Abstract
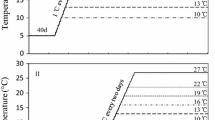
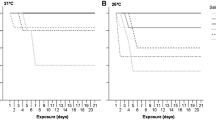
The negative effects of scyphozoan jellyfish blooms on ecosystems and economy are linked to planula survival, settlement success and subsequent polyp metamorphosis. A particular periderm covered stage formed by the newly settled planula, the planulocyst, has been reported for Cyanea lamarckii Péron and Lesueur, 1810 but not for Cyanea capillata (Linnaeus, 1758) from the Northeast Atlantic. Only a few planulocysts develop to polyps directly after settlement and the excystment process has not been understood in detail. By combining live observations with histological sections and scanning electron microscopy, present results clarified that the excysting C. lamarckii planula secretes a thin periderm stalk within the planulocyst and subsequently the polyp develops at the top of the stalk. No planulocysts but tiny periderm stalks appeared during the polyp development in C. capillata. Experiments with combined temperature (10, 15, 20 °C) and salinity (32, 25) treatments revealed significant effects of temperature on C. lamarckii planula settlement success (highest at 15 °C) and planulocyst excystment (highest at 20 °C) but no significant effects of salinity. Food supply did not affect excystment but enhanced the tentacle development of polyps. Our results demonstrate that studies on early life stages can reveal species-specific morphological differences in scyphozoan polyps which lack other distinct characters. The experimental results indicate that early C. lamarckii life stages are well adapted to environmental salinity changes and that increasing temperature due to global warming can be beneficial for their development which may support their northward distribution and increasing jellyfish populations in the Northeast Atlantic area.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data analyzed during the current study are available in the Supplementary Information. Additional datasets generated during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adler L, Jarms G (2009) New insights into reproductive traits of scyphozoans: special methods of propagation in Sanderia malayensis Goette, 1886 (Pelagiidae, Semaeostomeae) enable establishing a new classification of asexual reproduction in the class Scyphozoa. Mar Biol 156:1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-009-1181-6
Agassiz L (1860) Contributions to the natural history of the United States of America, vol 3. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 1–301
Agassiz L (1862) Contributions to the natural history of the United States of America, vol 4. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 1–380
Bayha K (2005) The molecular systematics and population genetics of four coastal ctenophores and scyphozoan jellyfish of the United States Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico. Dissertation, University of Delaware
Barz K, Hirche H-J (2007) Abundance, distribution and prey composition of scyphomedusae in the southern North Sea. Mar Biol 151:1021–1033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0545-4
Bosch-Belmar M, Milisenda G, Basso L, Doyle TK, Leone A, Piraino S (2020) Jellyfish Impacts on marine aquaculture and fisheries. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 29:242–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2020.1806201
Brandt JF (1835) Prodromus descriptionis animalium ab H. Mertensio observatorum: fascic. I. Polypos, Acalephas Discophoras et Siphonophoras, nec non Echinodermata continens. Recueil Des Actes De La Séance Publique De L’académie Impériale Des Sciences De St Pétersbourg 1834:201–275
Brewer RH (1976) Larval settling behaviour in Cyanea capillata (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Biol Bull 150:183–199. https://doi.org/10.2307/1540467
Brewer RH (1984) The influence of the orientation, roughness, and wettability of solid surfaces on the behavior and attachment of planulae of Cyanea (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Biol Bull 166:11–21. https://doi.org/10.2307/1541426
Brewer RH (1991) Morphological differences between, and reproductive isolation of, two populations of the jellyfish Cyanea in Long Island Sound, USA. Hydrobiologia 216(217):471–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00026501
Brewer RH, Feingold JS (1991) The effect of temperature on the benthic stages of Cyanea (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa), and their seasonal distribution in the Niantic River estuary, Connecticut. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 152:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(91)90134-I
