Abstract
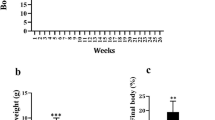
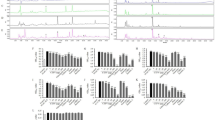
SIRT1 is the homologue of SIR2 that links to longevity in lower organisms and has a direct or indirect role that positively regulates the metabolic pathway via insulin signaling. RSV, a naturally occurring small polyphenol that activates SIRT1, has been reported to ameliorate the early development of metabolic syndrome of high-fat-diet-fed mice at a low dose (0.005 w/w) in 10 weeks through inhibition of fatty acid synthase and other relevant enzymes. However, what effect of a higher dose of dietary RSV on the long-term high-fat-diet-fed C57BL/6J mice has not been reported in view of regulating SIRT1 and related genes. This study investigated the effect of a higher dose of RSV (0.1 % w/w) on glucose and lipid metabolism in 13-week high-fat-diet-fed C57BL/6J mice as well as on mRNA and protein expression regulations with respect to relevant genes. The data showed that a higher dose of RSV supplementation significantly lowered the concentration of glucose, plasma total cholesterol, total triglyceride concentrations, and hepatic cholesterol in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Relative mRNA expressions of SIRT1, FOXO1, PPARγ, and PGC-1α were significantly up-regulated, and corresponding protein expressions were also enhanced.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RSV:
-
Resveratrol (3, 5, 4′-trihydroxystilbene)
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin 1
- SIR2:
-
Silent information regulator 2
- FOXO1:
-
Forkhead box O1
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ
- PGC-1α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1alpha
- HDL-C:
-
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- total-C:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
References
Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM, Puigserver P (2005) Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1α and SIRT1. Nature 434:113–118
Kitamura YI, Kitamura T, Kruse JP, Raum JC, Stein R, Gu W, Accili D (2005) FOXO1 protects against pancreatic beta cell failure through NeuroD and MafA induction. Cell Metab 2:153–163
Moynihan KA, Grimm AA, Plueger MM, Bernal-Mizrachi E, Ford E, Cras-Meneur C, Permutt MA, Imai S (2005) Increased dosage of mammalian sir2 in pancreatic beta cells enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mice. Cell Metab 2:105–117
Picard F, Kurtev M, Chung N, Topark-Ngarm A, Senawong T, Machado de Oliveira R, Leid M, McBurney MW, Guarente L (2004) SIRT1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPARγ. Nature 429:771–776
Wang H, Qiang L, Farmer SR (2008) Identification of a domain within peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor gamma regulating expression of a group of genes containing fibroblast growth factor 21 that are selectively repressed by SIRT1 in adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol 28:188–200
Rodgers JT, Puigserver P (2007) Fasting-dependent glucose and lipid metabolic response through hepatic sirtuin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12861–12866
Fulco M, Schiltz RL, Iezzi S, King MT, Zhao P, Kashiwaya Y, Hoffman E, Veech RL, Sartorelli V (2003) Sir2 regulates skeletal muscle differentiation as a potential sensor of the redox state. Mol Cell 12:51–62
Lamming DW, Wood JG, Sinclair DA (2004) Small molecules that regulate lifespan: evidence for xenohormesis. Mol Microbiol 53:1003–1009
Wood JG, Rogina B, Lavu S, Howitz K, Helfand SL, Tatar M, Sinclair D (2004) Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature 430:686–689
Bauer JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson HA et al (2006) Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 444:337–342
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL et al (2006) Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 444:337–342
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z et al (2006) Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha. Cell 127:1109–1122
Cintia dos Santos C, Rohden F, Hammes TO, Margis R, Bortolotto JW, Padoin AV, Mottin CC, Guaragna RM (2011) Resveratrol upregulated SIRT1, FOXO1 and adiponectin, and downregulated PPARγ1-3 mRNA expression in human visceral adipocytes. Obes Surg 21:356–361
Morita Y, Wada-Hiraike O, Yano T, Shirane A, Hirano M, Hiraike H, Koyama S, Oishi H, Yoshino O, Miyamoto Y (2012) Resveratrol promotes expression of SIRT1 and StAR in rat ovarian granulosa cells: an implicative role of SIRT1 in the ovary. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 10:14–30
Bai Liang, Pang Wei-Jun, Yang Yan-Jun, Yang Gong-She (2008) Modulation of Sirt1 by resveratrol and nicotinamide alters proliferation and differentiation of pig preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 307:129–140
