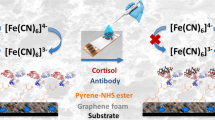
Abstract
Cortisol is a crucial hormone involving many physiological processes. Hence, cortisol detection is essential. This review highlights the key progress made on wearable electrochemical sensors using antibodies. It covers the design, principle, and electroanalytical methodology for detecting cortisol noninvasively. This article also analyzes and collects the analytical performances of electrochemical cortisol sensors. The development of these sensors continues to face challenges such as biofouling, sample management, sensitivity, flexibility, stability, and recognition layer performance. It is also necessary to develop a sensitive electrode and material. This article also presents potential strategies for designing antibody electrodes and provides examples of sensing systems. Additionally, it discusses the challenges in translating research into practical applications.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zorn JV, Schür RR, Boks MP, Kahn RS, Joëls M, Vinkers CH. Cortisol stress reactivity across psychiatric disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2017;77:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.11.036.
Fukuda S, Morimoto K. Lifestyle, stress and cortisol response: review II. Environ Health Prev Med. 2001;6(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02897304.
Corbalán-Tutau D, Madrid JA, Nicolás F, Garaulet M. Daily profile in two circadian markers “melatonin and cortisol” and associations with metabolic syndrome components. Physiol Behav. 2014;123:231–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.06.005.
Kinnamon D, Ghanta R, Lin K-C, Muthukumar S, Prasad S. Portable biosensor for monitoring cortisol in low-volume perspired human sweat. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13312. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13684-7.
Nijm J, Jonasson L. Inflammation and cortisol response in coronary artery disease. Ann Med. 2009;41(3):224–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890802508934.
Mohd Azmi NAS, Juliana N, Azmani S, Mohd Effendy N, Abu IF, Mohd Fahmi Teng NI, et al. Cortisol on circadian rhythm and its effect on cardiovascular system. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2021;18(2):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020676.
Russell E, Koren G, Rieder M, Van Uum SH. The detection of cortisol in human sweat: implications for measurement of cortisol in hair. Ther Drug Monit. 2014;36(1):30–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/FTD.0b013e31829daa0a.
Jia M, Chew WM, Feinstein Y, Skeath P, Sternberg EM. Quantification of cortisol in human eccrine sweat by liquid chromatography – tandem mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2016;141(6):2053–60. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN02387D.
Baid SK, Sinaii N, Wade M, Rubino D, Nieman LK. Radioimmunoassay and tandem mass spectrometry measurement of bedtime salivary cortisol levels: a comparison of assays to establish hypercortisolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(8):3102–7. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-2861.
Abraham G, Buster J, Lucas L, Corrales P, Teller R. Chromatographic separation of steroid hormones for use in radioimmunoassay. Anal Lett. 1972;5(8):509–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032717208062116.
Appel D, Schmid RD, Dragan C-A, Bureik M, Urlacher VB. A fluorimetric assay for cortisol. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005;383(2):182–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-0022-9.
Gatti R, Cappellin E, Zecchin B, Antonelli G, Spinella P, Mantero F, et al. Urinary high performance reverse phase chromatography cortisol and cortisone analyses before and at the end of a race in elite cyclists. J Chromatogr B. 2005;824(1):51–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.06.037.
Kim J, Campbell AS, Wang J. Wearable non-invasive epidermal glucose sensors: a review. Talanta. 2018;177:163–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.077.
Kim J, Sempionatto JR, Imani S, Hartel MC, Barfidokht A, Tang G, et al. Simultaneous monitoring of sweat and interstitial fluid using a single wearable biosensor platform. Advanced Science. 2018;5(10):1800880. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201800880.
Lipani L, Dupont BGR, Doungmene F, Marken F, Tyrrell RM, Guy RH, et al. Non-invasive, transdermal, path-selective and specific glucose monitoring via a graphene-based platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2018;13(6):504–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-018-0112-4.
Abdullah H, Phairatana T, Jeerapan I. Tackling the challenges of developing microneedle-based electrochemical sensors. Microchim Acta. 2022;189(11):440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05510-3.
Sempionatto JR, Jeerapan I, Krishnan S, Wang J. Wearable chemical sensors: emerging systems for on-body analytical chemistry. Anal Chem. 2020;92(1):378–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04668.
Bariya M, Nyein HYY, Javey A. Wearable sweat sensors. Nature Electronics. 2018;1(3):160–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-018-0043-y.