Browne ET (1905) Scyphomedusae. In: Gardiner IS (ed) The fauna and geography of the Maldive and Laccadive archipelagoes, vol 2, Suppl. 1. University Press, Cambridge, pp 958–971
Calder DR (1972) Development of the sea nettle Chrysaora quinquecirrha (Scyphozoa, Semaeostomeae). Chesap Sci 13:40–44. https://doi.org/10.2307/1350549
Calder DR (1982) Life history of the cannonball jellyfish, Stomolophus meleagris L. Agassiz, 1860 (Scyphozoa, Rhizostomida). Biol Bull 162:149–162. https://doi.org/10.2307/1540810
Calder DR (2009) Cubozoan and scyphozoan jellyfishes of the Carolinian biogeographic province, southeastern USA. Royal Ontario Museum contributions in science, Toronto
Cargo DG (1974) Comments on the laboratory culture of Scyphozoa. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum Publishing Corporation, New York, pp 145–154
Cargo DG (1984) Some laboratory techniques for the culture of Scyphozoa United Nations Environment Programme-Workshop on jellyfish blooms in the Mediterranean, Athens, pp 129–138
Collins AG, Morandini AC (2023) World list of Scyphozoa. Cyanea Péron and Lesueur, 1810. https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=135259. Accessed 23 March 2023
Conley K, Uye S-I (2015) Effects of hyposalinity on survival and settlement of moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) planulae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 462:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2014.10.018
Delap MJ (1905) Notes on the rearing, in an aquarium, of Cyanea lamarcki, Péron et Lesueur. Annual Report of Fisheries, Ireland 1902-03:20-22
Dong J, Liu C-Y, Wang Y-Q (2006a) Laboratory observations on the life cycle of Cyanea nozakii (Semeostomida, Scyphozoa). Acta Zool Sinica 52:389–395
Dong J, Wang B, Lui C-Y (2006b) Morphology of Cyanea nozakii in different developmental stages. J Fish China 30:761–766 (in Chinese)
Dong J, Sun M, Wang B, Liu H (2008) Comparison of life cycles and morphology of Cyanea nozakii and other scyphozoans. Plankton Benthos Res 3:118–124. https://doi.org/10.3800/pbr.3.118
Dong Z, Wang L, Liu Q, Sun T (2018) Effects of salinity and temperature on the recruitment of Aurelia coerulea planulae. Mar Biol Res 14:454–461. https://doi.org/10.1080/17451000.2018.1459725
Feng S, Lin J, Uye S-i, Sun S, Zhang F (2021) Effects of salinity, light intensity and biofouling on planula settlement and subsequent development to polyps in Cyanea nozakii (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 542–543:151608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2021.151608
Folino-Rorem NC, Renken CJ (2018) Effects of salinity on the growth and morphology of the invasive, euryhaline hydroid Cordylophora (Phylum Cnidaria, Class Hydrozoa). Invertebr Biol 137:78–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/ivb.12207
Fu Z, Xing Y, Gu Z, Liu C, Chen S (2019) Effects of temperature, salinity and dissolved oxygen on excystment of podocysts in the edible jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye, 1891. Indian J Fish. https://doi.org/10.21077/ijf.2019.66.4.91762-09
Gambill M, McNaughton SL, Kreus M, Peck MA (2018) Temperature-dependent settlement of planula larvae of two scyphozoan jellyfish from the North Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 201:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.08.042
Goldstein J, Augustin CB, Bleich S, Holst S (2017) A matter of tolerance: distribution potential of scyphozoan polyps in a changing environment. Mar Ecol 38:e12457. https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12457
Graham WM, Pagès F, Hamner WM (2001) A physical context for gelatinous zooplankton aggregations: a review. Hydrobiologia 451:199–212
Gröndahl F (1988) A comparative ecological study on the scyphozoans Aurelia aurita, Cyanea capillata and Cyanea lamarkii in the Gullmar Fjord, western Sweden. Mar Biol 97:541–550
Gueroun SKM, Torres TM, Dos Santos A, Vasco-Rodrigues N, Canning-Clode J, Andrade C (2021) Catostylus tagi (Class: Scyphozoa, Order: Discomedusae, Suborder: Rhizostomida, Family: Catostylidae) life cycle and first insight into its ecology. PeerJ 9:e12056. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12056
Haeckel E (1869) Ueber die Crambessiden, eine neue Meduse-Familie aus der Rhizostomeengruppe. Zeitschrift Für Wissenschaftliche Zoologie 19:509–537
