Abstract
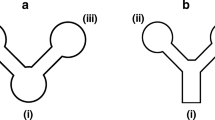
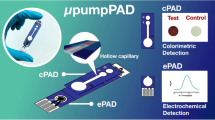
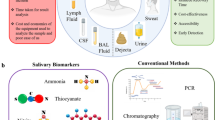
This paper describes the design and construction of dual microfluidic paper–based analytical devices (dual-μPADs) as a lab-on-paper platform involving a “do-it-yourself” fabrication protocol. The device comprises a colorimetric and electrochemical module to obtain a dual-mode signal readout sensing strategy. A 3D pen polymeric resin was used to prepare graphite carbon-based electrodes and hydrophobic barriers on paper substrates. The proposed carbon-based ink was employed to manufacture electrodes on paper based on a stencil-printing approach, which were further characterized by electrochemical and morphological analyses. The analytical performance of the dual-μPADs was simultaneously evaluated for lactate, pH, nitrite, and salivary amylase (sAA) analysis. To demonstrate the proof-of-concept, saliva samples collected from both healthy individuals and those with periodontitis were successfully tested to demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed devices. Samples collected from individuals previously diagnosed with periodontitis showed high levels of nitrite and sAA (> 94 μmol L−1 and > 610 U mL−1) in comparison with healthy individuals (≤ 16 μmol L−1 and 545 U mL−1). Moreover, periodontitis saliva resulted in acid solution and almost null lactate levels. Notably, this protocol supplies a simple way to manufacture dual-μPADs, a versatile platform for sensitive detecting of biomarkers in saliva playing a crucial role towards the point-of-care diagnosis of periodontal disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Butte MJ. Whitesides GM Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew Chemie. 2007;46:1318–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200603817.
Silva-Neto HA, Arantes IVS, Ferreira AL, do Nascimento HM, Meloni GN, Araujo WR, Paixão TRLC, Coltro WKT,. Recent advances on paper-based microfluidic devices for bioanalysis. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem. 2023;158:116893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2022.11.
Zheng W, Wang K, Xu H, Zheng C, Cao B, Qin Q, Jin Q. Cui D Strategies for the detection of target analytes using microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413:2429–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03213-x.
Ameku WA, Gonçalves JM, Ataide VN, Ferreira Santos MS, Gutz IGR, Araki K. Paixão TRLC Combined colorimetric and electrochemical measurement paper-based device for chemometric proof-of-concept analysis of cocaine samples. ACS Omega. 2021;6:594–605. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c05077.
Chaiyo S, Apiluk A, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O. High sensitivity and specificity simultaneous determination of lead, cadmium and copper using μpAD with dual electrochemical and colorimetric detection. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2016;233:540–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.04.109.
Apilux A, Dungchai W, Siangproh W, Praphairaksit N, Henry CS, Chailapakul O. Lab-on-paper with dual electrochemical/ colorimetric detection for simultaneous determination of gold and iron. Anal Chem. 2010;82:1727–32. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9022555.
Silva-Neto HA, Cardoso TMG, McMahon CJ, Sgobbi LF, Henry CS. Coltro WKT Plug-and-play assembly of paper-based colorimetric and electrochemical devices for multiplexed detection of metals. Analyst. 2021;146:3463–73. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1an00176k.
Yukird J, Soum V, Kwon OS, Shin K, Chailapakul O. Rodthongkum N 3D paper-based microfluidic device: a novel dual-detection platform of bisphenol A. Analyst. 2020;145:1491–8. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an01738k.
Yang H, Zhang Y, Li L, Zhang L, Lan F, Yu J. Sudoku-like lab-on-paper cyto-device with dual enhancement of electrochemiluminescence intermediates strategy. Anal Chem. 2017;89:7511–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01194.
Zhang X, Zhi H, Zhu M, Wang F, Meng H, Feng L. Electrochemical visual dual-readout aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection integrated into a miniaturized paper-based analytical device. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021;1180:113146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113146.
Pungjunun K, Yakoh A, Chaiyo S, Praphairaksit N, Siangproh W, Kalcher K, Chailapakul O. Laser engraved microapillary pump paper-based microfluidic device for colorimetric and electrochemical detection of salivary thiocyanate. Microchim Acta. 2021;188:140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04793-2.
Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhou S, Zhu L, Lv X, Zhang J, Zhang L, Zhu P. Yu J DNAzyme-triggered visual and ratiometric electrochemiluminescence dual-readout assay for Pb(II) based on an assembled paper device. Anal Chem. 2020;92:3874–81. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b05343.
Sun J, Li L, Ge S, Zhao P, Zhu P, Wang M. Jinghua Yu Dual-mode aptasensor assembled by a WO3_Fe2O3 heterojunction for paper-based colorimetric prediction/photoelectrochemical multicomponent analysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(3):3645–52. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c19853.
Wang H, Zhou C, Sun X, Jian Y, Kong Q, Cui K, Ge S. Yu J (2018) Polyhedral-AuPd nanoparticles-based dual-mode cytosensor with turn on enable signal for highly sensitive cell evalution on lab-on-paper device. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;117:651–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.07.004.
Rattanarat P, Dungchai W, Cate D, Volckens J, Chailapakul O. Henry CS Multilayer paper-based device for colorimetric and electrochemical quantification of metals. Anal Chem. 2014;86:3555–62. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500022.
Akyazi T, Basabe-Desmonts L. Benito-Lopez F Review on microfluidic paper-based analytical devices towards commercialisation. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1001:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.11.010.
Singhal HR, Prabhu A, Giri Nandagopal MS, Dheivasigamani T, Mani,. NK One-dollar microfluidic paper-based analytical devices: do-it-yourself approaches. Microchem J. 2021;165:106126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106126.
Dungchai W, Chailapakul O. Henry CS Electrochemical detection for paper-based microfluidics. Anal Chem. 2009;81:5821–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9007573.
Sousa LR, Duarte LC, Coltro WKT. Instrument-free fabrication of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices through 3D pen drawing. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2020;2020:312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128018.
Baima G, Iaderosa G, Citterio F, Grossi S, Romano F, Berta GN, Buduneli N. Aimetti M Salivary metabolomics for the diagnosis of periodontal diseases: a systematic review with methodological quality assessment. Metabolomics. 2021;17:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-020-01754-3.
Zhao C, Shi R, Wu J, Luo X. Liu X Point-of-care detection of salivary nitrite based on the surface plasmon-assisted catalytic coupling reaction of aromatic amines. Biosensors. 2021;11(7):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070223.
Yoshizawa JM, Schafer CA, Schafer JJ, Farrell JJ, Paster BJ. Wong DTW Salivary biomarkers: toward future clinical and diagnostic utilities. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:781–91. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00021-13.
Kim J, Valdés-Ramírez G, J BA, Jia W, Martinez AG, Ramírez J, Mercier P, Wang J. Non-invasive mouthguard biosensor forcontinuous salivary monitoring of metabolites. Analyst. 2014;139:1632–6. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN02359A.
Ramenzoni LL, Lehner MP, Kaufmann ME, Wiedemeier D, Attin T, Schmidlin PR Oral diagnostic methods for the detection of periodontal disease. Diagnostics. 2021;11: https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11030571
Liukkonen J, Gürsoy UK, Könönen E, Akhi R, Salminen A, Liljestrand JM, Pietiäinen PP-PM, Sorsa T, Persson GR, Mäntylä P, Buhlin K, Paju S, Sinisalo J, Hörkkö S, Pussine PJ Immunological and microbiological profiling of cumulative risk score for periodontitis. Doagnostics. 2020;10: https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080560.
de Castro LF, de Freitas SV, Duarte LC, de Souza JAC, Paixão TRLC. Coltro WKT Salivary diagnostics on paper microfluidic devices and their use as wearable sensors for glucose monitoring. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:4919–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01788-0.
Mollaie E, Asiaei S, Hiwa Aryan Nitrite enhanced detection from saliva by simple geometrical modifications of paper-based micromixers. Microfluid Nanofluidics 26:88 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-022-02596-2.
Zuliani C, Matzeu G. Diamond D A potentiometric disposable sensor strip for measuring pH in saliva. Electrochim Acta. 2014;132:292–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.03.140.
Yoon JH, Kim SM, Park HJ, Kim YK, Oh DX, Cho HW, Lee KG, Hwang SY, Park J. Choi BG Highly self-healable and flexible cable-type pH sensors for real-time monitoring of human fluids. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020;150:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111946.