Zhao C, Li X, Wu Q, Liu X. A thread-based wearable sweat nanobiosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2021;188:113270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113270
Ghaffari R, Rogers JA, Ray TR. Recent progress, challenges, and opportunities for wearable biochemical sensors for sweat analysis. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2021;332:129447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129447
Moonla C, Lee DH, Rokaya D, Rasitanon N, Kathayat G, Lee W-Y, et al. Review—Lab-in-a-mouth and advanced point-of-care sensing systems: detecting bioinformation from the oral cavity and saliva. ECS Sensors Plus. 2022;1(2):021603. https://doi.org/10.1149/2754-2726/ac7533
Arakawa T, Tomoto K, Nitta H, Toma K, Takeuchi S, Sekita T, et al. A wearable cellulose acetate-coated mouthguard biosensor for in vivo salivary glucose measurement. Anal Chem. 2020;92(18):12201–7. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01201.
Yang Y, Gao W. Wearable and flexible electronics for continuous molecular monitoring. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(6):1465–91. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00730B.
Lee W-C, Koh EH, Kim D-H, Park S-G, Jung HS. Plasmonic contact lens materials for glucose sensing in human tears. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2021;344:130297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130297
Iguchi S, Kudo H, Saito T, Ogawa M, Saito H, Otsuka K, et al. A flexible and wearable biosensor for tear glucose measurement. Biomed Microdevice. 2007;9(4):603–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9073-3.
Sempionatto JR, Brazaca LC, García-Carmona L, Bolat G, Campbell AS, Martin A, et al. Eyeglasses-based tear biosensing system: non-invasive detection of alcohol, vitamins and glucose. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019;137:161–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.04.058.
Xu J, Tao X, Liu X, Yang L. Wearable eye patch biosensor for noninvasive and simultaneous detection of multiple biomarkers in human tears. Anal Chem. 2022;94(24):8659–67. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00614.
Zhang Y, Wu H-L, Ding Y-J, Xia AL, Cui H, Yu R-Q. Simultaneous determination of cortisol and prednisolone in body fluids by using HPLC–DAD coupled with second-order calibration based on alternating trilinear decomposition. J Chromatogr B. 2006;840(2):116–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.04.043.
Li C, Zhang Z, Liu X, Shen K, Gu P, Kang X. Simultaneous quantification of cortisol and cortisone in urines from infants with packed-fiber solid-phase extraction coupled to HPLC–MS/MS. J Chromatogr B. 2017;1061–1062:163–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.07.012.
Pradhan S, Nicholson BD, Albin S, Heise RL, Yadavalli VK. Single-use biomimetic sensors for rapid and sensitive cortisol detection in blood. Biosensors and Bioelectronics: X. 2022;12:100280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosx.2022.100280
Gevaerd A, Watanabe EY, Belli C, Marcolino-Junior LH, Bergamini MF. A complete lab-made point of care device for non-immunological electrochemical determination of cortisol levels in salivary samples. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2021;332:129532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.129532
Zhou Q, Kannan P, Natarajan B, Maiyalagan T, Subramanian P, Jiang Z, et al. MnO2 cacti-like nanostructured platform powers the enhanced electrochemical immunobiosensing of cortisol. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2020;317:128134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128134
Jeerapan I, Sangsudcha W, Phokhonwong P. Wearable energy devices on mask-based printed electrodes for self-powered glucose biosensors. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research. 2022;38:100525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2022.100525
Lin P-H, Sheu S-C, Chen C-W, Huang S-C, Li B-R. Wearable hydrogel patch with noninvasive, electrochemical glucose sensor for natural sweat detection. Talanta. 2022;241:123187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123187
Jiang D, Xu C, Zhang Q, Ye Y, Cai Y, Li K, et al. In-situ preparation of lactate-sensing membrane for the noninvasive and wearable analysis of sweat. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2022;210:114303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114303
Sekar M, Pandiaraj M, Bhansali S, Ponpandian N, Viswanathan C. Carbon fiber based electrochemical sensor for sweat cortisol measurement. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):403. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37243-w.
Ku M, Kim J, Won J-E, Kang W, Park Y-G, Park J, et al. Smart, soft contact lens for wireless immunosensing of cortisol. 2020;6(28):eabb2891. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abb2891
Yang B, Kong J, Fang X. Bandage-like wearable flexible microfluidic recombinase polymerase amplification sensor for the rapid visual detection of nucleic acids. Talanta. 2019;204:685–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.06.031.
Patiti C, Sfragano PS, Laschi S, Pillozzi S, Boddi A, Crociani O, et al. Chip-based and wearable tools for isothermal amplification and electrochemical analysis of nucleic acids. Chemosensors. 2022;10(7):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10070278.
Zhang W, He Y, Feng Z, Zhang J. Recent advances of functional nucleic acid-based sensors for point-of-care detection of SARS-CoV-2. Microchim Acta. 2022;189(3):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05242-4.
Wu Y, Wang C-W, Wang D, Wei N. A whole-cell biosensor for point-of-care detection of waterborne bacterial pathogens. ACS Synth Biol. 2021;10(2):333–44. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.0c00491.
