Abstract
This work aims to rapidly detect toxic alkaloids in traditional Chinese medicines (TCM) using laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry (LDI-MS). We systematically investigated twelve nanomaterials (NMs) as matrices and found that MoS2 and defect-rich-WO3 (D-WO3) were the best NMs for alkaloid detection. MoS2 and D-WO3 can be used directly as matrices dipped onto conventional ground steel target plates. Additionally, they can be conveniently fabricated as three-dimensional (3D) NM plates, where the MoS2 or D-WO3 NM is doped into resin and formed using a 3D printing process. We obtained good quantification of alkaloids using a chemothermal compound as an internal standard and detected related alkaloids in TCM extracts, Fuzi (Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata), Caowu (Aconiti Kusnezoffii Radix), Chuanwu (Aconiti Radix), and Houpo (Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex). The work enabled the advantageous “dip and measure” method, demonstrating a simple and fast LDI-MS approach that achieves clean backgrounds for alkaloid detection. The 3D NM plates also facilitated mass spectrometry imaging of alkaloids in TCMs. This method has potential practical applications in medicine and food safety.
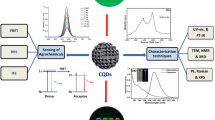
Graphical Abstract
Doped nanomaterial facilitates 3D printing target plate for rapid detection of alkaloids in laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bribi N. Pharmacological activity of alkaloids: a review. Asian J Bot. 2018; 1. https://doi.org/10.63019/ajb.v1i2.467.
Lu M, Cai Z. Advances of MALDI-TOF MS in the analysis of traditional Chinese medicines. In: Applications of MALDI-TOF spectroscopy.2012. Top Curr Chem. pp 143-164. https://doi.org/10.1007/128_2012_383.
Yu L, Xu Y, Feng H, Li SF. Separation and determination of toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids in traditional Chinese herbal medicines by micellar electrokinetic chromatography with organic modifier. Electrophoresis. 2005;26(17):3397–404. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200500233.
Chen J, Zhao H, Wang X, Lee FS, Yang H, Zheng L. Analysis of major alkaloids in Rhizoma coptidis by capillary electrophoresis-electrospray-time of flight mass spectrometry with different background electrolytes. Electrophoresis. 2008;29(10):2135–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200700797.
Ranieri TL, Ciolino LA. Rapid selective screening and determination of ephedrine alkaloids using GC-MS footnote mark. Phytochem Anal. 2008;19(2):127–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.1025.
Zhang J, Jin Y, Dong J, Xiao Y, Feng J, Xue X, Zhang X, Liang X. Systematic screening and characterization of tertiary and quaternary alkaloids from corydalis yanhusuo W.T. Wang using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Talanta. 2009;78(2):513–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.12.002.
Saptarini NM. Herawati IE The colorimetric method for determination of total alkaloids and flavonoids content in Indonesian black nightshade (Solanum nigrum L.). J Adv Pharm Educ Res. 2019;3:80–4.
Huang YF, He F, Wang CJ, Xie Y, Zhang YY, Sang Z, Qiu P, Luo P, Xiao SY, Li J, Wu FC, Liu L, Zhou H. Discovery of chemical markers for improving the quality and safety control of Sinomenium acutum stem by the simultaneous determination of multiple alkaloids using UHPLC-QQQ-MS/MS. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14182. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71133-4.
Wang J, van der Heijden R, Spijksma G, Reijmers T, Wang M, Xu G, Hankemeier T, van der Greef J. Alkaloid profiling of the Chinese herbal medicine Fuzi by combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216(11):2169–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.11.077.
Wu J, Cui C, Zhao H, Zhou G, Qin L, Li X, Chen L, Wang X, Wan Y. In-situ detection and imaging of Areca catechu fruit alkaloids by MALDI-MSI. Ind Crops Prod. 2022;188:115533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115533.
Chiang CK, Chen WT, Chang HT. Nanoparticle-based mass spectrometry for the analysis of biomolecules. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40(3):1269–81. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00050g.
Khajavinia A, El-Aneed A. Carbon-based nanoparticles and their surface-modified counterparts as MALDI matrices. Anal Chem. 2023;95(1):100–14. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c04537.
Lin Z, Cai Z. Negative ion laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometric analysis of small molecules by using nanostructured substrate as matrices. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2018;37(5):681–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21558.
Sunner J, Dratz E, Chen YC. Graphite surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins from liquid solutions. Anal Chem. 1995;67(23):4335–42. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac00119a021.
Picca RA, Calvano CD, Cioffi N, Palmisano F. Mechanisms of nanophase-induced desorption in LDI-MS A short review. Nanomaterials. 2017;7(4):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7040075.
Ma W, Li J, Li X, Bai Y, Liu H. Nanostructured substrates as matrices for surface assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: a progress report from material research to biomedical applications. Small Methods. 2021;5(10):e2100762. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202100762.
Chuang W, Lu-Yuan Q, Dong-Mei L, Jin-Juan X, Lei G, Li T. The application advance of nanomaterials in the LDI-MS technique. Chin J Anal Chem. 2023;51(2):172–83. https://doi.org/10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.221328.
Wang D, Huang X, Li J, He B, Liu Q, Hu L, Jiang G. 3D printing of graphene-doped target for “matrix-free” laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Chem Comm. 2018;54(22):2723–6. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc09649f.
