Abstract
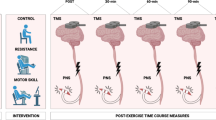
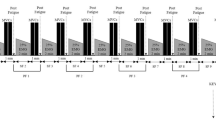
As the populations of the United States and developed nations age, motor control performance is adversely impacted, resulting in functional impairments that can diminish quality of life. Generally, force control in the lower limb worsens with age, with older adults (OA) displaying more variable and less accurate submaximal forces. Corticospinal inhibitory signaling may influence force control, with those OA who maintain corticospinal inhibitory signaling capacity achieving steadier forces. This study aimed to assess the relationships between lower limb force control and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) measures of corticospinal inhibition (i.e., cortical silent period (cSP) duration and depth). 15 OA and 14 young adults (YA) were recruited for this study. All subjects underwent a TMS protocol to elicit the cSP while maintaining 15% of their maximal force in their knee extensor muscles. OA and YA did not display differences in force control metrics or corticospinal inhibitory measures. However, in OA, maximal cSP depth (%dSP max) was associated with lower force variability. No other significant relationships existed in the YA or OA groups. Future studies will benefit from evaluating a range of target forces and target muscles to assess potential relationships between sensorimotor inhibitory capacity and control of muscle force output.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beynel L, Chauvin A, Guyader N, Harquel S, Marendaz C (2014) Age-related changes in intracortical inhibition are mental-cognitive state-dependent. Biol Psychol 101(1):9–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.05.011
Brasil-Neto JP, Cohen LG, Panizza M, Nilsson J, Roth BJ, Hallett M (1992) Optimal focal transcranial magnetic activation of the human motor cortex: effects of coil orientation, shape of the induced current pulse, and stimulus intensity. J Clin Neurophysiol 9(1):132–136. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004691-199201000-00014
Brown SH (1996) Control of simple arm movements in the elderly. Adv Psychol 114:27–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4115(96)80005-7
Calautti C, Serrati C, Baron JC (2001) Effects of age on brain activation during auditory-cued thumb-to-index opposition: a positron emission tomography study. Stroke 32(1):139–146. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.32.1.139
Carville SF, Perry MC, Rutherford OM, Smith ICH, Newham DJ (2007) Steadiness of quadriceps contractions in young and older adults with and without a history of falling. Eur J Appl Physiol 100:527–533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-006-0245-2
Cassady K, Gagnon H, Lalwani P, Simmonite M, Foerster B, Park D, Peltier SJ, Petrou M, Taylor SF, Weissman DH, Seidler RD, Polk TA (2019) Sensorimotor network segregation declines with age and is linked to GABA and to sensorimotor performance HHS public access. Neuroimage 186:234–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.11.008
Castronovo AM, Mrachacz-Kersting N, Stevenson AJT, Holobar A, Enoka RM, Farina D (2018) Decrease in force steadiness with aging is associated with increased power of the common but not independent input to motor neurons. J Neurophysiol 120(4):1616–1624. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00093.2018
Center for Chronic Disease Prevention, N., Promotion, H., & of Population Health, D. (2013). The state of aging and health in America 2013. Retrieved from www.cdc.gov/aging.