Garcia PT, Guimarães LN, Dias AA, Ulhoa CJ. Coltro WKT Amperometric detection of salivary Α-amylase on screen-printed carbon electrodes as a simple and inexpensive alternative for point-of-care testing. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2018;258:342–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.11.068.
Della Ventura B, Sakač N, Funari R. Velotta R Flexible immunosensor for the detection of salivary α-amylase in body fluids. Talanta. 2017;174:52–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.05.075.
Shetty V, Zigler C, Robles TF, Elashoff D, Yamaguchi M. Developmental validation of a point-of-care salivary α-amylase biosensor. Psychoneuroendorcrinology. 2011;36(2):193–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.07.008.
Rossini EL, Milani MI, Lima LS, Pezza HR. Paper microfluidic device using carbon dots to detect glucose and lactate in saliva samples. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021;248:119285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119285.
Gomes NO, Carrilho E, Machado SAS, Sgobbi LF Bacterial cellulose-based electrochemical sensing platform: a smart material for miniaturized biosensors. Electrochim Acta. 2020;349: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136341.
Yao Y, Li H, Dan W, Liu C. Zhang C An electrochemiluminescence cloth-basedbiosensor with smartphone-based imaging fordetection of lactate in saliva. Analyst. 2017;142:3715. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AN01008G.
Zhang X, Zhi H, Wang F, Zhu M, Meng H, Wan P. Liang Feng Target-responsive smart nanomaterials via a Au−S binding encapsulation strategy for electrochemical colorimetric dual-mode paper-based analytical devices. Anal Chem. 2022;94:2569–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04537.
Ulloa-Gomez AM, Lucas A, Koneru A, Barui A. Stanciu L Simultaneous colorimetric and electrochemical detection of trace mercury (Hg2+) using a portable and miniaturized aptasensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114419.
Fonseca WT, Castro KR, de Oliveira TR. Faria RC Disposable and flexible electrochemical paper-based analytical devices using low-cost conductive ink. Electroanalysis. 2021;33:1520–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060564.
Castro LF, Silva-Neto HA, Sousa LR, de Araujo WR, Coltro WKT Silicone glue-based graphite ink incorporated on paper platform as an affordable approach to construct stable electrochemical sensors. Talanta 2022;251: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123812.
Cao L, Liu Y, Zhang B. Lu L In situ controllable growth of Prussian blue nanocubes on reduced graphene oxide: facile synthesis and their application as enhanced nanoelectrocatalyst for H2O2 reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2010;2:2339–46. https://doi.org/10.1021/am100372m.
Sgobbi LF, Razzino CA. Machado SAS A disposable electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim antibiotics in urine based on multiwalled nanotubes decorated with Prussian blue nanocubes modified screen-printed electrode. Electrochim Acta. 2016;191:1010–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.11.151.
Oncescu V, O’Dell D, Erickson D. Smartphone based health accessory for colorimetric detection of biomarkers in sweat and saliva. Lab Chip. 2013;13:3232–8. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3lc50431j.
Funding
The authors would like to thank CNP (grant 307554/2020–1 and 405620/2021–7), CAPES (grant 88887.192880/2018–00 and finance code 001), FAPEG and INCTBio (grant 465389/2014–7) for the financial support and granted scholarships. CONICET and CNPq are thanked for the scholarships granted to H.A.S.N., and L.F.C. The authors also acknowledge the High-Resolution Multi-User Microscopy Laboratory (LabMic) from Federal University of Goias for providing SEM analysis and the School of Dentistry from Federal University of Goiás for supporting the collection of saliva samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Saliva samples were collected in accordance with the ethical principles involving human participants under the approval of the ethical committee from Federal University of Goias (CAAE n° 68271817.9.0000.5083).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection Young Investigators in (Bio-)Analytical Chemistry 2023 with guest editors Zhi-Yuan Gu, Beatriz Jurado-Sánchez, Thomas H. Linz, Leandro Wang Hantao, Nongnoot Wongkaew, and Peng Wu.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sousa, L.R., Silva-Neto, H.A., Castro, L.F. et al. “Do it yourself” protocol to fabricate dual-detection paper-based analytical device for salivary biomarker analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 4391–4400 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04581-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04581-2