Abstract
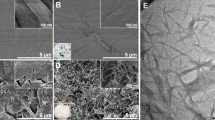
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) are difficult to redisperse after drying unless chemical modification or adding additives has been adopted. The production, transportation and application of CNCs in large-scale are restricted owing to the poor redispersion ability. To this end, CNCs with redispersion ability were successfully extracted by nickel chloride hydrate enhanced deep eutectic solvent (Ni-DES), which is composed of choline chloride and oxalic acid dihydrate, from microcrystalline cellulose. C2O42− and Ni2+ are integrated with each other owing to the incorporation of deionized water at the end of Ni-DES extraction. As a result, the particles of NiC2O4·2H2O are found on the surface of obtained CNCs. The NiC2O4·2H2O particles, which can be removed by acid-washing, are beneficial to the redispersion of dried CNCs because they can prevent the formation of hydrogen bond during CNCs drying, as demonstrated by the results of SEM, XRD and size distribution. In addition, the results of FTIR, XRD, SEM, and TEM reveal that the crystalline structure, chemical structure, and microstructure morphology of CNCs are scarcely varied during the drying and redispersion. Nevertheless, the slight flocculation of CNCs is unavoidable during the drying and redispersion, which is responsible for the insignificant depravation in the size and size distribution of redispersed CNCs. Fortunately, the satisfied redispersion ability of CNCs is obtained by Ni-DES extraction. It is obvious that using Ni-DES for the extraction of redispersible CNCs can provide a potential strategy for improving the economic and environmental viability of CNC industrial production and application.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott AP, Boothby D, Capper G, Davies DL, Rasheed RK (2004) Deep eutectic solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 126:9142–9147. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja048266j
Baldrian P, Valaskova V (2008) Degradation of cellulose by basidiomycetous fungi. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:501–521. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00106.x
Beck S, Bouchard J, Berry R (2012) Dispersibility in water of dried nanocrystalline cellulose. Biomacromol 13:1486–1494. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm300191k
Beguin P, Aubert JP (1994) The biological degradation of cellulose. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:25–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-6445(94)90099-x
Blifernez-Klassen O, Klassen V, Doebbe A, Kersting K, Grimm P, Wobbe L, Kruse O (2012) Cellulose degradation and assimilation by the unicellular phototrophic eukaryote Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nat Commun 3:1214. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2210
Brinchi L, Cotana F, Fortunati E, Kenny JM (2013) Production of nanocrystalline cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass: technology and applications. Carbohydr Polym 94:154–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.033
Chen Z, Sun Y, Wan C (2019) Effects of alkaline hydrogen peroxide treatment on cellulose accessibility of switchgrass pretreated by acidic deep eutectic solvent. Cellulose 26:9439–9446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02759-5
Cui S, Zhang S, Ge S, Xiong L, Sun Q (2016) Green preparation and characterization of size-controlled nanocrystalline cellulose via ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis. Ind Crops Prod 83:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.01.019
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
Grzabka-Zasadzinska A, Skrzypczak A, Borysiak S (2019) The influence of the cation type of ionic liquid on the production of nanocrystalline cellulose and mechanical properties of chitosan-based biocomposites. Cellulose 26:4827–4840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02412-1
Hakkinen R, Abbott A (2019) Solvation of carbohydrates in five choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents and the implication for cellulose solubility. Green Chem 21:4673–4682. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc00559e
Ilyas RA, Sapuan SM, Ishak MR, Zainudin ES (2018) Development and characterization of sugar palm nanocrystalline cellulose reinforced sugar palm starch bionanocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 202:186–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.002
Jongaroontaprangsee S, Chiewchan N, Devahastin S (2018) Production of nanofibrillated cellulose with superior water redispersibility from lime residues via a chemical-free process. Carbohydr Polym 193:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.008
Jordan JH, Easson MW, Condon BD (2020) Cellulose hydrolysis using ionic liquids and inorganic acids under dilute conditions: morphological comparison of nanocellulose. RSC Adv 10:39413–39424. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra05976e
Kian LK, Saba N, Jawaid M, Alothman OY, Fouad H (2020) Properties and characteristics of nanocrystalline cellulose Isolated from olive fiber. Carbohydr Polym 241:116423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116423
