Abstract
Objective
Catheter-related bladder discomfort (CRBD) is a common complication of intraoperative urinary catheterization. Various studies have evaluated the efficacy of different interventions in postoperative CRBD. The present review was performed to assess the efficacy of these interventions.
Methods
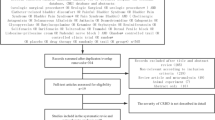
PubMed, Embase, and CENTRAL (Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials) databases were systematically searched to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the efficacy of different drugs for the prevention of postoperative CRBD. This review evaluated the incidence and severity of CRBD after different interventions at 0, 1, 2, and 6 h postoperatively.
Results
Forty-five studies including 31 different drugs were analyzed. Eleven drugs were investigated in more than two RCTs, of which dexmedetomidine, gabapentin, tolterodine, tramadol, ketamine, nefopam, oxybutynin, pregabalin, and pudendal nerve block (PNB) generally showed significantly higher efficacy than controls postoperatively. Solifenacin only showed significant efficacy compared with the control at 0 h, and intravenous lidocaine only showed significant efficacy compared with the control at 6 h. There were insufficient trials to draw conclusions regarding atropine, butylscopolamine, chlorpheniramine, clonidine, darifenacin, diphenhydramine, glycopyrrolate, intravesical bupivacaine, ketamine-haloperidol, pethidine-haloperidol, ketorolac, lidocaine-prilocaine cream, magnesium, hyoscine n-butyl bromide, oxycodone, paracetamol, parecoxib, trospium, resiniferatoxin, or amikacin. However, all but pethidine-haloperidol and chlorpheniramine showed some efficacy at various time points compared with controls.
Conclusion
This review suggests that dexmedetomidine, gabapentin, tolterodine, tramadol, ketamine, nefopam, oxybutynin, pregabalin, and PNB are effective in preventing postoperative CRBD. Considering the efficacy and adverse effects of all drugs, dexmedetomidine and gabapentin were ranked best.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson KE (1993) The pharmacology of lower urinary tract smooth muscles and penile erectile tissues. Pharmacol Rev 45:253–308
Binhas M, Motamed C, Hawajri N, Yiou R, Martly J (2011) Predictors of catheter-related bladder discomfort in the postanaesthesia care unit. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 30:122–125
Bai Y, Wang X, Li X, Pu C, Yuan H, Tang Y et al (2015) Management of catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients who underwent elective surgery. J Endourol 29:640–649
Tu Q, Gan J, Shi J, Yu H, He S, Zhang J (2019) Effect of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on postoperative analgesia after ureteroscopic lithotripsy: a randomized controlled trial. Urolithiasis 47:279–287
Imai H, Seino Y, Baba H (2020) Efficacy of a novel urinary catheter for men with a local anesthetic injection port for catheter-related bladder discomfort: a randomized controlled study. J Anesth 34:688–693
Zhou L, Zhou L, Tian L, Zhu D, Chen Z, Zheng C et al (2018) Preoperative education with image illustrations enhances the effect of tetracaine mucilage in alleviating postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. BMC Anesthesiol 18:204
Kim HC, Park HP, Lee J, Jeong MH, Lee KH (2017) Sevoflurane vs. propofol in post-operative catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective randomized study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 61:773–780
Kim HC, Hong WP, Lim YJ, Park HP (2016) The effect of sevoflurane versus desflurane on postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing transurethral excision of a bladder tumour: a randomized controlled trial. Can J Anaesth 63:596–602
Hur M, Park SK, Yoon HK, Yoo S, Lee HC, Kim WH et al (2019) Comparative effectiveness of interventions for managing postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Anesth 33:197–208
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269, W64
Lan X, Liu MG, Chen HX, Liu HM, Zeng W, Wei D et al (2014) Efficacy of immunosuppression monotherapy after liver transplantation: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 20:12330–12340