Chung-Hoon K, Tracy BL, Dibble LE, Marcus RL, Burgess P, LaStayo PC (2016) The association between knee extensor force steadiness, force accuracy, and mobility in older adults who have fallen. J Geriatr Phys Ther 39(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1519/JPT.0000000000000044
Davidson T, Tremblay F (2013) Hemispheric differences in corticospinal excitability and in transcallosal inhibition in relation to degree of handedness. PLoS ONE 8(7):e70286. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070286
de C. Hamilton AF, Jones KE, Wolpert DM (2004) The scaling of motor noise with muscle strength and motor unit number in humans. Exp Brain Res 157(4):417–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-1856-7
Enoka RM, Christou EA, Hunter SK, Kornatz KW, Semmler JG, Taylor AM, Tracy BL (2003) Mechanisms that contribute to differences in motor performance between young and old adults. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 13(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1050-6411(02)00084-6
Feeney DF, Mani D, Enoka RM, Taylor J, Farina D, Feeney DF (2018) Variability in common synaptic input to motor neurons modulates both force steadiness and pegboard time in young and older adults. J Physiol C 596:3793–3806. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP275658
Fleming MK, Newham DJ (2017) Reliability of transcallosal inhibition in healthy adults. Front Hum Neurosci 10:681. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00681
Fling BW, Seidler RD (2012a) Fundamental differences in callosal structure, neurophysiologic function, and bimanual control in young and older adults. Cereb Cortex 22(11):2643–2652. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr349
Fling BW, Seidler RD (2012b) Task-dependent effects of interhemispheric inhibition on motor control. Behav Brain Res 226(1):211–217
Fujiyama H, Garry MI, Levin O, Swinnen SP, Summers JJ (2009) Age-related differences in inhibitory processes during interlimb coordination. Brain Res 1262:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.01.023
Galganski ME, Fuglevand AJ, Enoka RM (1993) Reduced control of motor output in a human hand muscle of elderly subjects during submaximal contractions. J Neurophysiol 69:2108–2115
Garvey MA, Ziemann U, Becker DA, Barker CA, Bartko JJ (2001) New graphical method to measure silent periods evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol 112(8):1451–1460. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2457(01)00581-8
Gramsbergen A (2005) Postural control in man: the phylogenetic perspective. Neural Plast 12:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1155/NP.2005.77
Groppa S, Oliviero A, Eisen A, Quartarone A, Cohen LG, Mall V, Kaelin-Lang A, Mina T, Rossi S, Thickbroom GW, Rossini PM, Ziemann U, Valls-Solé J, Siebner HR (2012) A practical guide to diagnostic transcranial magnetic stimulation: report of an IFCN committee. Clin Neurophysiol 123(5):858. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLINPH.2012.01.010
Heuninckx S, Wenderoth N, Swinnen SP (2008) Systems neuroplasticity in the aging brain: recruiting additional neural resources for successful motor performance in elderly persons. J Neurosci 28(1):91. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3300-07.2008
Holmes MR, Gould JR, Peña-González I, Enoka RM (2015) Force steadiness during a co-contraction task can be improved with practice, but only by young adults and not by middle-aged or old adults. Exp Physiol 100(2):182–192. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2014.083741
Homan RW, Herman J, Purdy P (1987) Cerebral location of international 10–20 system electrode placement. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 66(4):376–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(87)90206-9
Hunter SK, Pereira HM, Keenan KG (2016) The aging neuromuscular system and motor performance. J Appl Physiol 121(4):982–995. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00475.2016
Hunter SK, Todd G, Butler JE, Gandevia SC, Taylor JL (2008) Recovery from supraspinal fatigue is slowed in old adults after fatiguing maximal isometric contractions. J Appl Physiol 105(4):1199–1209. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01246.2007
Hupfeld KE, Swanson CW, Fling BW, Seidler RD (2020) TMS-induced silent periods: a review of methods and call for consistency. J Neurosci Methods 346:108950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108950
Jung P, Ziemann U (2006) Differences of the ipsilateral silent period in small hand muscles. Muscle Nerve 34(4):431–436. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.20604
Keck ME, Pijnappels M, Schubert M, Colombo G, Curt A, Dietz V (1998) Stumbling reactions in man: influence of corticospinal input. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 109(3):215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-980X(98)00009-5
Laidlaw DH, Bilodeau M, Enoka RM (2000) Steadiness is reduced and motor unit discharge is more variable in old adults. Muscle Nerve 23(4):600–612
Marchini A, Pereira R, Pedroso W, Christou E, Neto OP (2017) Age-associated differences in motor output variability and coordination during the simultaneous dorsiflexion of both feet. Somatosens Mot Res 34(2):96–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/08990220.2017.1313220
McGinley M, Hoffman RL, Russ DW, Thomas JS, Clark BC (2010) Older adults exhibit more intracortical inhibition and less intracortical facilitation than young adults. Exp Gerontol 45(9):671–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2010.04.005
