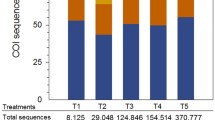
Abstract
Introduction and spread of invasive non-indigenous species (NIS) has been clearly recognized as a growing global problem in marine and coastal ecosystems. Early detection of NIS has been recognized as one of the first priorities and effective ways in management programs. However, the detection of an array of rare NIS based on traditional morphological methods represents enormous technical challenges in the marine realm, as numerous poorly studied organisms may be small and/or have insufficient morphological distinctive features. The use of DNA-based approaches has largely increased the detection accuracy and efficiency. Owing to many obvious advantages such as the high capacity to detect extremely low-abundance species and low cost per sequence, high-throughput sequencing (HTS)-based methods have been popularly proposed for early detection of marine NIS. Although HTS-based approaches have been approved robust for the census of NIS in aquatic ecosystems, especially for those present at extremely low abundance, many factors in experimental design and data collection can cause errors including both false negatives and false positives. Here we identify factors responsible for both error types, discuss causes and consequences, and propose possible solutions when utilizing HTS for early detection of NIS in marine and coastal ecosystems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellemain E, Carlsen T, Brochmann C, Coissac E, Taberlet P, Kauserud H (2010) ITS as an environmental DNA barcode for fungi: an in silico approach reveals potential PCR biases. BMC Microbiol 10:189
Blaalid R, Davey ML, Kauserud H, Carlsen T, Halvorsen R, Høiland K, Eidesen PB (2014) Arctic root-associated fungal community composition reflects environmental filtering. Mol Ecol 23:649–659
Boessenkool S, Epp LS, Haile J, Bellemain E (2012) Blocking human contaminant DNA during PCR allows amplification of rare mammal species from sedimentary ancient DNA. Mol Ecol 21:1806–1815
Botnen S, Vik U, Carlsen T et al (2014) Low host specificity of root-associated fungi at an Arctic site. Mol Ecol 23:975–985
Briski E, Cristescu ME, Bailey SA, MacIsaac HJ (2011) Use of DNA barcoding to detect invertebrate invasive species from diapausing eggs. Biol Invasions 13:1325–1340
Brown SP, Veach AM, Rigdon-Huss AR, Grond K, Lickteig SK, Lothamer K, Oliver AK, Jumpponen A (2014) Scraping the bottom of the barrel: are rare high throughput sequences artifacts? Fungal Ecol 13:221–225
Carew ME, Pettigrove VJ, Metzeling L, Hoffmann AA (2013) Environmental monitoring using next generation sequencing: rapid identification of macroinvertebrate bioindicator species. Front Zool 10:45
Carlsen T, Aas AB, Lindner D, Vra lstad T, Chumacher T, Kauserud H (2012) Don’t make a mista(g)ke: is tag switching an overlooked source of error in amplicon pyrosequencing studies? Fungal Ecol 5:747–749
Carlton JT, Gellar JB (1993) Ecological roulette: the global transport of nonindigenous marine organisms. Science 261:78–82
Carugati L, Corinaldesi C, Dell’Anno A, Danovaro R (2015) Metagenetic tools for the census of marine meiofaunal biodiversity. Mar Genomics 24:11–20. doi:10.1016/j.margen.2015.04.010
Clarke LJ, Soubrier J, Weyrich LS, Cooper A (2014) Environmental metabarcodes for insects: in silico PCR reveals potential for taxonomic bias. Mol Ecol Resour 14:1160–1170
Comtet T, Sandionigi A, Viard F, Casiraghi M (2015) DNA (meta) barcoding of biological invasions: a powerful tool to elucidate invasion processes and help managing aliens. Biol Invasions 17:905–922
Cowart DA, Pinheiro M, Mouchel O, Maguer M, Grall J, Miné J, Arnaud-Haond S (2015) Metabarcoding is powerful yet still blind: a comparative analysis of morphological and molecular surveys of seagrass communities. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0117562
Creer S (2010) Second-generation sequencing derived insights into the temporal biodiversity dynamics of freshwater protists. Mol Ecol 19:2829–2831