Koshani R, Zhang J, Van De Ven TGM, Lu X, Wang Y (2021) Modified hairy nanocrystalline cellulose as photobactericidal nanofillers for food packaging application. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9:10513–10523. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c02289
Kusmono, Affan MN (2020) Isolation and characterization of nanocrystalline cellulose from Ramie fibers via phosphoric acid hydrolysis. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2020.1821292
Kuznetsov BN, Sudakova IG, Garyntseva NV, Tarabanko VE, Yatsenkova OV, Djakovitch L, Rataboul F (2020) Processes of catalytic oxidation for the production of chemicals from softwood biomass. Catal Today 375:132–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.05.044
Leung ACW, Hrapovic S, Lam E, Liu Y, Male KB, Mahmoud KA, Luong JHT (2011) Characteristics and properties of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals prepared from a novel one-step procedure. Small 7:102–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201001715
Li L, Tao H, Wu B, Zhu G, Li k, Lin N, (2018) Triazole end-grafting on cellulose nanocrystals for water-redispersion improvement and reactive enhancement to nanocomposites. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:14888–14900. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03407
Li X, Ning C, Li L, Liu W, Ren Q, Hou Q (2021) Fabricating lignin-containing cellulose nanofibrils with unique properties from agricultural residues with assistance of deep eutectic solvents. Carbohydr Polym 274:118650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118650
Lu Q, Wu J, Li Y, Huang B (2021) Isolation of thermostable cellulose II nanocrystals and their molecular bridging for electroresponsive and pH-sensitive bio-nanocomposite. Ind Crops Prod 173:114127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114127
Martins MAR, Pinho SP, Coutinho JAP (2019) Insights into the nature of eutectic and deep eutectic mixtures. J Solution Chem 48:962–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-018-0793-1
Nagarajan KJ, Balaji AN, Rajan STK, Ramanujam NR (2020) Preparation of bio-eco based cellulose nanomaterials from used disposal paper cups through citric acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr Polym 235:115997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115997
Nezhad-Mokhtari P, Akrami-Hasan-Kohal M, Ghorbani M (2020) An injectable chitosan-based hydrogel scaffold containing gold nanoparticles for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol 154:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.112
Ngwabebhoh FA, Erdem A, Yildiz U (2018) A design optimization study on synthesized nanocrystalline cellulose, evaluation and surface modification as a potential biomaterial for prospective biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 114:536–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.155
Nicu R, Ciolacu F, Ciolacu DE (2021) Advanced functional materials based on nanocellulose for pharmaceutical/medical applications. Pharmaceutics 13:1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081125
Peng L, Lin L, Zhang J, Zhuang J, Zhang B, Gong Y (2010) Catalytic conversion of cellulose to levulinic acid by metal chlorides. Molecules 15:5258–5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15085258
Posada P, Velásquez-Cock J, Gómez-Hoyos C et al (2020) Drying and redispersion of plant cellulose nanofibers for industrial applications: a review. Cellulose 27:10649–10670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03348-7
Ramdzan NSM, Fen YW, Omar NAS, Anas NAA, Liew JYC, Daniyal WMEMM, Hashim HS (2021) Detection of mercury ion using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy based on nanocrystalline cellulose/poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) thin film. Measurement 182:109728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109728
Rohaizu R, Wanrosli WD (2017) Sono-assisted TEMPO oxidation of oil palm lignocellulosic biomass for isolation of nanocrystalline cellulose. Ultrason Sonochem 34:631–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.06.040
Rosddi NNM, Fen YW, Anas NAA, Omar NAS, Daniyal WMEMM (2020) Cationically modified nanocrystalline cellulose/carboxyl-functionalized graphene quantum dots nanocomposite thin film: characterization and potential sensing application. Crystals 10:875. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst10100875
Sartika D, Syamsu K, Warsiki E, Fahma F, Arnata IW (2021) Nanocrystalline cellulose from Kapok fiber (Ceiba pentandra ) and its reinforcement effect on alginate hydrogel bead. Starch Starke 73:2100033. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.202100033
Schwarz WH (2001) The cellulosome and cellulose degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:634–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100710
Segal LC, Creely J, Martin AEJ, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-Ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Shang Z, An X, Seta FT et al (2019) Improving dispersion stability of hydrochloric acid hydrolyzed cellulose nano-crystals. Carbohydr Polym 222:115037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115037
