Abstract
Purpose
This study was conducted to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexlansoprazole injection in healthy subjects.
Methods
Dexlansoprazole (20–90 mg) or lansoprazole (30 mg) was administrated intravenously to healthy male and female volunteers. All the subjects were sampled for pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis and 64 of them were monitored for 24-h intragastric pH prior to and after administration in the pharmacodynamic (PD) study.
Results
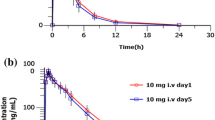
Maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration–time curve (AUC0-τ) for dexlansoprazole injection was dose-proportional over the range of 20–90 mg following a single intravenous administration. Total clearance and half-life (t1/2) was independent of dose, and ranged from 4.69 L/h to 5.85 L/h and from 1.24 h to 2.17 h, respectively. A single dose of dexlansoprazole (30 mg) resulted in higher gastric pH compared to that of lansoprazole, evidenced by a mean 24-h gastric pH of 6.1 ± 1.2 (lansoprazole: 5.4 ± 1.1) and 24-h gastric pH > 6 post drug dose holding time of 64.2 ± 21.0% (lansoprazole: 49.5 ± 21.5%).
Conclusion
Dexlansoprazole injection was safe and well tolerated for up to 5-day repeated intravenous administration dose of 30 mg. The recommended dosage for dexlansoprazole injection is 30 mg for an adequate gastric acid control.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lau JY, Barkun A, Fan DM, Kuipers EJ, Yang YS, Chan FK (2013) Challenges in the management of acute peptic ulcer bleeding. Lancet 381(9882):2033–2043. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60596-6
Gralnek IM, Dumonceau JM, Kuipers EJ, Lanas A, Sanders DS, Kurien M, Rotondano G, Hucl T, Dinis-Ribeiro M, Marmo R, Racz I, Arezzo A, Hoffmann RT, Lesur G, de Franchis R, Aabakken L, Veitch A, Radaelli F, Salgueiro P, Cardoso R, Maia L, Zullo A, Cipolletta L, Hassan C (2015) Diagnosis and management of nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 47(10):a1–a46. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1393172
Li H, Meng L, Liu F, Wei JF, Wang YQ (2013) H+/K+-ATPase inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 23(1):99–111. doi:10.1517/13543776.2013.741121
Wang Y, Zhang H, Meng L, Wang M, Yuan H, Ou N, Zhang H, Li Z, Shi R (2010) Influence of CYP2C19 on the relationship between pharmacokinetics and intragastric pH of omeprazole administered by successive intravenous infusions in Chinese healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66(6):563–569. doi:10.1007/s00228-010-0821-6
Wang Y, Yuan Y, Meng L, Fan H, Xu J, Zhang H, Wang M, Yuan H, Ou N, Zhang H, Chao Y, Shi R (2011) Study of the pharmacokinetics and intragastric pH of rabeprazole given as successive intravenous infusion to healthy Chinese volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67(1):25–31. doi:10.1007/s00228-010-0949-4
Gawrońska-Szklarz B, Adamiak-Giera U, Wyska E, Kurzawski M, Gornik W, Kaldonska M, Drozdzik M (2012) CYP2C19 polymorphism affects single-dose pharmacokinetics of oral pantoprazole in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68(9):1267–1274. doi:10.1007/s00228-012-1252-3
Yang ZC, Yu F, Wang YQ, Wei JF (2016) Stereoselective pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of proton pump inhibitors. Curr Drug Metab 17(7):692–702
Katsuki H, Yagi H, Arimori K, Nakamura C, Nakano M, Katafuchi S, Fujioka Y, Fujiyama S (1996) Determination of R(+)- and S(−)-lansoprazole using chiral stationary-phase liquid chromatography and their enantioselective pharmacokinetics in humans. Pharm Res 13(4):611–615
Vakily M, Zhang W, Wu J, Atkinson SN, Mulford D (2009) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a known active PPI with a novel Dual Delayed Release technology, dexlansoprazole MR: a combined analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Curr Med Res Opin 25(3):627–638. doi:10.1185/03007990802693883
Sun L, Cao Y, Jiao H, Fang Y, Yang Z, Bian M, Zhang H, Gong X, Wang Y (2015) Enantioselective determination of (R)- and (S)-lansoprazole in human plasma by chiral liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and its application to a stereoselective pharmacokinetic study. J Sep Sci 38(21):3696–3703. doi:10.1002/jssc.201500653
Lee RD, Vakily M, Mulford D, Wu J, Atkinson SN (2009) Clinical trial: the effect and timing of food on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexlansoprazole MR, a novel Dual Delayed Release formulation of a proton pump inhibitor—evidence for dosing flexibility. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 29(8):824–833. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.03979.x
Metz DC, Vakily M, Dixit T, Mulford D (2009) Review article: dual delayed release formulation of dexlansoprazole MR, a novel approach to overcome the limitations of conventional single release proton pump inhibitor therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 29(9):928–937. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.03984.x
Klein A, Gralnek IM (2015) Acute, nonvariceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Curr Opin Crit Care 21(2):154–162. doi:10.1097/MCC.0000000000000185
Lu Y, Loffroy R, Lau JY, Barkun A (2014) Multidisciplinary management strategies for acute non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Br J Surg 101(1):e34–e50. doi:10.1002/bjs.9351
Armstrong D (2004) Review article: gastric pH—the most relevant predictor of benefit in reflux disease? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20(Suppl 5):19–26. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2004.02140.x, discussion 38–39
Hershcovici T, Jha LK, Fass R (2011) Dexlansoprazole MR: a review. Ann Med 43(5):366–374. doi:10.3109/07853890.2011.554429
Zhan XB, Guo XR, Li ZS, Gong YF, Gao J, Liao Z, Li Z, Gao S, Liu P (2012) Inhibitory effects of intravenous lansoprazole 30 mg and pantoprazole 40 mg twice daily on intragastric acidity in healthy Chinese volunteers: a randomized, open-labeled, two-way crossover study. Med Sci Monit 18(2):CR125–CR130
Acknowledgements
This project was sponsored by grants from the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, National Natural Science Foundation of China (81673515, 81503160), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20161591), Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (2014-YY-001) and Key Talents of Medical Science in Jiangsu Province (H201108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zheng-Yu Yan co-first authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YQ., Yan, ZY., Zhang, HW. et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexlansoprazole injection in healthy Chinese subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 73, 547–554 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-017-2206-6