98:332–351
Achari AM, Das MK (2015) Conjugate heat transfer study of turbulent slot impinging jet. Trans ASME J Therm Sci Eng Appl. doi:10.1115/1.4030882
Al-Sanea S (1992) A numerical study of the flow and heat transfer characteristics of an impinging laminar slot-jet including crossflow effects. Int J Heat Mass Transf 35(10):2501–2513
Antonia RA, Browne LWB, Rajagopalan S, Chambers AJ (1983) On the organized motion of a turbulent plane jet. J Fluid Mech 134:49–66
Beitelmal AH, Saad MA, Patel CD (2000) The effect of inclination on the heat transfer between a flat surface and an impinging two-dimensional air jet. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 21:156–163
Biswas G (2002) Turbulent flows: fundamentals, experiments and modeling, chapter The k-\(\epsilon\) model, the RNG k-\(\epsilon\) model and phase-averaged model. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 339–374
Bula AJ, Rahman MM, Leland JE (2000a) Axial steady free surface jet impinging over a flat disk with discrete heat sources. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 21:11–21
Bula AJ, Rahman MM, Leland JE (2000b) Numerical modeling of conjugate heat transfer during impingement of free liquid jet issuing from a slot nozzle. Numer Heat Transf Part A 38:45–66
Chattopadhyay H, Biswas G, Mitra NK (2002) Heat transfer from a moving surface due to impinging slot jets. Trans ASME J Heat Transf 124:433–440
Chattopadhyay H, Saha SK (2001) Numerical investigations of heat transfer over a moving surface due to impinging knife-jets. Numer Heat Transf Part A 39:531–549
Chattopadhyay H, Saha SK (2002) Simulation of laminar slot jets impinging on a moving surface. Trans ASME J Heat Transf 124:1049–1055
Chattopadhyay H, Saha SK (2003) Turbulent flow and heat transfer from a slot jet impinging on a moving plate. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 24:685–697
Chiriac VA, Ortega A (2002) A numerical study of the unsteady flow and heat transfer in a transitional confined slot jet impinging on an isothermal surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:1237–1248
Chung YM, Luo KH (2002) Unsteady heat transfer analysis of an impinging jet. Trans ASME J Heat Transf 124:1039–1048
Deshpande MD, Vaishnav RN (1982) Submerged laminar jet impingement on a plane. J Fluid Mech 114:213–236
Dewan A, Dutta R, Srinivasan B (2012) Recent trends in computation of turbulent jet impingement heat transfer. Heat Transf Eng 33(4–5):447–460
Gutmark E, Wolfshtein M, Wygnanski I (1978) The plane turbulent impinging jet. J Fluid Mech 88(04):737–756
Hattori H, Nagano Y (2004) Direct numerical simulation of turbulent heat transfer in plane impinging jet. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 25:749–758
Jambunathan K, Lai E, Moss MA, Button BL (1992) A review of heat transfer data for single circular jet impingement. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 13(2):106–115
Lallave JC, Rahman MM, Kumar A (2007) Numerical analysis of heat transfer on a rotating disk surface under confined liquid jet impingement. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 28:720–734
Launder BE, Spalding DB (1974) The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 3:269–289
Lou ZQ, Mujumdar AS, Yap C (2005) Effects of geometric parameters on confined impinging jet heat transfer. Appl Therm Eng 25:2687–2697
Luikov AV, Aleksashenko VA, Aleksashenko AA (1971) Analytical methods of solution of conjugated problems in convective heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf 14:1047–1056
Marple VA, Liu BYH, Whitby KT (1974) On the flow fields of inertial impactors. Trans ASME J Fluids Eng 96:394–400
Pamadi BN, Belov IA (1980) A note on the heat transfer characteristics of circular impinging jet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 23:783–787
Panda RK, Prasad BVSSS (2011) Conjugate heat transfer from a flat plate with shower head impinging jets. Front Heat Mass Transf 2(1):1–10
Patankar SV (1980) Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. Hemisphere, New York
Polat S, Huang B, Mujumdar AS, Douglas WJM (1989) Numerical flow and heat transfer under impinging jets: a review. Annu Rev Heat Transf 2:157–197
Pramanik S, Achari AM, Das MK (2012) Numerical simulation of a turbulent confined slot impinging jet. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(26):9153–9163
Rahman MM, Bula AJ, Leland JE (1999) Conjugate heat transfer during free jet impingement of a high Prandtl number fluid. Numer Heat Transf Part B 36:139–162
Rahman MM, Lallave JC (2009) Transient conjugate heat transfer during free liquid jet impingement on a rotating solid disk. Numer Heat Transf Part A 55:229–251
Rahman MM, Lallave JC, Kumar A (2008) Heat transfer from a spinning disk during semi-confined axial impingement from a rotating nozzle. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:4400–4414
Raju KS, Schlunder EU (1977) Heat transfer between an impinging jet and a continuously moving flat surface. Waerme Stoffuebertrag 10:131–136
Sakakibara J, Hishida K, Maeda M (1997) Vortex structure and heat transfer in the stagnation region of an impinging plane jet (simultaneous measurements of velocity and temperature fields by digital particle image velocimetry and laser-induced fluorescence). Int J Heat Mass Transf 13:3163–3176
Senter J, Solliec C (2007) Flow field analysis of a turbulent slot air jet impinging on a moving flat surface. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 28:708–719
Shi YL, Ray MB, Mujumdar AS (2003) Effects of Prandtl number on impinging jet heat transfer under a semi-confined laminar slot jet. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 30(4):455–464
Sparrow EM, Wong TC (1975) Impingement transfer coefficients due to initially laminar slot jets. Int J Heat Mass Transf 18:597–605
Versteeg HK, Malalasekera W (1996) An introduction to computational fluid dynamics. The finite volume method. Longman, London
Viskanta R (1993) Heat transfer to impinging isothermal gas and flame jets. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 6:111–134
Wang M, Wang R, Liu X (2011) Numerical simulation of a semi-confined slot turbulent impinging jet. Adv Mater Res 268–270:345–350
Wang XS, Dagan Z, Jiji LM (1989) Conjugate heat transfer between a laminar impinging liquid jet and a solid disk. Int J Heat Mass Transf 32(11):2189–2197
Weigand B, Spring S (2011) Multiple jet impingement—a review. Heat Transf Res 42(2):101–142
Yang Y, Tsai S (2007) Numerical study of transient conjugate heat transfer of a turbulent impinging jet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50:799–807
Yang Z, Shih TH (1993) New time scale based k-\(\epsilon\) model for near-wall turbulence. Am Inst Aeronaut Astronaut J 31(7):1191–1198
Zumbrunnen DA (1991) Convective heat and mass transfer in the stagnation region of a laminar planar jet impinging on a moving surface. Trans ASME J Heat Transf 113:563–570
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Achari, A.M., Das, M.K. Conjugate heat transfer study of a turbulent slot jet impinging on a moving plate. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 1017–1035 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-016-1873-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-016-1873-7