McGregor KM, Crosson B, Mammino K, Omar J, García PS, Nocera JR (2018) Influences of 12-week physical activity interventions on TMS measures of cortical network inhibition and upper extremity motor performance in older adults-a feasibility study. Front Aging Neurosci 9:422. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00422
Moritz CT, Barry BK, Pascoe MA, Enoka RM (2005) Discharge rate variability influences the variation in force fluctuations across the working range of a hand muscle. J Neurophysiol 93:2449–2459. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01122.2004
Oomen NMCW, Van Dieën JH (2017) Effects of age on force steadiness: a literature review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev 35:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.11.004
Pereira HM, Schlinder-Delap B, Nielson KA, Hunter SK (2018) Force steadiness during a cognitively challenging motor task is predicted by executive function in older adults. Front Physiol 9:1316. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01316
Petitjean M, Ko JYL (2013) An age-related change in the ipsilateral silent period of a small hand muscle. Clin Neurophysiol 124(2):346–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2012.07.006
Rossini PM, Barker AT, Berardelli A, Caramia MD, Caruso G, Cracco RQ, Tomberg C (1994) Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord and roots: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical application. Report of an IFCN committee. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 91(2):79–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(94)90029-9
Säisänen L, Pirinen E, Teitti S, Könönen M, Julkunen P, Määttä S, Karhu J (2008) Factors influencing cortical silent period: optimized stimulus location, intensity and muscle contraction. J Neurosci Methods 169(1):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.12.005
Seidler RD, Bernard JA, Burutolu TB, Fling BW, Gordon MT, Gwin JT, Kwak Y, Lipps DB (2010) Motor control and aging: links to age-related brain structural, functional, and biochemical effects. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34(5):721–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2009.10.005
Sherrington CS (1910) Flexion-reflex of the limb, crossed extension-reflex, and reflex stepping and standing. J Physiol 40(1–2):28–121. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001362
Siebner HR, Dressnandt J, Auer C, Conrad B (1998) Continuous intrathecal baclofen infusions induced a marked increase of the transcranially evoked silent period in a patient with generalized dystonia. Muscle Nerve 21(9):1209–1212. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199809)21:9%3c1209::AID-MUS15%3e3.0.CO;2-M
Sorond FA, Cruz-Almeida Y, Clark DJ, Viswanathan A, Scherzer CR, De Jager P, Csiszar A, Laurienti PJ, Hausdorff JM, Chen WG, Ferrucci L, Rosano C, Studenski SA, Black SE, Lipsitz LA (2015) Aging, the central nervous system, and mobility in older adults: neural mechanisms of mobility impairment. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 70(12):1526–1532. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glv130
Surgent OJ, Dadalko OI, Pickett KA, Travers BG (2019) Balance and the brain: a review of structural brain correlates of postural balance and balance training in humans. Gait Posture 71:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GAITPOST.2019.05.011
Swanson CW, Fling BW (2018) Associations between gait coordination, variability and motor cortex inhibition in young and older adults. Exp Gerontol 113:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2018.10.002
Swanson CW, Fling BW (2020) Associations between turning characteristics and corticospinal inhibition in young and older adults. Neuroscience 425:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.10.051
Tracy BL, Enoka RM (2002) Older adults are less steady during submaximal isometric contractions with the knee extensor muscles. J Appl Physiol 92(3):1004–1012. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00954.2001
Tracy BL, Mehoudar PD, Ortega JD (2007) The amplitude of force variability is correlated in the knee extensor and elbow flexor muscles. Exp Brain Res 176(3):448–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0631-3
Tsatsaki E, Amiridis IG, Holobar A, Trypidakis G, Arabatzi F, Kellis E, Enoka RM (2021) The length of tibialis anterior does not influence force steadiness during submaximal isometric contractions with the dorsiflexors. Eur J Sport Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2021.1922506
Wassermann EM, Fuhr P, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1991) Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on ipsilateral muscles. Neurology 41(11):1795–1799. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.41.11.1795
Welsh SJ, Dinenno DV, Tracy BL (2007) Variability of quadriceps femoris motor neuron discharge and muscle force in human aging. Exp Brain Res 179(2):219–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0785-z
Werhahn KJ, Kunesch E, Noachtar S, Benecke R, Classen J (1999) Differential effects on motorcortical inhibition induced by blockade of GABA uptake in humans. J Physiol 517(2):591–597. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0591t.x
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by John G. Semmler.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanson, M.R., Swanson, C.W., Whittier, T.T. et al. Inhibitory signaling as a predictor of leg force control in young and older adults. Exp Brain Res 240, 1005–1016 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-022-06321-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-022-06321-x