Creer S, Fonseca VG, Porazinska DL, Giblin-Davis M, Sung W, Power DM, Packer M, Carvalho GR, Blaxter ML, Lambshead PJD, Thomas WK (2010) Ultrasequencing of the meiofaunal biosphere: practice, pitfalls, and promises. Mol Ecol 19:4–20
Darling JA, Mahon AR (2011) From molecules to management: adopting DNA-based methods for monitoring biological invasions in aquatic environments. Environ Res 111:978–988
Deagle BE, Jarman SN, Coissac E, Pompanon F, Taberlet P (2014) DNA metabarcoding and the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I marker: not a perfect match. Biol Lett 10:20140562
Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, Wrighton K, Zvenigorodsky N, Chen F, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P (2010) Experimental factors affecting PCR-based estimates of microbial species richness and evenness. ISME J 4:642–647
Esling P, Lejzerowicz F, Pawlowski J (2015) Accurate multiplexing and filtering for high-throughput amplicon-sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv107
Ficetola GF, Pansu J, Bonin A, Coissac E, Giguet-Covex C, De Barba M, Gielly L, Lopes CM, Boyer F, Pompanon F, Rayé G, Taberlet P (2015) Replication levels, false presences and the estimation of the presence/absence from eDNA metabarcoding data. Mol Ecol Resour 15:543–556
Finnoff D, Shogren JF, Leung B, Lodge D (2007) Take a risk: preferring prevention over control of biological invaders. Ecol Econ 62:216–222
Flynn JM, Brown EA, Chain FJJ, MacIsaac HJ, Cristescu ME (2015) Toward accurate molecular identification of species in complex environmental samples: testing the performance of sequence filtering and clustering methods. Ecol Evol 5:2252–2266
Harvey CT, Qureshi SA, MacIsaac HJ (2009) Detection of a colonizing, aquatic, non-indigenous species. Divers Distrib 15:429–437
Huse SM, Welch DM, Morrison HG, Sogin ML (2010) Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ Microbiol 12:1889–1898
Ihrmark K, Bödeker ITM, Cruz-Martinez K, Friberg H, Kubartova A, Schenck J, Strid Y, Stenlid J, Brandström-Durling M, Clemmensen KE, Lindahl BD (2012) New primers to amplify the fungal ITS2 region-evaluation by 454-sequencing of artificial and natural communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 82:666–677
Jerde CL, Mahon AR, Chadderton WL, Lodge DM (2011) “Sightunseen” detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conserv Lett 4:150–157
Keskİn E, Atar HH (2013) DNA barcoding commercially important fish species of Turkey. Mol Ecol Resour 13:788–797
Kircher M, Sawyer S, Meyer M (2011) Double indexing overcomes inaccuracies in multiplex sequencing on the Illumina platform. Nucleic Acids Res. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr771
Knebelsberger T, Landi M, Neumann H, Kloppmann M, Sell AF, Campbell PD, Campbell PD, Laakmann S, Raupach MJ, Carvalho GR, Costa FO (2014) A reliable DNA barcode reference library for the identification of the North European shelf fish fauna. Mol Ecol Resour 14:1060–1071
Kunin V, Engelbrektson A, Ochman H, Hugenholtz P (2010) Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environ Microbiol 12:118–123
Lawler JJ, Aukema JE, Grant JB, Halpern BS, Kareiva P, Nelson CR, Ohleth K, Olden JD, Schlaepfer MA, Silliman BR, Zaradic P (2006) Conservation science: a 20-year report card. Front Ecol Environ 4:473–480
Lin Y, Gao Z, Zhan A (2015) Introduction and use of non-native species for aquaculture in China: status, risks and management solutions. Rev Aquac 7:28–58
Liu S, Li Y, Lu J, Su X, Tang M, Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhou C, Yang Q, Ji Y, Yu DW, Zhou X (2013) SOAPBarcode: revealing arthropod biodiversity through assembly of Illumina shotgun sequences of PCR amplicons. Methods Ecol Evol 4:1142–1150
Lobo J, Teixeira MAL, Borges LMS, Ferreira MSG, Hollatz C, Gomes PT, Sousa R, Ravara A, Costa MH, Costa FO (2015) Starting a DNA barcode reference library for shallow water polychaetes from the southern European Atlantic coast. Mol Ecol Resour. doi:10.1111/1755-0998.12441