Xiong S, Salazar G, San Martin A, Ahmad M, Patrushev N, Hilenski L, Nazarewicz RR, Ma M, Ushio-Fukai M, Alexander RW (2010) PGC-1α serine 570 phosphorylation and GCN5-mediated acetylation by angiotensin II drive catalase down-regulation and vascular hypertrophy. J Biol Chem 285:2474–2487
Ajmo JM, Liang X, Rogers CQ, Pennock B, You M (2008) Resveratrol alleviates alcoholic fatty liver in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:833–842
Um JH, Park SJ, Kang H, Yang S, Foretz M, McBurney MW, Kim MK, Viollet B, Chung JH (2010) AMP-activated protein kinase-deficient mice are resistant to the metabolic effects of resveratrol. Diabetes 59(2010):554–563
Jeon BT, Jeong EA, Shin HJ, Lee Y, Lee DH, Kim HJ, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Choi WS, Roh GS (2012) Resveratrol attenuates obesity-associated peripheral and central inflammation and improves memory deficit in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetes 61:1444–1454
Qin F, Siwik DA, Luptak I, Hou X, Wang L, Higuchi A, Weisbrod RM, Ouchi N, Tu VH, Calamaras TD (2012) The polyphenols resveratrol and S17834 prevent the structural and functional sequelae of diet-induced metabolic heart disease in mice. Circulation 125:1757–1764
Kang W, Honga HJ, Guan J, Kim DG, Yang EJ, Koh G, Park D, Han CH, Lee YJ, Lee DH (2012) Resveratrol improves insulin signaling in a tissue-specific manner under insulin-resistant conditions only: in vitro and invivo experiments in rodents. Metab Clin Exp 61:424–433
Chen Sifan, Li Jinghua, Zhang Zili, Li Wenxue, Sun Yanshuang, Zhang Quanxin, Feng Xiang, Zhu Wei (2012) Effects of resveratrol on the amelioration of insulin resistance in KKAy mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90:237–242
Louis XL, Thandapilly SJ, MohanKumar SK, Yu L, Taylor CG, Zahradka P, Netticadan T (2012) Treatment with low-dose resveratrol reverses cardiac impairment in obese prone but not in obese resistant rats. J Nutr Biochem 23:1163–1169
Chen Q, Wang E, Ma L, Pei Zhai (2012) Dietary resveratrol increases the expression of hepatic 7α-hydroxylase and ameliorates hypercholesterolemia in high-fat fed C57BL/6J mice. Lipids Health Dis 11:56
Xin P, Han H, Gao D, Cui W, Yang X, Ying C, Sun X, Hao L (2013) Alleviative effects of resveratrol on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are associated with up regulation of hepatic low density lipoprotein receptor and scavenger receptor class B type I gene expressions in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 52:12–18
Alberdi G, Rodríguez VM, Miranda J, Macarulla MT, Churruca I, Portillo MP (2013) Thermogenesis is involved in the body-fat lowering effects of resveratrolin rats. Food Chem 141(2013):1530–1535
Alberdi G, Rodrıguez VM, Macarulla MT, Miranda J, Churruca I, Portillo MP (2013) Hepatic lipid metabolic pathways modified by resveratrol in rats fed an obesogenic diet. Nutrition 29:562–567
Poulsen MM, Larsen JØ, Hamilton-Dutoit S, Clasen BF, Jessen N, Paulsen SK, Kjær TN, Richelsen B, Pedersen SB (2012) Resveratrol up-regulates hepatic uncoupling protein 2 and prevents development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats fed a high-fat diet. Nutr Res 32:701–708
Cho SJ, Jung UJ, Choi MS (2012) Differential effects of low-dose resveratrol on adiposity and hepatic steatosis in diet-induced obese mice. Br J Nutr 108:2166–2175
Azorín-Ortuño M, Yáñez-Gascón MJ, González-Sarrías A, Larrosa M, Vallejo F, Pallarés FJ, Lucas R, Morales JC, Tomás-Barberán FA, García-Conesa MT, Espín JC (2012) Effects of long-term consumption of low doses of resveratrol on diet-induced mild hypercholesterolemia in pigs: a transcriptomic approach to disease prevention. J Nutr Biochem 23:829–837
Mukherjee S, Dudley JI, Das DK (2010) Dose-dependency of resveratrol in providing health benefits. Dose-Response 8(4):478–500
Shannon RS, Minakshi N, Nihal A (2008) Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. Faseb J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 22(3):659–661
Chan PT, Fong WP, Cheung YL, Huang Y et al (1999) Jasmine green epicatechins are hypolipidemic in hamsters fed a high fat diet. J Nutr 129:1094–1101
Poritsanos NJ, Wong D, Vrontakis ME, Mizuno TM (2008) Regulation of hepatic PPARgamma2 and lipogenic gene expression by melanocortin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:384–388
Revollo JR, Grimm AA, Imai S (2004) The NAD biosynthesis pathway mediated by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase regulates Sir2 activity in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 279:50754–50763
Michishita E, Park JY, Burneskis JM (2005) Evolutionarily conserved and nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT proteins. Mol Biol Cell 16:4623–4635
Giannakou ME, Partridge L (2004) The interaction between FOXO and SIRT1: tipping the balance towards survival. Trends Cell Biol 14:408–412
