Abstract
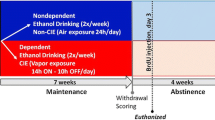
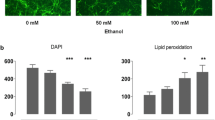
Alcohol exposure can reduce adult proliferation and/or neurogenesis, but its impact on the ultimate neurogenic precursors, neural stem cells (NSCs), has been poorly addressed. Accordingly, the impact of voluntary consumption of alcohol on NSCs in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle was examined in this study. The NSC population in adult male C57BL/6J mice was measured after voluntary alcohol exposure in a two-bottle choice task using the neurosphere assay, while the number of NSCs that had proliferated 2 weeks prior to tissue collection was indexed using bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) retention. There was a significant decrease in the number of BrdU-retaining cells in alcohol-consuming mice compared with controls, but no difference in the number of neurosphere-forming cells that could be derived from the SVZ of alcohol-consuming mice compared with controls. Additionally, PCNA-labeled cells in the SVZ tended to be lower, but there was no difference in BrdU labeling in the dentate gyrus following alcohol exposure. To determine alcohol’s direct impact on NSCs and their progeny, neurospheres derived from naïve mice were treated with alcohol in vitro. Neurosphere formation was reduced by 100 mM alcohol without reducing cell viability. These findings are the first to assess the impact of moderate voluntary alcohol consumption on selective measures of adult NSCs and indicate that such exposure alters NSC proliferation dynamics in vivo and alcohol has direct but dissociable effects on the expansion and viability on NSCs and their progeny in vitro.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
Aberg E, Hofstetter CP, Olson L, Brene S (2005) Moderate ethanol consumption increases hippocampal cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8:557–567
Akers KG, Kushner SA, Leslie AT, Clarke L, van der Kooy D, Lerch JP, Frankland PW (2011) Fetal alcohol exposure leads to abnormal olfactory bulb development and impaired odor discrimination in adult mice. Mol Brain 4:29
Anderson ML, Nokia MS, Govindaraju KP, Shors TJ (2012) Moderate drinking? Alcohol consumption significantly decreases neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Neuroscience 224:202–209
Bravo R, Macdonald-Bravo H (1987) Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol 105(4):1549–1554
Burns KA, Kuan CY (2005) Low doses of bromo- and iododeoxyuridine produce near-saturation labeling of adult proliferative populations in the dentate gyrus. Eur J Neurosci 21:803–807
Campbell JC, Kippin TE (2011) The interaction of neural stem cells and chronic alcohol consumption. In: Olive MF (ed) Drug addiction and adult neurogenesis. Research Signpost, Kerala, pp 121–138
Chiasson BJ, Tropepe V, Morshead CM, van der Kooy D (1999) Adult mammalian forebrain ependymal and subependymal cells demonstrate proliferative potential, but only subependymal cells have neural stem cell characteristics. J Neurosci 19:4462–4471
Clarke L, van der Kooy D (2011) The adult mouse dentate gyrus contains populations of committed progenitor cells that are distinct from subependymal zone neural stem cells. Stem Cells 29:1448–1458
Coles-Takabe BLK, Brain I, Purpura KA, Karpowicz P, Zandstra PW, Morshead CM, van der Kooy D (2008) Don’t look: growing clonal versus nonclonal neural stem cell colonies. Stem Cells 26(11):2938–2944
Collins MA, Corso TD, Neafsey EJ (1996) Neuronal degeneration in rat cerebrocortical and olfactory regions during subchronic “binge” intoxication with ethanol: possible explanation for olfactory deficits in alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 20:284–292
Contet C, Kim A, Le D, Iyengar SK, Kotzebue RW, Yuan CJ, Kieffer BL, Mandyam CD (2013) µ-Opioid receptors mediate the effects of chronic ethanol binge drinking on the hippocampal neurogenic niche. Addict Biol. [Epub ahead of print]
Costa LG, Vitalone A, Guizzetti M (2004) Signal transduction mechanisms involved in the antiproliferative effects of ethanol in glial cells. Toxicol Lett 149:67–73
Crabbe JC, Belknap JK, Buck KJ, Metten P (1994) Use of recombinant inbred strains for studying genetic determinants of responses to alcohol. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl 2:67–71
Crews FT, Miller MW, Ma W, Nixon K, Zawada WM, Zakhari S (2003) Neural stem cells and alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:324–335
Crews FT, Nixon K, Wilkie ME (2004) Exercise reverses ethanol inhibition of neural stem cell proliferation. Alcohol 33:63–71
Dole VP, Gentry T (1984) Toward an analogue of alcoholism in mice: scale factors in the model. PNAS 81:3543–3546
