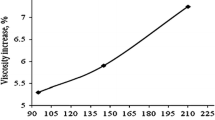
Abstract
A new model which includes liquid molecule nanolayer, aggregation and nanoconvection is developed to discuss the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Dimensionless numbers (particle size and thermal conductivity) are firstly defined, and it is confirmed that the particle size including powder and aggregate sizes is one of the key parameters to affect the thermal conductivity. It is found that the maximum enhancement of thermal conductivity is to be 64.4 %.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SUS, Eastman JA (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles In: International mechanical engineering congress and exhibition: San Francisco CA 12-17
Keblinski P, Eastman JA, Cahill DG (2005) Nanofluids for thermal transport. Mater Today 8:36–44
Das SK, Choi SUS, Yu W, Pradeep T (2007) Nanofluids: science and technology, 1st edn. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken
Vajjha RS, Das DK (2012) A review and analysis on influence of temperature and concentration of nanofluids on thermophysical properties. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:4063–4078
Lee JH, Lee SH, Choi CJ, Jang SP, Choi SUS (2010) A review of thermal conductivity data, mechanisms and models for nanofluids. Int J Micro-Nano Scale Transp 1:269–322
Wang XQ, Mujumdar AS (2007) Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: a review. Int J Therm Sci 46:1–19
Yu W, France DM, Routbort JL, Choi SUS (2008) Review and comparison of nanofluid thermal conductivity and heat transfer enhancements. Heat Transf Eng 29:432–460
Krishnamurthy S, Bhattacharya P, Phelan PE (2006) Enhanced mass transport in nanofluids. Nano Lett 6:419–423
Saidur R, Leong KY, Mohammad HA (2011) A review on applications and challenges of nanofluids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15:1646–1668
Özerinç S, Kakaç S, Yazıcıoğlu AG (2010) Enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: a state of the art review. Microfluid Nanofluid 8:145–170
Keblinski P, Phillpot SR, Choi SUS, Eastman JA (2002) Mechanism of heat flow in suspensions of nano-sized particles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:855–863
Yu W, Choi SUS (2003) The role of interfacial layers in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: arenovated Maxwell model. J Nanoparticle Res 5:167–171
Yu W, Choi SUS (2004) The role of interfacial layers in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: a renovated Hamilton–Crosser model. J Nanoparticle Res 6:355–361
Prasher R, Phelan PE, Bhattacharya P (2006) Effect of aggregation kinetics on the thermal conductivity of nanoscale colloidal solutions (nanofluid). Nano Lett 6:1529–1534
Gao JW, Zheng RT, Ohtani H, Zhu DS, Chen G (2009) Experimental investigation of heat conduction mechanisms in nanofluids: clue on clustering. Nano Lett 9:4128–4132
Wang JJ, Zheng RT, Gao JW, Chen G (2012) Heat conduction mechanisms in nanofluids and suspensions. Nano Today 7:124–136
Wang X, Xu X, Choi SUS (1999) Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-fluid mixture. J Thermophys Heat Transf 13:474–480
Jang SP, Choi SUS (2004) Role of Brownian motion in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids. Appl Phys Lett 84:4316–4318
Koo J, Kleinstreuer C (2004) A new thermal conductivity model for nanofluids. J Nanoparticle Res 6:577–588
Prasher R, Bhattacharya P, Phelan PE (2005) Thermal conductivity of nanoscale colloidal solutions (nanofluids). Phys Rev Lett 94:025901
Pang C, Jung JY, Lee JW, Kang YT (2012) Thermal conductivity measurement of methanol-based nanofluids with Al2O3 and SiO2 nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:5597–5602
Maxwell-Garnett JC (1904) Colours in metal glasses and in metallic films. Philos Trans R Soc A 203:385–420
Bruggeman DAG (1935) Berechnung Verschiedener Physikalischer Konstanten von Heterogenen Substanzen I. Dielektrizitatskonstanten und Leitfahigkeiten der Mischkorper aus Isotropen Substanzen. Ann der Phys Leipz 24:636–679
Wang BX, Zhou LP, Peng XF (2003) A fractal model for predicting the effective thermal conductivity of liquid with suspension of nanoparticles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 46:2665–2672
Hashimoto T, Fujimura M, Kawai H (1980) Domain-boundary structure of Styrene–Isoprene block copolymer films cast from solutions. 5. Molecular-weight dependence of spherical microdomains. Macromolecules 13:1660–1669
Potanin AA, De Rooij R, Van den Ende D, Mellema J (1995) Microrheological modeling of weakly aggregated dispersions. J Chem Phys 102:5845
Hunter RJ (2001) Foundations of colloid science. Oxford University Press, NY
Waite TD, Cleaver JK, Beattie JK (2001) Aggregation kinetics and fractal structure of γ-alumina assemblages. J Colloid Interface Sci 241:333–339
Zheng R, Gao J, Wang J, Chen G (2011) Reversible temperature regulation of electrical and thermal conductivity using liquid-solid phase transitions. Nat Commun 2:289
Chen G (2005) Nanoscale energy transport and conversion a parallel treatment of electrons, molecules, phonons and photons. Oxford University Press, NY
Balandin AA (2011) Thermal properties of graphene and nanostructured carbon materials. Nat Mater 10:569–581
Hsu T Lecture notes on nanoscale heat transfer web site: http://www.engr.sjsu.edu/trhsu
Kikugawa G, Ohara T, Kawaguchi T, Torigoe E, Hagiwara Y, Matsumoto Y (2009) A molecular dynamics study on heat transfer characteristics at the interfaces of alkanethiolate self-assembled monolayer and organic solvent. J Chem Phys 130:074706
Evans W, Prasher R, Fish J, Meakin P, Phelan P, Keblinski P (2008) Effect of aggregation and interfacial thermal resistance on thermal conductivity of nanocomposites and colloidal nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:1431–1438
Dong RY, Cao BY (2014) Anomalous orientations of s rigid carbon nanotube in a sheared fluid. Sci Rep 4:6120. doi:10.1038/srep06120
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (No. 20100029120).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, C., Lee, J.W. & Kang, Y.T. Enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids by nanoconvection and percolation network. Heat Mass Transfer 52, 511–520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1569-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1569-4