Haeckel E (1880) Das System der Acraspeden. 2te Hälfte des Systems der Medusen. Acht Nachträge zur Vervollständigung des Systems. Denkschriften der Medizinisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Gesellschaft zu Jena. 2:361–672
Hagmeier A (1933) Die Züchtung verschiedener wirbelloser Meerestiere. In: Abderhalden E (ed) Handbuch der Biologischen Arbeitsmethoden. Urban and Schwarzberg, Berlin, pp 465–598
Hargitt CW, Hargitt GT (1910) Studies on the development of Scyphomedusae. J Morphol 21:217–262
Hay SJ, Hislop JRG, Shanks AM (1990) North Sea scyphomedusae; summer distribution, estimated biomass and significance particularly for 0-Group gadoid fish. Neth J Sea Res 25:113–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0077-7579(90)90013-7
Helm RR (2018) Evolution and development of scyphozoan jellyfish. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 93:1228–1250. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12393
Holst S (2012a) Morphology and development of benthic and pelagic life stages of North Sea jellyfish (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria) with special emphasis on the identification of ephyra stages. Mar Biol 159:2707–2722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2028-0
Holst S (2012b) Effects of climate warming on strobilation and ephyra production of North Sea scyphozoan jellyfish. Hydrobiologia 690:127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1043-y
Holst S, Jarms G (2007) Substrate choice and settlement preferences of planula larvae of five Scyphozoa (Cnidaria) from German Bight, North Sea. Mar Biol 151:863–871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0530-y
Holst S, Jarms G (2010) Effects of low salinity on settlement and strobilation of Scyphozoa (Cnidaria): is the lion’s mane Cyanea capillata (L.) able to reproduce in the brackish Baltic Sea? Hydrobiologia 645:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0214-y
Holst S, Laakmann S (2014) Morphological and molecular discrimination of two closely related jellyfish species, Cyanea capillata and C. lamarckii (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa), from the northeast Atlantic. J Plankton Res 36:48–63. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbt093
Hyde (1894) Entwicklungsgeschichte einiger Scyphomedusen. Z Wiss Zool 58:531–565
Ikeda H, Ohtsu K, Uye S (2011) Fine structure, histochemistry, and morphogenesis during excystment of the podocysts of the giant jellyfish “Nemopilema nomurai” (Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Biol Bull 221:248–260. https://doi.org/10.1086/BBLv221n3p248
Jarms G, Morandini AC (2019) World atlas of jellyfish. Dölling und Galitz, Hamburg
Kawahara M, Uye S, Ohtsu K, Iizumi H (2006) Unusual population explosion of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) in East Asian waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 307:161–173. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps307161
Kennerley A, Wood LE, Luisetti T, Ferrini S, Lornzo I (2022) Economic impacts of jellyfish blooms on coastal recreation in a UK coastal town and potential management options. Ocean Coast Manag 227:106284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106284
Kienberger K, Riera-Buch M, Schonemann AM, Bartsch V, Halbauer R, Prieto L (2018) First description of the life cycle of the jellyfish Rhizostoma luteum (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). PLoS ONE 13:e0202093. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202093
Kishinouye K (1891) Cyanea nozakii, nov. sp. Zool Maga (dobutsugaku Zasshi) 3:93–95
Kishinouye K (1922) Echizen kurage. Zoological Magazine (dobutsugaku Zasshi) 34:343–346
Kramp PL (1961) Synopsis of the medusae of the world. J Mar Biol Ass U K 40:5–469
Lesh-Laurie GE, Suchy E (1991) Cnidaria: Scyphozoa and Cubozoa. In: Harrison FW, Westfall JA (eds) Microscopic anatomy of the invertebrates, vol 2. Wiley, New York, pp 185–266
Lesson RP (1830) Centurie zoologique, ou, Choix d'animaux rares, nouveaux ou imparfaitement connus. Paris and Strasbourg: FG Levrault and Bruxelles: Librairie Parisienne, pp 11–244
Linnaeus C (1758) Systema Naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Editio decima, reformata. Laurentius Salvius: Holmiae
Liu C-s, Zhuang Z-m, Chen S-q, Yan J-p, Liu C-l, Sun J-m (2015) A large-scale breeding experiment and observations on development of Cyanea nozakii (Scyphozoa, Cyaneidae) from fertilized eggs to larval medusae. Hydrobiologia 754:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-1883-8
Macri DS (1778). Nuove osservazioni intorno la storia naturale del polmone marino degli antichi
