Abstract
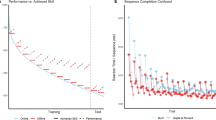
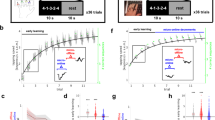
Children show motor learning deficits relative to adults across a diverse range of tasks. One mechanism that has been proposed to underlie these differences is the contribution of online and offline components to overall learning; however, these tasks have almost focused exclusively on sequence learning paradigms which are characterized by performance gains in the offline phase. Here, we examined the role of online and offline learning in a novel motor task which was characterized by warm-up decrement, i.e., a performance loss, during the offline phase. In particular, using a relatively extended practice period, we examined if differences between children and adults persist across relatively long practice periods, and if the contribution of online and offline learning is affected by age and by practice itself. Two groups of children, 8–10 years and 11–13 years old, and one group of young adults (N = 30, n = 10/group) learned a novel task that required control of upper body movements to control a cursor on a screen. Participants learned the task over 5 days and we measured movement time as the primary task performance variable. Consistent with prior results, we found that 8–10 year olds had longer movement times compared to both 11–13 year olds and adults. We also found distinct changes in online and offline learning with practice; the amount of online learning decreased with practice, whereas offline learning was relatively stable across practice. However, there was no detectable effect of age group on either online or offline learning. These results suggest that age-related differences in learning among children 8–10 years old are persistent even after extended practice but are not necessarily accounted for by differences in online and offline learning.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JA (1961) The second facet of forgetting: a review of warm-up decrement. Psychol Bull 58:257–273. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0044798
Ajemian R, D’Ausilio A, Moorman H, Bizzi E (2010) Why professional athletes need a prolonged period of warm-up and other peculiarities of human motor learning. J Mot Behav 42:381–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222895.2010.528262
Bönstrup M, Iturrate I, Thompson R et al (2019) A rapid form of offline consolidation in skill learning. Curr Biol 29:1346–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.02.049
Dayan E, Cohen LG (2011) Neuroplasticity subserving motor skill learning. Neuron 72:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.008
Doyon J, Benali H (2005) Reorganization and plasticity in the adult brain during learning of motor skills. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2005.03.004
Doyon J, Korman M, Morin A et al (2009) Contribution of night and day sleep vs. simple passage of time to the consolidation of motor sequence and visuomotor adaptation learning. Exp Brain Res 195:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1748-y
Du Y, Prashad S, Schoenbrun I, Clark JE (2016) Probabilistic motor sequence yields greater offline and less online learning than fixed sequence. Front Hum Neurosci 10:87. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00087
Du Y, Valentini NC, Kim MJ et al (2017) Children and adults both learn motor sequences quickly, but do so differently. Front Psychol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00158
Farshchiansadegh A, Abdollahi F, Chen D et al (2014) A body machine interface based on inertial sensors. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2014:6120–6124. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2014.6945026
Ferrel-Chapus C, Hay L, Olivier I et al (2002) Visuomanual coordination in childhood: adaptation to visual distortion. Exp Brain Res 144:506–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1064-2
Heathcote A, Brown S, Mewhort DJ (2000) The power law repealed: the case for an exponential law of practice. Psychon Bull Rev 7:185–207
JASP Team (2018) JASP (Version 0.9) [Computer software]
Joseph ME, King AC, Newell KM (2013) Task difficulty and the time scales of warm-up and motor learning. J Mot Behav 45:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222895.2013.784240
Julius MS, Adi-Japha E (2015) Learning of a simple grapho-motor task by young children and adults: similar acquisition but age-dependent retention. Front Psychol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00225
Krishnan C, Washabaugh EP, Reid CE et al (2018) Learning new gait patterns: age-related differences in skill acquisition and interlimb transfer. Exp Gerontol 111:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2018.07.001
Lee M-H, Farshchiansadegh A, Ranganathan R (2018) Children show limited movement repertoire when learning a novel motor skill. Dev Sci 21:e12614. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.12614
Lukacs A, Kemeny F (2015) Development of different forms of skill learning throughout the lifespan. Cogn Sci 39:383–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/cogs.12143
Nacson J, Schmidt RA (1971) The activity-set hypothesis for warm-up decrement. J Mot Behav 3:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222895.1971.10734887
Newell KM, Liu YT, Mayer-Kress G (2001) Time scales in motor learning and development. Psychol Rev 108:57–82
Newell KM, Mayer-Kress G, Hong SL, Liu Y-T (2009) Adaptation and learning: characteristic time scales of performance dynamics. Hum Mov Sci 28:655–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2009.07.001
Pan SC, Rickard TC (2015) Sleep and motor learning: is there room for consolidation? Psychol Bull 141:812–834. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000009
Ranganathan R, Lee M-H, Padmanabhan MR et al (2019) Age-dependent differences in learning to control a robot arm using a body-machine interface. Sci Rep 9:1960. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38092-3
Reis J, Schambra HM, Cohen LG et al (2009) Noninvasive cortical stimulation enhances motor skill acquisition over multiple days through an effect on consolidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:1590–1595. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0805413106
Robertson EM, Pascual-Leone A, Miall RC (2004) Current concepts in procedural consolidation. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:576–582. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1426
Smith MA, Ghazizadeh A, Shadmehr R (2006) Interacting adaptive processes with different timescales underlie short-term motor learning. PLoS Biol 4:e179. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040179
Stratton SM, Liu Y-T, Hong SL et al (2007) Snoddy (1926) revisited: time scales of motor learning. J Mot Behav 39:503–515. https://doi.org/10.3200/JMBR.39.6.503-516
Thomas JR (1980) Acquisition of motor skills: information processing differences between children and adults. Res Q Exerc Sport 51:158–173. https://doi.org/10.1080/02701367.1980.10609281
Vasudevan EV, Torres-Oviedo G, Morton SM et al (2011) Younger is not always better: development of locomotor adaptation from childhood to adulthood. J Neurosci 31:3055–3065. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5781-10.2011
Verhoeven FM, Newell KM (2018) Unifying practice schedules in the timescales of motor learning and performance. Hum Mov Sci 59:153–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2018.04.004
Voelcker-Rehage C, Willimczik K (2006) Motor plasticity in a juggling task in older adults—a developmental study. Age Ageing 35:422–427. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afl025
Wade MG (1976) Developmental motor learning. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 4:375–394
Walker MP, Stickgold R (2006) Sleep, memory, and plasticity. Annu Rev Psychol 57:139–166. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070307
Wilhelm I, Metzkow-Mészàros M, Knapp S, Born J (2012a) Sleep-dependent consolidation of procedural motor memories in children and adults: the pre-sleep level of performance matters. Dev Sci 15:506–515. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2012.01146.x
Wilhelm I, Prehn-Kristensen A, Born J (2012b) Sleep-dependent memory consolidation—what can be learnt from children? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:1718–1728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.03.002
Yan JH (2017) Children benefit differently from night- and day-time sleep in motor learning. Hum Mov Sci 54:297–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2017.05.015
Yan JH, Thomas JR, Stelmach GE, Thomas KT (2000) Developmental features of rapid aiming arm movements across the lifespan. J Mot Behav 32:121–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222890009601365
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant nos. 1654929 and 1703735. The author wishes to thank the members of the Sensorimotor Development Lab for assistance with data collection and Rajiv Ranganathan for comments on a previous draft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, MH. Online and offline contributions to motor learning change with practice, but are similar across development. Exp Brain Res 237, 2865–2873 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-019-05639-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-019-05639-3