Sinquefield S, Ciesielski PN, Li K, Gardner DJ, Ozcan S (2020) Nanocellulose dewatering and drying: current state and future perspectives. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:9601–9615. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01797
Sirvio JA, Visanko M, Liimatainen H (2016) Acidic deep eutectic solvents as hydrolytic media for cellulose nanocrystal production. Biomacromol 17:3025–3032. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00910
Surov OV, Voronova MI, Rubleva NV et al (2018) A novel effective approach of nanocrystalline cellulose production: oxidation-hydrolysis strategy. Cellulose 25:5035–5048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1910-4
Sze LL, Pandey S, Ravula S, Pandey S, Zhao H, Baker GA, Baker SN (2014) Ternary deep eutectic solvents tasked for carbon dioxide capture. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:2117–2123. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc5001594
Trache D, Donnot A, Khimeche K, Benelmir R, Brosse N (2014) Physico-chemical properties and thermal stability of microcrystalline cellulose isolated from alfa fibres. Carbohydr Polym 104:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.058
Trache D, Hussin MH, Chuin CTH et al (2016) Microcrystalline cellulose: isolation, characterization and bio-composites application-a review. Int J Biol Macromol 93:789–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.09.056
Tritt-Goc J, Jankowska I, Pogorzelec-Glaser K, Pankiewicz R, Ławniczak P (2018) Imidazole-doped nanocrystalline cellulose solid proton conductor: synthesis, thermal properties, and conductivity. Cellulose 25:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1555-8
Vaezi K, Asadpour G, Sharifi SH (2019) Effect of coating with novel bio nanocomposites of cationic starch/cellulose nanocrystals on the fundamental properties of the packaging paper. Polym Test 80:106080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.106080
Visanko M, Sirvio JA, Piltonen P, Sliz R, Liimatainen H, Illikainen M (2017) Mechanical fabrication of high-strength and redispersible wood nanofibers from unbleached groundwood pulp. Cellulose 24:4173–4187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1406-7
Xu Y, Xu Y, Yue X (2017) Changes of hydrogen bonding and aggregation structure of cellulose fiber due to microwave-assisted alkali treatment and its impacts on the application as fluff pulp. Cellulose 24:967–976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1147-z
Xu H, Jin M, Geng J, Zhang S, Zhang H (2022a) Bacterial cellulose-regulated synthesis of metallic Ni catalysts for high-efficiency electrosynthesis of hydrogen peroxide. Sci China Mater 65:721–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-021-1795-9
Xu Y, Xu Y, Chen H, Gao M, Yue X, Ni Y (2022b) Redispersion of dried plant nanocellulose: a review. Carbohydr Polym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119830
Yang X, Xie H, Du H et al (2019) Facile extraction of thermally stable and dispersible cellulose nanocrystals with high yield via a green and recyclable FeCl3-catalyzed deep eutectic solvent system. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:7200–7208. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00209
Yue X, Xu Y, Li X, Xu Y (2017) Purification of cellulose from bleached pulp by lewis base-enhanced high-temperature liquid water treatment. BioResources 12:8725–8733. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.12.4.8725-8733
Yue X, He J, Xu Y, Yang M, Xu Y (2018) A novel method for preparing microcrystalline cellulose from bleached chemical pulp using transition metal ions enhanced high temperature liquid water process. Carbohydr Polym 208:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.072
Zhong C, Wang C, Wang F, Jia H, Wei P, Zhao Y (2016) Application of tetra-n-methylammonium hydroxide on cellulose dissolution and isolation from sugarcane bagasse. Carbohydr Polym 136:979–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.001
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Opening Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control (grant NO. 2019KF16), the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training program of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (grant NO. S202010708103) and the Shaanxi University of Science and Technology Academic Leader Training program (grant NO. 2013XSD25).
Funding
The Opening Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control (grant NO. 2019KF16), the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training program of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology (grant NO. S202010708103), the Shaanxi University of Science and Technology Academic Leader Training program (grant NO. 2013XSD25).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YX, HC and MG. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YX. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Xu, Y., Chen, H. et al. Extraction of cellulose nanocrystals with redispersion ability via deep eutectic solvents enhanced with nickel chloride hydrate. Wood Sci Technol 56, 1761–1781 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-022-01422-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-022-01422-w