Escande C, Chini CCS et al (2010) Deleted in breast cancer–1 regulates SIRT1 activity and contributes to high-fat diet–induced liver steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest 120:545–548
Gojkovic-Bukarica L, Novakovic A, Kanjuh V, Bumbasirevic M, Lesic A, Heinle H (2008) A role of ion channels in the endothelium-independent relaxation of rat mesenteric artery induced by resveratrol. Jpn J Pharmacol 108(1):124–130
Olas B, Wachowicz B, Saluk-Juszczak J, Zieliński T, Kaca W, Buczyński A (2001) Antioxidant activity of resveratrol in endotoxin-stimulated blood platelets. Cell Biol Toxicol 17(17):117–125
Martinez J, Moreno J (2000) Effect of resveratrol, a natural polyphenolic compound, on reactive oxygen species and prostaglandin production. Biochem Pharmacol 59(7):865–870
Sharma S, Anjaneyulu M, Kulkarni SK, Chopra K (2006) Resveratrol, a polyphenolic phytoalexin; attenuates diabetic nephropathy in rats. Pharmacology 76:69–75
Chang S, Graham B, Yakubu F, Lin D, Peters JC, Hill JO (1990) Metabolic differences between obesity-prone and obesity-resistant rats. Am J Physiol 259:R1103–R1110
Ghibaudi L, Cook J, Farley C, van Heek M, Hwa JJ (2002) Fat intake affects adiposity, comorbidity factors, energy metabolism of Sprague-Dawley rats. Obes Res 10:956–963
Campfield LA, Smith FJ (1999) The pathogenesis of obesity, Baillieres Best Pract. Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 13:13–30
de Sousa Abreu R, Penalva LO, Marcotte EM, Vogel C (2009) Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels. Mol BioSyst 5:1512–1526
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF, Chua KF, Greer PL, Lin Y, Tran H, Ross SE, Mostoslavsky R, Cohen HY, Hu LS, Cheng HL, Jedrychowski MP, Gygi SP, Sinclair DA, Alt FW, Greenberg ME (2004) Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303:2011–2015
Greer EL, Brunet A (2005) FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 24:7410–7425
Subauste AR, Burant CF (2007) Role of FoxO1 in FFA-induced oxidative stress in adipocytes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E159–E164
Chen Q, Ganapathy S, Singh KP, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2010) Resveratrol induces growth arrest and Apoptosis through activation of FOXO transcription factors in prostate cancer cells. Plos One 5:15288
Wu L, Zhang Y, Ma X, Zhang N, Qin G (2012) The effect of resveratrol on FOXO1 expression in kidneys of diabetic nephropathy rats. Mol Biol Rep 39:9085–9093
Goldberg DM, Yan J, Soleas GJ (2003) Absorption of three wine-related polyphenols in three different matrices by healthy subjects. Clin Biochem 36:79–87
Matsusue K, Haluzik M, Lambert G, Yim SH, Gavrilova O, Ward JM, Brewer B Jr, Reitman ML, Gonzalez FJ (2003) Liver-specific disruption of PPARgamma in leptin-deficient mice improves fatty liver but aggravates diabetic phenotypes. J Clin Invest 111:737–747
Ge H, Zhang J, Guo B (2007) Resveratrol inhibits macrophage expression of EMMPRIN by activating PPARγ. Vascul Pharmacol 46:114–121
Shin JA, Lee KE, Kim HS (2012) Park EM acute resveratrol treatment modulates multiple signaling pathways in the ischemic brain. Neurochem Res. doi:10.1007/s11064-012-0858-2
Yoshino J, Conte C, Fontana L, Mittendorfer B, Imai S, Schechtman KB, Gu C, Kunz I, Fanelli FR, Patterson BW (2012) Resveratrol supplementation does not improve metabolic function in nonobese women with normal glucose tolerance. Cell Metab 16:658–664
Poulsen MM, Vestergaard PF, Clasen BF, Radko Y, Christensen LP, Stoedkilde-Joergensen H, Moeller N, Jessen N, Pedersen SB, Joergensen JOL (2013) High-dose resveratrol supplementation in obese men: an investigator-initiated, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of substrate metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition. Diabetes 62:1186–1195
Crandall JP, Oram V, Trandafirescu G, Reid M, Kishore P, Hawkins M, Cohen HW, Barzilai N (2012) Pilot study of resveratrol in older adults with impaired glucose tolerance. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci 67:1307–1312
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81072521), Tianjin University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 20100411). and Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (STIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Compliance with ethics requirements
The mice were all treated in strict accordance with the Tianjin University of Science & Technology guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Zhang, N., Jiang, H. et al. Resveratrol treatment improves plasma and blood glucose concentration and lipid metabolism in high-fat-fed C57BL/6J mice. Eur Food Res Technol 242, 1849–1856 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-016-2684-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-016-2684-2