Şahiner Y, Yağan Ö, Akdağlı Ekici A, Ekici M, Demir E (2020) The effect of atropine in preventing catheter-related pain and discomfort in patients undergoing transurethral resection due to bladder tumor; prospective randomized, controlled study. Korean J Pain 33:176–182
Nam K, Seo JH, Ryu JH, Oh AY, Lee T, Park HP et al (2015) Randomized, clinical trial on the preventive effects of butylscopolamine on early postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort. Surgery 157:396–401
In CB, Lee SJ, Sung TY, Cho CK, Jee YS (2021) Effects of Chlorpheniramine Maleate on Catheter-Related Bladder Discomfort in Patients Undergoing Ureteroscopic Stone Removal: A Randomized Double-Blind Study. Int J Med Sci 18:1075–1081
Kohli S, Agrawal S, Jindal P, Biswas M (2018) Comparison of preoperative tramadol, pregabalin or clonidine on incidence and severity of catheter related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing percutaneous nephrolithotomy: a prospective, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial. MEJ Anesth 25:21–29
Srivastava VK, Nigam R, Agrawal S, Kumar S, Rambhad S, Kanaskar J (2016) Evaluation of the efficacy of solifenacin and darifenacin for prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Minerva Anestesiol 82:867–873
Akça B, Aydoğan-Eren E, Canbay Ö, Karagöz AH, Üzümcügil F, Ankay-Yilbaş A et al (2016) Comparison of efficacy of prophylactic ketamine and dexmedetomidine on postoperative bladder catheter-related discomfort. Saudi Med J 37:55–59
Li SY, Li H, Ni J, Ma YS (2019) Comparison of intravenous lidocaine and dexmedetomidine infusion for prevention of postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol 19:37
Singh TK, Sahu S, Agarwal A, Gupta D, Mishra P (2018) Dexmedetomidine for prevention of early postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in voluntary kidney donors: Prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol 34:211–215
Zhao Yun Y, Jun Mei X, Rong Z, Ru Ping D, Lei L (2016) Dexmedetomidine reduces Catheter-Related Bladder Discomfort: A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo- Controlled, Double-Blind Study. P R Health Sci J 35:191–196
Kwon Y, Jang JS, Hwang SM, Lee JJ, Tark H (2018) Intraoperative administration of dexmedetomidine reduced the postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort and pain in patients undergoing lumbar microdiscectomy. J Anesth 32:41–47
Kim HC, Lee YH, Jeon YT, Hwang JW, Lim YJ, Park JE, Park HP (2015) The effect of intraoperative dexmedetomidine on postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing transurethral bladder tumour resection: A double-blind randomised study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 32:596–601
Li YY, Zeng YS, Chen JY, Wang KF, Hsing CH, Wu WJ, Wang JJ, Feng PH, Chu CC (2020) Prophylactic diphenhydramine attenuates postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopic surgery: a randomized double-blind clinical study. J Anesth 34:232–237
Göger YE, Özkent MS, Göger E, Kılınç MT, Ecer G, Pişkin MM et al (2021) A randomised-controlled, prospective study on the effect of dorsal penile nerve block after TURP on catheter-related bladder discomfort and pain. Int J Clin Pract 75:e13963
Xiaoqiang L, Xuerong Z, Juan L, Mathew BS, Xiaorong Y, Qin W, Lili L, Yingying Z, Jun L (2017) Efficacy of pudendal nerve block for alleviation of catheter-related bladder discomfort in male patients undergoing lower urinary tract surgeries: A randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e8932
Agarwal A, Dhiraaj S, Pawar S, Kapoor R, Gupta D, Singh PK (2007) An evaluation of the efficacy of gabapentin for prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Anesth Analg 105:1454–1457
Maghsoudi R, Farhadi-Niaki S, Etemadian M, Kashi AH, Shadpour P, Shirani A et al (2018) Comparing the Efficacy of Tolterodine and Gabapentin Versus Placebo in Catheter Related Bladder Discomfort After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Endourol 32:168–174
Wang J, Fu G, Liu J, Yu Y, Wang N (2020) Effect of preoperative gabapentin after transurethral prostate resection under general anesthesia. A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Saudi Med J 41:640–644