Martin VJ, Koss R (2006) Phylum Cnidaria. In: Young CM (ed) Atlas of marine invertebrate larvae. Academic Press, London, pp 51–108
McMurrich, (1891) The development of Cyanea arctica. Amer Natur 25:287–289
Miyake H, Terazaki M, Kakinuma Y (2002) On the polyps of the common jellyfish Aurelia aurita in Kagoshima Bay. J Oceanogr 58:451–459. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021628314041
Miyake H, Honda S, Nishikawa J, Yusoff FM (2021) Life cycle of edible jellyfish Acromitus hardenbergi Stiasny, 1934 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) inhabiting a brackish-water environment. Animals 11:2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072138
Morandini AC, Silveira DFL, Jarms G (2004) The life cycle of Chrysaora lactea Eschscholz, 1829 (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) with notes on the scyphistoma stages of three other species. Hydrobiologia 530(531):347–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-2694-0
Müller OF, Fabricii O (1786) Animalcula infusoria fluviatilia et marina que detexit, systematice descripsit et ad vivum delineari curavit Otho Fridericus Müller sistit opus hoc posthumum quod cum tabulis Aeneis L. in lucem tradit vidua ejus nobilissima cura Othonis Fabricii, p 344
Neumann R (1979) Bacterial induction of settlement and metamorphosis in the planula larvae of Cassiopea andromeda (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa, Rhizostomae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 1:21–28
Palmieri MG, Schaafsma M, Luisetti T, Barausse A, Harwood A, Sen A, Turner RK (2015) Jellyfish blooms and their impacts on welfare benefits: recreation in the UK and fisheries in Italy. In: Turner RK, Schaafsma M (eds) Coastal zones ecosystem services. Springer, London, pp 219–240
Péron F, Lesueur CA (1810) Tableau des des caractères génériques et spécifiques de toutes les espèces de méduses connues jusqu’à ce jour. Ann Mus Hist Nat Paris 14:325–366
Pitt KA (2000) Life history and settlement preferences of the edible jellyfish Catostylus mosaicus (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). Mar Biol 136:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050685
Prieto L, Astorga D, Navarro G, Ruiz J (2010) Environmental control of phase transition and polyp survival of a massive-outbreaker jellyfish. PLoS ONE 5:e13793. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013793
Purcell JE, Bondyale-Juez DR, Romero-Kutzner V, Martínez I, Caprioli R, Tames-Espinosa M, Almunia J, Alonso E, Packard TT, Gómez M (2019) Food supply effects on the asexual reproduction and respiratory metabolism of Aurelia aurita polyps. Hydrobiologia 846:135–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-04057-4
Quoy JRC, Gaimard JP (1824) Des zoophytes ou animaux rayonnés. In: de Freycinet ML (ed) Voyage au tour du monde fait par ordre du roi, sur les corvettes de S M: l'Uranie et la Physicienne pendant les années 1817 à 1820, Zoologie IV. Paris: Chez Pillet Aîné, Imprimeur-Libraire, pp 559−571
Quoy JRC, Gaimard JP (1827) Observations zoologiques faites à bord de l'Astrolabe, en mai 1826, dans le Détroit de Gibraltar. Ann Sci Nat 10:5–21, 172–193, 225–239
Rees WJ (1957) Evolutionary trends in the classification of capitate hydroids and medusae. Bull Br Mus (Nat Hist) Zool 4:455–534
Riascos JM, Paredes L, González K, Cáceres I, Pacheco AS (2013) The larval and benthic stages of the scyphozoan medusa Chrysaora plocamia under El Niño–La Niña thermal regimes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 446:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2013.05.006
Rippingale RJ, Kelly SJ (1995) Reproduction and survival of Phyllorhiza punctata (Cnidaria: Rhizostomeae) in a seasonally fluctuating salinity regime in western Australia. Mar Freshw Res 46:1145–1151. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF9951145
Russell FS (1970) The medusae of the British Isles II. Pelagic Scyphozoa with a supplement to the first volume on hydromedusae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Schäfer S, Gueroun SKM, Andrade C, Canning-Clode J (2021) Combined effects of temperature and salinity on polyps and ephyrae of Aurelia solida (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Diversity 13:573. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13110573
Schiariti A, Kawahara M, Uye S, Mianzan HW (2008) Life cycle of the jellyfish Lychnorhiza lucerna (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). Mar Biol 156:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-008-1050-8