Dudek BC, Underwood KA (1993) Selective breeding, congenic strains, and other classical genetic approaches to the analysis of alcohol-related polygenic pleiotropisms. Behav Genet 23:179–189
Fein G, Shimotsu R, Barakos J (2010) Age-related gray matter shrinkage in a treatment naïve actively drinking alcohol-dependent sample. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34(1):175–182
Gage FH (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287:1433–1438
Grant BF, Dawson DA, Stinson FS, Chou SP, Dufour MC, Pickering RP (2004) The 12-month prevalence and trends in DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: United States, 1991–1992 and 2001–2002. Drug Alcohol Depend 74:223–234
Hansson AC, Nixon K, Rimondini R, Damadzic R, Sommer WH, Eskay R, Crews FT, Heilig M (2010) Long-term suppression of forebrain neurogenesis and loss of neuronal progenitor cells following prolonged alcohol dependence in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13:583–593
Harper C, Matsumoto I (2005) Ethanol and brain damage. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:73–78
Herrera DG, Yague AG, Johnsen-Soriano S, Bosch-Morell F, Collado-Morente L, Muriach M, Romero FJ, Garcia-Verdugo JM (2003) Selective impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis by chronic alcoholism: protective effects of an antioxidant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7919–7924
Hitoshi S, Kippin TE, van der Kooy D (2011) Culturing neural stem cells: Application to the study of neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric pathology. In: Seki T, Sawamotot K, Parent JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (eds) Neurogenesis in the adult brain II: clinical implications. Springer, Tokyo, pp 189–208
Kim JW, Lee DY, Lee BC, Jung MH, Kim H, Choi YS, Choi IG (2012) Alcohol and cognition in the elderly: a review. Psychiatry Investig. 9(1):8–16
Kippin TE, Cain SW, Masum Z, Ralph MR (2004) Neural stem cells show bidirectional experience-dependent plasticity in the perinatal mammalian brain. J Neurosci 24:2832–2836
Kippin TE, Kapur S, van der Kooy D (2005a) Dopamine specifically inhibits forebrain neural stem cell proliferation, suggesting a novel effect of antipsychotic drugs. J Neurosci 25:5815–5823
Kippin TE, Martens DJ, van der Kooy D (2005b) p21 loss compromises the relative quiescence of forebrain stem cell proliferation leading to exhaustion of their proliferation capacity. Genes Dev 19:756–767
Lledo PM, Saghatelyan A (2005) Integrating new neurons into the adult olfactory bulb: joining the network, life-death decisions, and the effects of sensory experience. Trends Neurosci 28:248–254
Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A (1994) Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 264:1145–1148
Luo J, Miller MW (1998) Growth factor-mediated neural proliferation: target of ethanol toxicity. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 27:157–167
Luskin MB (1993) Restricted proliferation and migration of postnatally generated neurons derived from the forebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 11:173–189
Luskin MB (1994) Neuronal cell lineage in the vertebrate central nervous system. FASEB J. 8:722–730
Mann K, Agartz I, Harper C, Shoaf S, Rawlings RR, Momenan R, Hommer DW, Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV, Anton RF et al (2001) Neuroimaging in alcoholism: ethanol and brain damage. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:104S–109S
McBride WJ (2002) Central nucleus of the amygdala and the effects of alcohol and alcohol-drinking behavior in rodents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:509–515
McClain JA, Hayes DM, Morris SA, Nixon K (2011) Adolescent binge alcohol exposure alters hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation in rats: effects on cell cycle kinetics. J Comp Neurol. 519:2697–2710
Mikami K, Haseba T, Ohno Y (1997) Ethanol induces transient arrest of cell division (G2 + M block) followed by G0/G1 block: dose effects of short- and longer-term ethanol exposure on cell cycle and cell functions. Alcohol Alcohol 32(2):145–152
Morshead CM, van der Kooy D (1992) Postmitotic death is the fate of constitutively proliferating cells in the subependymal layer of the adult mouse brain. J Neurosci 12:249–256
Morshead CM, Reynolds BA, Craig CG, McBurney MW, Staines WA, Morassutti D, Weiss S, van der Kooy D (1994) Neural stem cells in the adult mammalian forebrain: a relatively quiescent subpopulation of subependymal cells. Neuron 13:1071–1082
Morshead CM, Craig CG, van der Kooy D (1998) In vivo clonal analyses reveal the properties of endogenous neural stem cell proliferation in the adult mammalian forebrain. Development. 125:2251–2261