Lodge DM, Williams S, MacIsaac HJ, Hayes K, Leung B, Reichard S, Mack RN, Moyle PB, Smith M, Andow DA, Carlton JT, McMichael A (2006) Biological invasions: recommendations for U.S. policy and management. Ecol Appl 16:2035–2054
Lodge DM, Turner CR, Jerde CL, Barnes MA, Chadderton L, Egan SP, Feder JL, Mahon AR, Pfrender ME (2012) Conservation in a cup of water: estimating biodiversity and population abundance from environmental DNA. Mol Ecol 21:2555–2558
Machida RJ, Knowlton N (2012) PCR primers for metazoan nuclear 18S and 28S ribosomal DNA sequences. PLoS One 7:e46180
MacKenzie DIM, Nichols JD, Lachman GB, Droege S, Royle JA, Langtimm CA (2002) Estimating site occupancy rates when detection probabilities are less than one. Ecology 83:2248–2255
Mackie JA, Geller J (2010) Experimental parameters affecting quantitative PCRofArtemia franciscana: amodel for amarine zooplanktonic target in natural plankton samples. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 8:337–347
Mahon AR, Barnes MA, Senapati S, Feder JL, Darling JA, Chang H, Lodge DM (2011) Molecular detection of invasive species in heterogeneous mixtures using a microfluidic carbon nanotube platform. PLoS ONE 6:e17280. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017280
McDonald LL (2004) Sampling rare populations. In: Thompson WL (ed) Sampling rare or elusive species: concepts, designs, and techniques for estimating population parameters. Island Press, NewYork, pp 11–42
Ovaskainen O, Schigel D, Ali-Kovero H, Auvinen P, Paulin L, Nordén B, Nordén J (2013) Combining high–throughput sequencing with fruit body surveys reveals contrasting lifehistory strategies in fungi. ISME J 7:1696–1709
Paavola M, Olenin S, Leppakoski E (2005) Are invasive species most successful in habitats of low native species richness across European brackish water seas? Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64:738–750
Pochon X, Bott NJ, Smith KF, Wood SA (2013) Evaluating detection limits of next-generation sequencing for the surveillance and monitoring of international marine pests. PLoS ONE 8:e73935
Pompanon F, Samadi S (2015) Next generation sequencing for characterizing biodiversity promises and challenges. Genetica 143:133–138
Quince C, Lanzén A, Curtis TP, Davenport RJ, Hall N, Head IM, Read LF, Sloan WT (2009) Accurate determination of microbial diversity from 454 pyrosequencing data. Nat Methods 6:639–641
Ratnasingham S, Hebert PDN (2007) BOLD: the barcode of life data system (www.barcodinglife.org). Mol Ecol Notes 7:355–364
Reeder J, Knight R (2009) The ‘rare biosphere’: a reality check. Nat Methods 6:636–637
Schmieder R, Edwards R (2011) Fast identification and removal of sequence contamination from genomic and metagenomic datasets. PLoS ONE 6:e17288
Schnell IB, Bohmann K, Gilbert MTP (2015) Tag jumps illuminated-reducing sequence-to-sample misidentifications in metabarcoding studies. Mol Ecol Resour 15:1289–1303
Schoch CL, Seifert KA, Huhndorf S, Robert V, Spouge JL, Levesque CA, Chen W, Fungal Barcoding Consortium (2012) Nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region as a universal DNA barcode marker for Fungi. P Natl Acad Sci USA 109:6241–6246
Srivathsan A, Sha JCM, Vogler AP, Meier R (2015) Comparing the effectiveness of metagenomics and metabarcoding for diet analysis of a leaf-feeding monkey (Pygathrix nemaeus). Mol Ecol Resour 15:250–261
Sun C, Zhao Y, Li H, Dong Y, MacIsaac HJ, Zhan A (2015) Unreliable quantitation of species abundance based on high-throughput sequencing data of zooplankton communities. Aquat Biol 24:9–15
Taberlet P, Coissac E, Hajibabaei M, Rieseberg LH (2012) Environmental DNA. Mol Ecol 21:1789–1793
Tang CQ, Leasi F, Obertegger U, Kieneke A, Barraclough TG, Fontaneto D (2012) The widely used small subunit 18S rDNA molecule greatly underestimates true diversity in biodiversity surveys of the meiofauna. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:16208–16212
