Abstract
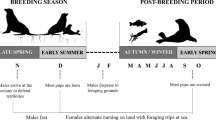
Intersexual foraging variation is a strategy that is usually adopted by sexually dimorphic species. The northern elephant seal (Mirounga angustirostris) exhibits one of the most pronounced examples of sexual dimorphism in pinnipeds and segregation in this species’ migration toward foraging grounds in the North Pacific is well-documented for colonies in California; however, we lack comparable data from colonies in Mexico. The aim of this study was to use stable isotope analysis (δ13C and δ15N) to evaluate diet variation between adult males and females from a Mexican colony. Fur was collected from adult males (N = 15) and pups (N = 42) on the San Benito Archipelago during the 2012 molting season (summer) and the 2013 breeding season (winter). Values for adult females were inferred from their pups, based on previous studies. The resulting δ13C and δ15N values were significantly lower than those of their male counterparts. This difference may be due to the higher trophic position and a probable consumption of benthic prey (δ15N) by males, and the use of mostly oceanic habitats (δ13C) by adult females; the latter also had a larger isotopic niche than that of the former, as a probable consequence of more variable foraging grounds. Although our results are not the reflection of a simultaneous segregation, we obtained solid evidence on intersexual variation, which is common among dimorphic pinnipeds, particularly in terms of trophic position and habitat use, which tend to be the result of a marked difference in body mass and different energetic requirements.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JA (1880) History of North American pinniped, a monograph of the walruses, sea lions, sea bears, and seals of North America. US Geol Geogr Surv Terr Misc Publ 12:1–785
Altabet MA, Pilskaln C, Thunell R, Pride C, Sigman D, Chavez F, Francois R (1999) The nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry of sinking particles from the margin of the eastern North Pacific. Deep Sea Res 46:655–679. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(98)00084-3
Antonelis GA, Lowry MS, DeMaster DP, Fiscus CH (1987) Assessing northern elephant seal feeding habits by stomach lavage. Mar Mamm Sci 3:308–322. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1987.tb00318.x
Antonelis GA, Lowry MS, Fiscus CH, Stewart BS, DeLong RL (1994) Diet of the northern elephant seal. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 211–223
Aurioles-Gamboa D, Koch PL, Le Boeuf BJ (2006) Differences in foraging location of Mexican and California elephant seals: evidence from stable isotopes in pups. Mar Mamm Sci 22:326–338. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2006.00023.x
Bearhop S, Adams CE, Waldron S, Fuller RA, MacLeod H (2004) Determining trophic niche width: a novel approach using stable isotope analysis. J Anim Ecol 73:1007–1012. doi:10.1111/j.0021-8790.2004.00861.x
Bond NA, Cronin MC, Freeland H, Mantua N (2015) Causes and impacts of the 2014 warm anomaly in the NE Pacific. Geophys Res Lett 42:414–3420. doi:10.1002/2015GL063306
Burton RK, Koch PL (1999) Isotopic tracking of foraging and long-distance migration in northeastern Pacific pinnipeds. Oecologia 119:578–585. doi:10.1007/s004420050822
Cherel Y, Kernaléguen L, Richard P, Guinet C (2009) Whisker isotopic signature depicts migration patterns and multi-year intra- and inter-individual foraging strategies in fur seals. Biol Lett 5:830–832. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2009.0552
Condit R, Le Boeuf BJ (1984) Feeding habits and feeding grounds of the northern elephant seal. J Mamm 65:281–290. doi:10.2307/1381167
Crocker DE, Costa DP, Le Boeuf BJ, Webb PM, Houser DS (2006) Impact of El Niño on the foraging behavior of female northern elephant seals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 309:1–10. doi:10.3354/meps309001
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1978) Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:495–506. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(78)90199-0
Deutsch CJ, Crocker DE, Costa DP, Le Boeuf BJ (1994) Sex-and age-related variation in reproductive effort of northern elephant seals. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 169–210
Ducatez S, Dalloyau S, Richard P, Guinet C, Cherel Y (2008) Stable isotopes document winter trophic ecology and maternal investment of adult female southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) breeding at the Kerguelen Islands. Mar Biol 155:413–420. doi:10.1007/s00227-008-1039-3
Elorriaga-Verplancken FR (2009) Variación de δ15N y δ13C en colágeno dental de lobos marinos del género Zalophus: patrones ontogénicos y geográficos. Dissertation, CICIMAR-IPN, La Paz BCS, México
Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Aurioles-Gamboa D, Newsome SD, Martınez-Dıaz SF (2013) δ15N and δ13C values in dental collagen as a proxy for age-and sex-related variation in foraging strategies of California sea lions. Mar Biol 160:641–652. doi:10.1007/s00227-012-2119-y
Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Ferretto G, Angell OC (2015) Current status of the California sea lion (Zalophus californianus) and the northern elephant seal (Mirounga angustirostris) at the San Benito Archipelago, Mexico. Cienc Mar 41:269–281. doi:10.7773/cm.v41i4.2545
Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Juárez A, Baleyto M, Galván F, Aguíñiga S (2016a) Isotopic variation between adult female Guadalupe fur seals and their offspring: implications for the use of neonates as proxies for maternal foraging. Aquat Mamm 43:268–275. doi:10.1578/AM.42.3.2016.268
Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Sierra-Rodríguez GE, Rosales-Nanduca H, Acevedo-Whitehouse K, Sandoval-Sierra J (2016b) Impact of the 2015 El Niño-Southern Oscillation on the abundance and foraging habits of Guadalupe fur seals and California sea lions from the San Benito Archipelago, México. PLoS ONE 11:e0155034. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0155034
Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Morales-Luna L, Heckel G, Schramm Y (2016c) Foraging ecology of harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) and northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris) from Baja California, México: inferences from stable isotopes in pups. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 96:1–6. doi:10.1017/S0025315415002143
Estes JA, Riedman ML, Staedler MM, Tinker MT, Lyon BE (2003) Individual variation in prey selection by sea otters: patterns, causes and implications. J Anim Ecol 72:144–155. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2656.2003.00690.x
France RL (1995) Carbon-13 enrichment in benthic compared to planktonic algae: foodweb implications. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 124:307–312. doi:10.3354/meps12430
Franzreb KE (1983) Intersexual habitat partitioning in yellow-rumped warblers during the breeding season. Wilson Bull 95:581–590
Fry B, Wainright SC (1991) Diatom sources of 13C-rich carbon in marine food webs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 76:149–157. doi:10.3354/meps076149
Goericke R, Fry B (1994) Variations of marine plankton δ13C with latitude, temperature, and dissolved CO2 in the world ocean. Glob Biogeochem Cycl 8:85–90. doi:10.1029/93GB03272
Habran S, Debier C, Crocker DE, Houser DS, Lepoint G, Bouquegneau JM, Das K (2010) Assessment of gestation, lactation and fasting on stable isotope ratios in northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris). Mar Mamm Sci 26:880–895. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2010.00372.x
Hückstädt L (2015) Mirounga angustirostris. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015: e.T13581A45227116. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T18306A50663128.en. Accessed 27 June 2016
Jackson AL, Inger R, Parnell AC, Bearhop S (2011) Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—stable isotope Bayesian ellipses in R. Anim Ecol 80:595–602. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2011.01806.x
Jennings S, Pinnegar JK, Polunin NVC, Boon TW (2001) Weak cross-species relationships between body size and trophic level belie powerful size-based trophic structuring in fish communities. J Anim Ecol 70:934–944. doi:10.1046/j.0021-8790.2001.00552.x
Laws RM (1993) Identification of species. In: Laws RM (ed) Antarctic seals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–28
Le Boeuf BJ (1974) Male–male competition and reproductive success in elephant seals. Am Zool 14:163–176. doi:10.1093/icb/14.1.163
Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (1994) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley
Le Boeuf BJ, Crocker DE, Blackwell SB, Morris PA, Thorson PH (1993) Sex differences in diving and foraging behaviour of northern elephant seals. Symp Zool Soc Lond 66:149–178
Le Boeuf BJ, Crocker DE, Costa DP, Blackwell SB, Webb PM, Houser DS (2000) Foraging ecology of northern elephant seals. Ecol Monogr 70:353–382. doi:10.2307/2657207
Lewis R, O’Connell TC, Lewis M, Campagna C, Hoelzel AR (2006) Sex-specific foraging strategies and resource partitioning in the southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina). Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 273:2901–2907. doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3642
Loor-Andrade P, Galván-Magaña F, Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Polo-Silva C, Delgado-Huertas A (2015) Population and individual foraging patterns of two sympatric hammerhead sharks using stable isotopes. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 29:821–829. doi:10.1002/rcm.7169