Morshead CM, Garcia AD, Sofroniew MV, van Der Kooy D (2003) The ablation of glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive cells from the adult central nervous system results in the loss of forebrain neural stem cells but not retinal stem cells. Eur J Neurosci 18:76–84
Mukamal KJ (2004) Alcohol consumption and abnormalities of brain structure and vasculature. Am J Geriatr Cardiol. 13:22–28
National Institute of Health (NIH) (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th edn. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Nixon K, Crews FT (2002) Binge ethanol exposure decreases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 83:1087–1093
Obernier JA, Bouldin TW, Crews FT (2002) Binge ethanol exposure in adult rats causes necrotic cell death. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:547–557
Pawlak R, Skrzypiec A, Sulkowski S, Buczko W (2002) Ethanol-induced neurotoxicity is counterbalanced by increased cell proliferation in mouse dentate gyrus. Neurosci Lett 327:83–86
Pfefferbaum A, Lim KO, Zipursky RB, Mathalon DH, Rosenbloom MJ, Lane B, Ha CN, Sullivan EV (1992) Brain gray and white matter volume loss accelerates with aging in chronic alcoholics: a quantitative MRI study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 16:1078–1089
Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV, Mathalon DH, Lim KO (1997) Frontal lobe volume loss observed with magnetic resonance imaging in older chronic alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21(3):521–529
Rhodes JS, Best K, Belknap JK, Finn DA, Crabbe JC (2005) Evaluation of a simple model of ethanol drinking to intoxication in C57BL/6J mice. Physiol Behav 84(1):53–63
Richardson HN, Chan SH, Crawford EF, Lee YK, Funk CK, Koob GF, Mandyam CD (2009) Permanent impairment of birth and survival of cortical and hippocampal proliferating cells following excessive drinking during alcohol dependence. Neurobiol Dis 36:1–10
Rubert G, Miñana R, Pascual M, Guerri C (2006) Ethanol exposure during embryogenesis decreases the radial glial progenitor pool and affects the generation of neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 84:483–496
Santillano DR, Kumar LS, Prock TL, Camarillo C, Tingling JD, Miranda RC (2005) Ethanol induces cell-cycle activity and reduces stem cell diversity to alter both regenerative capacity and differentiation potential of cerebral cortical neuroepithelial precursors. BMC Neurosci 6:59
Schoenfeld TJ, Gould E (2012) Stress, stress hormones, and adult neurogenesis. Exp Neurol 233:12–21
Seaberg RM, van der Kooy D (2002) Adult rodent neurogenic regions: the ventricular subependyma contains neural stem cells, but the dentate gyrus contains restricted progenitors. J Neurosci 22:1784–1793
Stevenson JR, Schroeder JP, Nixon K, Besheer J, Crews FT, Hodge CW (2009) Abstinence following alcohol drinking produces depression-like behavior and reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology. 34:1209–1222
Taupin P (2007) BrdU immunohistochemistry for studying adult neurogenesis: paradigms, pitfalls, limitations, and validation. Brain Res Rev 53:198–214
Toschi L, Bravo R (1988) Changes in cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen distribution during DNA repair synthesis. J Cell Biol 107:1623–1638
van der Kooy D, Weiss S (2000) Why stem cells? Science 287:1439–1441
van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH (2002) Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 415:1030–1034
Vangipuram SD, Grever WE, Parker GC, Lyman WD (2008) Ethanol increases fetal human neurosphere size and alters adhesion molecule gene expression. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32(2):339–347
Wahlsten D, Bachmanov A, Finn DA, Crabbe JC (2006) Stability of inbred mouse strain differences in behavior and brain size between laboratories and across decades. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(44):16364–16369
World Health Organization (2004) Global Status Report on Alcohol 2004. World Health Organization Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse, Geneva
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institute on Drug Abuse grant (DA-027115 and DA-027525) and an Alcoholic Beverage Medical Research Foundation grant to Professor Tod E. Kippin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dr. Tamara Stipcevic was on leave from Rudjer Boskovic Institute, Zagreb, Croatia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campbell, J.C., Stipcevic, T., Flores, R.E. et al. Alcohol exposure inhibits adult neural stem cell proliferation. Exp Brain Res 232, 2775–2784 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-3958-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-3958-1