Tedersoo L, Nilsson RH, Abarenkov K, Jairus T, Sadam A, Saar I, Bahram M, Bechem E, Chuyong G, Kõljalg U (2010) 454 Pyrosequencing and Sanger sequencing of tropical mycorrhizal fungi provide similar results but reveal substantial methodological biases. New Phytol 188:291–301
Toju H, Tanabe AS, Yamamoto S, Sato H (2012) High-coverage ITS primers for the DNA-based identification of Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes in environmental samples. PLoS ONE 7:e40863
van Orsouw NJ, Hogers RCJ, Janssen A, Yalcin F, Snoeijers S, Verstege E, Schneiders H, Hvd Poel, Jv Oeveren, Verstege H, Schneiders H, van der Poel H, van Oeveren J, Verstegen H, van Eijk MJT (2007) Complexity reduction of polymorphic sequences (CRoPSTM): a novel approach for large-scale polymorphism discovery in complex genomes. PLoS ONE 2:e1172
van Velzen R, Weitschek E, Felici G, Bakker FT (2012) DNA barcoding of recently diverged species: relative performance of matching methods. PLoS ONE 7:e30490
Vander Zanden MJ, Hansen GJA, Higgins SN, Kornis MS (2010) A pound of prevention, plus a pound of cure: early detection and eradication of invasive species in the Laurentian Great Lakes. J Great Lakes Res 36:199–205
Vestheim H, Jarman SN (2008) Blocking primers to enhance PCR amplification of rare sequences in mixed samples-a case study on prey DNA in Antarctic krill stomachs. Front Zool 5:12
Williamson M, Fitter A (1996) The varying success of invaders. Ecology 77:1661–1666
Zaiko A, Martinez JL, Schmidt-Petersen J, Ribicic D, Samuiloviene A, Garcia-Vazquez E (2015) Metabarcoding approach for the ballast water surveillance—an advantageous solution or an awkward challenge? Mar Pollut Bull 92:25–34
Zhan A, MacIsaac HJ (2015) Rare biosphere exploration using high-throughput sequencing: research progress and perspectives. Conserv Genet 16:513–522
Zhan A, Hulák M, Sylvester F, Huang X, Adebayo AA, Abbott CL, Adamowicz SJ, Heath DD, Cristescu ME, MacIsaac HJ (2013) High sensitivity of 454 pyrosequencing for detection of rare species in aquatic communities. Methods Ecol Evol 4:558–565
Zhan A, Bailey SA, Heath DD, MacIsaac HJ (2014a) Performance comparison of genetic markers for high-throughput sequencing-based biodiversity assessment in complex communities. Mol Ecol Resour 14:1049–1059
Zhan A, Xiong W, He S, MacIsaac HJ (2014b) Influence of artifact removal on rare species recovery in natural complex communities using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 9:e96928
Zhan S, He EA, Brown FJJ, Chain TW, Therriault CL, Abbott DD, Heath ME, MacIsaac Cristescu HJ (2014c) Reproducibility of pyrosequencing data for biodiversity assessment in complex communities. Methods Ecol Evol 5:881–890
Zhan A, Briski E, Bock DG, Ghabooli S, MacIsaac HJ (2015) Ascidians as models for studying invasion success. Mar Biol 162:2449–2470
Zhou J, Wu L, Deng Y, Zhi X, Jiang Y, Tu Q, Xie J, Van Nostrand JD, He Z, Yang Y (2011) Reproducibility and quantitation of amplicon sequencing-based detection. ISME J 5:1303–1313
Zhou J, Jiang Y, Deng Y, Shi Z, Zhou B, Xue K, Wu L, He Z, Yang Y (2013a) Random sampling process leads to overestimation of bdiversity of microbial communities. mBio 4:324. doi:10.1128/mBio.00324-13
Zhou X, Li Y, Liu S, Yang Q, Su X, Zhou L, Tang M, Fu R, Li J, Huang Q (2013b) Ultra-deep sequencing enables high-fidelity recovery of biodiversity for bulk arthropod samples without PCR amplification. Gigascience 2:4
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272665) and 100 Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences to A.Z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: T. Reusch.
Reviewed by Undisclosed expert.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Invasive Species.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, W., Li, H. & Zhan, A. Early detection of invasive species in marine ecosystems using high-throughput sequencing: technical challenges and possible solutions. Mar Biol 163, 139 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2911-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2911-1