Bala I, Bharti N, Chaubey VK, Mandal AK (2012) Efficacy of gabapentin for prevention of postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing transurethral resection of bladder tumor. Urology 79:853–857
Kim JA, Min JH, Lee HS, Jo HR, Je UJ, Paek JH (2016) Effects of glycopyrrolate premedication on preventing postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients receiving ureteroscopic removal of ureter stone. Korean J Anesthesiol 69:563–567
Pournajafian A, Ghodraty MR, Shafighnia S, Rokhtabnak F, Khatibi A, Tavoosian S et al (2020) The Effect of Intravesical Diluted Bupivacaine on Catheter-Related Bladder Discomfort in Young and Middle-Aged Male Patients During Postanaesthetic Recovery. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim 48:454–459
Kim DH, Park JY, Yu J, Lee SA, Park S, Hwang JH et al (2020) Intravenous Lidocaine for the Prevention of Postoperative Catheter-Related Bladder Discomfort in Male Patients Undergoing Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumors: A Randomized, Double-Blind. Controlled Trial Anesth Analg 131:220–227
Maquoi I, Joris JL, Dresse C, Vandenbosch S, Venneman I, Brichant JF et al (2016) Transversus abdominis plane block or intravenous lignocaine in open prostate surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 60:1453–1460
Shariat Moharari R, Lajevardi M, Khajavi M, Najafi A, Shariat Moharari G, Etezadi F (2014) Effects of intra-operative ketamine administration on postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort: a double-blind clinical trial. Pain Pract 14(2):146–150
Khajavi MR, Kamalzadeh N, Pourfakhr P, Moharari RS, Etezadi F (2019) The Efficacy of Intraoperative Ketamine-Haloperidol for Prevention of Catheter-related Bladder Discomfort After Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Surgery. Oman Med J 34:212–217
Park JY, Hong JH, Yu J, Kim DH, Koh GH, Lee SA et al (2019) Effect of Ketorolac on the Prevention of Postoperative Catheter-Related Bladder Discomfort in Patients Undergoing Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: A Randomized, Double-Blinded. Placebo-Controlled Study J Clin Med 8:759
Mu L, Geng LC, Xu H, Luo M, Geng JM, Li L (2017) Lidocaine-prilocaine cream reduces catheter-related bladder discomfort in male patients during the general anesthesia recovery period: A prospective, randomized, case-control STROBE study. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e6494
Park JY, Hong JH, Kim DH, Yu J, Hwang JH, Kim YK (2020) Magnesium and Bladder Discomfort after Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor: A Randomized, Double-blind. Placebo-controlled Study Anesthesiology 133:64–77
Sabetian G, Zand F, Asadpour E, Ghorbani M, Adibi P, Hosseini MM et al (2017) Evaluation of hyoscine N-butyl bromide efficacy on the prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort after transurethral resection of prostate: a randomized, double-blind control trial. Int Urol Nephrol 49:1907–1913
Cheon YW, Kim SH, Paek JH, Kim JA, Lee YK, Min JH et al (2018) Effects of nefopam on catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing ureteroscopic litholapaxy. Korean J Anesthesiol 71:201–206
Park M, Jee CH, Kwak KH, Park JM, Kim JH (2018) The effect of preoperative nefopam treatment on postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing transurethral bladder tumor resection: a randomized double-blind study. Scand J Urol 52:389–394
Agarwal A, Dhiraaj S, Singhal V, Kapoor R, Tandon M (2006) Comparison of efficacy of oxybutynin and tolterodine for prevention of catheter related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Br J Anaesth 96:377–380
Tauzin-Fin P, Sesay M, Svartz L, Krol-Houdek MC, Maurette P (2007) Sublingual oxybutynin reduces postoperative pain related to indwelling bladder catheter after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Br J Anaesth 99:572–575
Xiong J, Chen X, Weng C, et al (2019). Intra-operative Oxycodone Reduced Postoperative Catheter-Related Bladder Discomfort Undergoing Transurethral Resection Prostate. A Prospective, Double Blind Randomized Study. Urology Journal 16: 392-396