Lowry MS, Condit R, Hatfield B, Allen SG, Berger R, Morris PA, Le Boeuf BJ, Reiter J (2014) Abundance, distribution, and population growth of the northern elephant seal (Mirounga angustirostris) in the United States from 1991 to 2010. Aquat Mamm 40:20–31. doi:10.1578/AM.40.1.2014.20
Macko SA, Estep MLF (1984) Microbial alteration of stable nitrogen and carbon isotopic compositions of organic matter. Org Geochem 6:787–790. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(84)90100-1
Michener RH, Schell DM (1994) Stable isotope ratios as tracers in marine aquatic food webs. In: Lajtha H, Michener RH (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. Blackwell, Boston, pp 138–157
Newsome S, Martínez del Río C, Bearhop S, Phillips D (2007) A niche for isotopic ecology. Front Ecol Environ 5:429–436. doi:10.1890/060150.1
Noske RA (1986) Intersexual niche segregation among three bark-foraging birds of eucalypt forests. Aust J Ecol 11:255–267
Ortega-Ortiz CD, Elorriaga-Verplancken FR, Olivos-Ortiz A, Liñán-Cabello MA, Vargas-Bravo MH (2014) Insights into the feeding habits of false killer whales (Pseudorca crassidens) in the Mexican Central Pacific. Aquat Mamm 40:386–393. doi:10.1578/AM.40.4.2014.386
Porras-Peters HD, Aurioles-Gamboa D, Cruz-Escalona V, Koch P (2008) Trophic level and overlap of sea lion (Zalophus californianus) in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Mar Mamm Sci 24:554–576. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2008.00197.x
Post DM (2002) Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 83:703–718. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[0703:USITET]2.0.CO;2
Riofrío-Lazo M, Aurioles-Gamboa D, Le Boeuf BJ (2012) Ontogenetic changes in feeding habits of northern elephant seals revealed by δ15N and δ13C analysis of growth layers in teeth. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 450:229–241. doi:10.3354/meps09562
Robinson PW, Costa DP, Crocker DE, Gallo-Reynoso JP, Champagne CD, Fowler MA, Kuhn CE (2012) Foraging behavior and success of a mesopelagic predator in the northeast Pacific Ocean: insights from a data-rich species, the northern elephant seal. PLoS ONE 7:e36728. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036728
Ruiz-Cooley RI, Gendron D, Aguíñiga S, Mesnick S, Carriquiry JD (2004) Trophic relationships between sperm whales and jumbo squid using stable isotopes of C and N. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 277:275–283. doi:10.3354/meps27727
Ryan C, McHugh B, Trueman CN, Sabin R, Deaville R, Harrod C, Berrow SD, O’Connor I (2013) Stable isotope analysis of baleen reveals resource partitioning among sympatric rorquals and population structure in fin whales. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 479:251–261. doi:10.3354/meps10231
Sandoval-Sierra J (2016) Nicho isotópico de dos colonias de lobo marino de California (Zalophus californianus): Análisis de amplitud y de la relación entre crías y adultos. Dissertation, UABCS, La Paz, BCS, México
Simmons SE, Crocker DE, Kudela RM, Costa DP (2007) Linking foraging behaviour of the northern elephant seal with oceanography and bathymetry at mesoscales. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 346:265–275. doi:10.3354/meps07014
Stewart BS, DeLong RL (1994) Postbreeding foraging migrations of northern elephant seals. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 290–309
Voss M, Dippner JW, Montoya JP (2001) Nitrogen isotope patterns in the oxygen-deficient waters of the Eastern Tropical North Pacific Ocean. Deep Sea Res 48:1905–1921. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(00)00110-2
Weise MJ, Costa DP (2007) Total body oxygen stores and physiological diving capacity of California sea lions as a function of sex and age. J Exp Biol 210:278–289. doi:10.1242/jeb.02643
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT, Mexico, Grant Number CB-181876). We thank the Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT, Mexico), through the Dirección General de Vida Silvestre, for granting us research permits SGPA/DGVS/11309/12 and 11744/13. We also thank Cooperativa Pesquera “Pescadores Nacionales de Abulón” from Cedros Island, for their support in the field. FREV thanks the Instituto Politécnico Nacional for the support received through the Programa de Contratación por Excelencia (Contracting Excellence Program) and the EDI Fellowship. We thank Kristin Sullivan for editing the English version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest, of any kind. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: G. H. Engelhard.
Reviewed by C. McMahon, Ch. Ortega-Ortiz and an undisclosed expert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velázquez-Castillo, M.A., Elorriaga-Verplancken, F.R. Isotopic evidence for intersexual foraging variation in northern elephant seals from Baja California, Mexico. Mar Biol 164, 168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3192-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3192-z