Zhai X-P, Gao L-F, Zhang H, Peng Y, Zhang X-D, Wang Q, Zhang H-L. Defect engineering of ultrathin WO3 nanosheets: implications for nonlinear optoelectronic devices. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2022;5(1):1169–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c03791.
Eda G, Yamaguchi H, Voiry D, Fujita T, Chen M, Chhowalla M. Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett. 2011;11(12):5111–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl201874w.
Ferey G, Mellot-Draznieks C, Serre C, Millange F, Dutour J, Surble S, Margiolaki I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science. 2005;309(5743):2040–2. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1116275.
Dong Y, Hu T, Pudukudy M, Su H, Jiang L, Shan S, Jia Q. Influence of microwave-assisted synthesis on the structural and textural properties of mesoporous MIL-101(Fe) and NH2-MIL-101(Fe) for enhanced tetracycline adsorption. Mater Chem Phys. 2020;251:123060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123060.
Li H, Guo L, Huang A, Xu H, Liu X, Ding H, Dong J, Li J, Wang C, Su X, Ge X, Sun L, Bai C, Shen X, Fang T, Li Z, Zhou Y, Zhan L, Li S, Xie J, Shao N. Nanoparticle-conjugated aptamer targeting hnRNP A2/B1 can recognize multiple tumor cells and inhibit their proliferation. Biomaterials. 2015;63:168–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.06.013.
Xu Y, Li Y, Zhang P, Yang B, Wu H, Guo X, Li Y, Zhang Y. Sensitive UHPLC-MS/MS quantitation and pharmacokinetic comparisons of multiple alkaloids from Fuzi- Beimu and single herb aqueous extracts following oral delivery in rats. J Chromatogr B. 2017;1058:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.05.016.
McLean JA, Stumpo KA, Russell DH. Size-selected (2–10 nm) gold nanoparticles for matrix assisted laser desorption ionization of peptides. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(15):5304–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja043907w.
Chen WY, Chen YC. Affinity-based mass spectrometry using magnetic iron oxide particles as the matrix and concentrating probes for SALDI MS analysis of peptides and proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2006;386(3):699–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0427-0.
Yang X, Hu XK, Loboda AV, Lipson RH. Microstructured tungsten oxide: a generic desorption/ionization substrate for mass spectrometry. Adv Mater. 2010;22(40):4520–3. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201001627.
Kim YK, Wang LS, Landis R, Kim CS, Vachet RW, Rotello VM. A layer-by-layer assembled MoS2 thin film as an efficient platform for laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry analysis of small molecules. Nanoscale. 2017;9(30):10854–60. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr02949g.
Yagnik GB, Hansen RL, Korte AR, Reichert MD, Vela J, Lee YJ. Large scale nanoparticle screening for small molecule analysis in laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2016;88(18):8926–30. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02732.
Yamada Y, Murase M, Yatsugi K, Mizoshita N. Laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using TiO2 nanopillar array substrates with tunable surface roughness and wettability. ACS Appl Nano Mater. 2021;4(12):13884–95. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c03222.
Muller WH, Verdin A, De Pauw E, Malherbe C, Eppe G. Surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging: a review. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2022;41(3):373–420. https://doi.org/10.1002/mas.21670.
Bian J, Olesik SV. Ion desorption efficiency and internal energy transfer in polymeric electrospun nanofiber-based surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(4):923–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02315-x.
Sakai R, Ichikawa T, Kondo H, Ishikawa K, Shimizu N, Ohta T, Hiramatsu M, Hori M. Effects of carbon nanowalls (CNWs) substrates on soft ionization of low-molecular-weight organic compounds in surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI-MS). Nanomaterials. 2021;11(2):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020262.
Ng KM, Lai SK, Chen Z, Cheng YH, Tang HW, Huang W, Su Y, Yang J. Harvesting more energetic photoexcited electrons from closely packed gold nanoparticles. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021;32(3):815–24. https://doi.org/10.1021/jasms.0c00480.
Wang P, Giese RW. Recommendations for quantitative analysis of small molecules by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1486:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.01.040.
Wu W, Liang Z, Zhao Z, Cai Z. Direct analysis of alkaloid profiling in plant tissue by using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2007;42(1):58–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.1138.
Guo K, Tong C, Fu Q, Xu J, Shi S, Xiao Y. Identification of minor lignans, alkaloids, and phenylpropanoid glycosides in Magnolia officinalis by HPLC-DAD-QTOF-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019;170:153–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.03.044.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21974152, 81873397).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C. Wang conducted the experiments, analyzed data, interpreted the results, and wrote the primary manuscript. X. Zhai and Q. Wang prepared six NMs with full characterization. L. Hu offered the first batch of 3D RGO plates and according 3D fabrication experience. L. Qin, D. Li, and J. Xue assisted with the experiments and provided valuable suggestions. L. Guo supervised the experiments, revised the manuscript, and provided financial support; L. Tang and J. Xie reviewed the manuscript and approved it for the final release; and L. Tang also provided financial support. All authors provided critical feedback, helped shape the research, and authorized the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Qin, LY., Li, DM. et al. Doped nanomaterial facilitates 3D printing target plate for rapid detection of alkaloids in laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 6825–6838 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04961-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04961-8