Ergenoglu P, Akin S, Yalcin Cok O, Eker E, Kuzgunbay B, Turunc T et al (2012) Effect of intraoperative paracetamol on catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 73:186–194
Jendoubi A, Aissi W, Abbes A, Bouzouita A, Fourati S, Necib H et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of Parecoxib for prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing transurethral resection of bladder tumor: Prospective randomised trial. Indian J Anaesth 62:461–465
Srivastava VK, Agrawal S, Kadiyala VN, Ahmed M, Sharma S, Kumar R (2015) The efficacy of pregabalin for prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind study. J Anesth 29:212–216
Zhang N, Zhang P, Zhang X, Yang Y (2012) The efficacy of resiniferatoxin in prevention of catheter related bladder discomfort in patients after TURP – a pilot, randomized, open study. Transl Androl Urol 1:14–18
Chung JM, Ha HK, Kim DH, Joo J, Kim S, Sohn DW et al (2017) Evaluation of the Efficacy of Solifenacin for Preventing Catheter-Related Bladder Discomfort After Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumors in Patients With Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Prospective, Randomized. Multicenter Study Clin Genitourin Cancer 15:157–162
Zhang Z, Cao Z, Xu C, Wang H, Zhang C, Pan A et al (2014) Solifenacin is able to improve the irritative symptoms after transurethral resection of bladder tumors. Urology 84:117–121
Tijani KH, Akanmu NO, Olatosi JO, Ojewola RW (2017) Role of tolterodine in the management of postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort: Findings in a Nigerian teaching hospital. Niger J Clin Pract 20:484–488
Agarwal A, Raza M, Singhal V, Dhiraaj S, Kapoor R, Srivastava A et al (2005) The efficacy of tolterodine for prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Anesth Analg 101:1065–1067
Manandhar S, Manandhar K (2019) Efficacy of intravenous Tramadol in prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort in upper urinary tract surgery. J Patan Acad Health Sci 6:45–50
Agarwal A, Yadav G, Gupta D, Singh PK, Singh U (2008) Evaluation of intra-operative tramadol for prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Br J Anaesth 101:506–510
Kumar SV, Sanjay A, Anil DS, Febin N, Saima K, Raj K (2020) Efficacy of trospium for prevention of catheter-related bladder discomfort: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Korean J Anesthesiol 73:145–150
Verma R, Agarwal A, Singh PK, Gupta D, Shamim R (2016) Evaluation of efficacy of amikacin for attenuation of catheter-related bladder discomfort in patients undergoing percutaneous nephrolithotomy: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Anesth Essays Res 10:613–617
Yu D, Chai W, Sun X, Yao L (2010) Emergence agitation in adults: risk factors in 2000 patients. Can J Anaesth 57:843–848
de Groat WC (1993) Anatomy and physiology of the lower urinary tract. Urol Clin North Am 20:383–401
Andersson KE (1999) Advances in the pharmacological control of the bladder. Exp Physiol 84:195–213
Chess-Williams R (2002) Muscarinic receptors of the urinary bladder: detrusor, urothelial and prejunctional. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol 22:133–145
Shi H, Zhang H, Pan W, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Chen L et al (2021) Pooled analysis of the efficacy and safety of intraoperative dexmedetomidine on postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort. Low Urin Tract Sympt 13:38–44
Funding
There is no funding to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shuying Li designed and prepared this protocol; Shuying Li and Ping Li contributed to the revision of the protocol and to data collection and analysis; Rurong Wang and Hui Li revised the manuscript. All co-authors contributed to the preparation and approval of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Li, P., Wang, R. et al. Different interventions for preventing postoperative catheter-related bladder discomfort: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 78, 897–906 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-021-03251-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-021-03251-5