Schiariti A, Morandini AC, Jarms G, von Glehn PR, Franke S, Mianzan H (2014) Asexual reproduction strategies and blooming potential in Scyphozoa. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 510:241–253. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps10798
Schnedler-Meyer NA, Kiørboe T, Mariani P (2018) Boom and bust: life history, environmental noise, and the (un)predictability of Jellyfish Blooms. Front Mar Sci 5:257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00257
Shahrestani S, Bi H (2018) Settlement and survival of Chrysaora chesapeakei polyps: implications for adult abundance. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 601:139–151. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps12665
Stiasny G (1934) Acromitus hardenbergi nov. spec., eine neue rhizostome Meduse aus dem Malayischen archipel. Zoologische Mededelingen 17:1–7
Takao M, Uye S-i (2018) Effects of low salinity on the physiological ecology of planulae and polyps of scyphozoans in the East Asian marginal seas: potential impacts of monsoon rainfall on medusa population size. Hydrobiologia 815:165–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-018-3558-3
Toyokawa M (2011) First record of wild polyps of Chrysaora pacifica (Goette, 1886) (Scyphozoa, Cnidaria). Plankton Benthos Res 6:175–177. https://doi.org/10.3800/pbr.6.175
Van Walraven L, Langenberg VT, Dapper R, Witte JIJ, Zuur AF, van der Veer HW (2015) Long-term patterns in 50 years of scyphomedusae catches in the western Dutch Wadden Sea in relation to climate change and eutrophication. J Plank Res 37:151–167. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbu088
van Walraven L, van Bleijswijk J, van der Veer HW (2020) Here are the polyps: in situ observations of jellyfish polyps and podocysts on bivalve shells. PeerJ 8:e9260. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9260
Webster CN, Lucas CH (2012) The effects of food and temperature on settlement of Aurelia aurita planula larvae and subsequent somatic growth. J Exp Marine Biol Ecol 436–437:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2012.08.014
Widersten B (1966) On the development of septal muscles, supporting fibrils and periderm in the scyphistoma of semaeostome Scyphozoa. Arkiv Zool 18:567–575
Widersten B (1968) On the morphology and development in some cnidarian larvae. Zool Bidr Upps 37:139–182
Widersten B (1969) Development of the periderm and podocysts in Cyanea palmstruchi Swartz 1809. Zool Bidr 38:51–60
Widmer CL (2006) Life cycle of Phacellophora camtschatica (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Invertebr Biol 125:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7410.2006.00043.x
Widmer CL (2008) Life cycle of Chrysaora fuscescens (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and a key to sympatric ephyrae. Pac Sci 62:71–82
Wright DA, Purcell JE (1997) Effect of salinity on ionic shifts in mesohaline scyphomedusae, Chrysaora quinquecirrha. Biol Bull 192:332–339. https://doi.org/10.2307/1542726
Acknowledgements
We thank the Biological Institute Helgoland (BAH) of the Alfred Wegener Institute for providing samples and thank the crew of the RV Senckenberg for their support. We are grateful for the assistance by the staff of Senckenberg am Meer Hamburg (DZMB) and the University of Hamburg with special thanks to Sabine Gaude, Renate Walter and Frank Friedrich.
Funding
The work of Lisa-Renana Kaiser, which was carried out during her Bachelor thesis, was financially supported by the University of Hamburg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by SH, L-RK and IS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Sabine Holst and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The invertebrates investigated in the study are not endangered or protected species. The collection of samples has been carried out with the help and permission from the Biologische Anstalt Helgoland (Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research) and during an approved research cruise with the RV Senckenberg (SEN 30-21).
Additional information
Responsible Editor: X. Irigoien.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Holst, S., Kaiser, LR. & Sötje, I. Planula settlement and polyp morphogenesis in two bloom forming jellyfish species of the genus Cyanea Péron and Lesueur, 1810 and effects of abiotic factors on planulocysts. Mar Biol 171, 6 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-023-04315-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-023-04315-z