Woo S-G, Moon S-J, Kim SK, Kim TH, Lim HS, Yeon G-H, et al. A designed whole-cell biosensor for live diagnosis of gut inflammation through nitrate sensing. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2020;168:112523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112523
Dhull N, Kaur G, Gupta V, Tomar M. Highly sensitive and non-invasive electrochemical immunosensor for salivary cortisol detection. Sens Actuators, B Chem. 2019;293:281–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.020.
Madhu S, Ramasamy S, Manickam P, Nagamony P, Chinnuswamy V. TiO2 anchored carbon fibers as non-invasive electrochemical sensor platform for the cortisol detection. Materials Letters. 2022;308:131238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.131238
Torrente-Rodríguez RM, Tu J, Yang Y, Min J, Wang M, Song Y, et al. Investigation of cortisol dynamics in human sweat using a graphene-based wireless mHealth system. Matter. 2020;2(4):921–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2020.01.021.
Nah JS, Barman SC, Zahed MA, Sharifuzzaman M, Yoon H, Park C, et al. A wearable microfluidics-integrated impedimetric immunosensor based on Ti3C2Tx MXene incorporated laser-burned graphene for noninvasive sweat cortisol detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2021;329:129206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129206
Cheng C, Li X, Xu G, Lu Y, Low SS, Liu G, et al. Battery-free, wireless, and flexible electrochemical patch for in situ analysis of sweat cortisol via near field communication. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2021;172:112782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112782
Liu Q, Shi W, Tian L, Su M, Jiang M, Li J, et al. Preparation of nanostructured PDMS film as flexible immunosensor for cortisol analysis in human sweat. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2021;1184:339010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339010
Liu X, Zhao R, Mao W, Feng H, Liu X, Wong DKY. Detection of cortisol at a gold nanoparticle|Protein G-DTBP-scaffold modified electrochemical immunosensor. Analyst. 2011;136(24):5204–10. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1AN15411G.
Sun B, Gou Y, Ma Y, Zheng X, Bai R, Ahmed Abdelmoaty AA, et al. Investigate electrochemical immunosensor of cortisol based on gold nanoparticles/magnetic functionalized reduced graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;88:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.047.
Tu J, Torrente-Rodríguez RM, Wang M, Gao W. The era of digital health: a review of portable and wearable affinity biosensors. Adv Func Mater. 2020;30(29):1906713. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201906713.
Sekar M, Sriramprabha R, Sekhar PK, Bhansali S, Ponpandian N, Pandiaraj M, et al. Review—Towards wearable sensor platforms for the electrochemical detection of cortisol. Journal of The Electrochemical Society. 2020;167(6):067508. https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ab7e24
Zea M, Bellagambi FG, Ben Halima H, Zine N, Jaffrezic-Renault N, Villa R, et al. Electrochemical sensors for cortisol detections: almost there. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2020;132:116058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116058
Parlak O. Portable and wearable real-time stress monitoring: a critical review. Sensors and Actuators Reports. 2021;3:100036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snr.2021.100036
Mathew M, Radhakrishnan S, Vaidyanathan A, Chakraborty B, Rout CS. Flexible and wearable electrochemical biosensors based on two-dimensional materials: recent developments. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413(3):727–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03002-y.
Kaushik A, Vasudev A, Arya SK, Pasha SK, Bhansali S. Recent advances in cortisol sensing technologies for point-of-care application. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;53:499–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.09.060.
Parlak O, Keene ST, Marais A, Curto VF, Salleo A. Molecularly selective nanoporous membrane-based wearable organic electrochemical device for noninvasive cortisol sensing. Science Advances. 2018;4(7):eaar2904. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar2904
Lee H-B, Meeseepong M, Trung TQ, Kim B-Y, Lee N-E. A wearable lab-on-a-patch platform with stretchable nanostructured biosensor for non-invasive immunodetection of biomarker in sweat. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2020;156:112133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112133
Laochai T, Yukird J, Promphet N, Qin J, Chailapakul O, Rodthongkum N. Non-invasive electrochemical immunosensor for sweat cortisol based on L-cys/AuNPs/MXene modified thread electrode. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2022;203:114039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114039
Wang Y, Ye Z, Ying Y. New trends in impedimetric biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors. 2012;12(3):3449–71. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120303449.
Trilling AK, Beekwilder J, Zuilhof H. Antibody orientation on biosensor surfaces: a minireview. Analyst. 2013;138(6):1619–27. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AN36787D.
Gao S, Guisán JM, Rocha-Martin J. Oriented immobilization of antibodies onto sensing platforms - a critical review. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2022;1189:338907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338907
Hashemi P, Afkhami A, Baradaran B, Halabian R, Madrakian T, Arduini F, et al. Well-orientation strategy for direct immobilization of antibodies: development of the immunosensor using the boronic acid-modified magnetic graphene nanoribbons for ultrasensitive detection of lymphoma cancer cells. Anal Chem. 2020;92(16):11405–12. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02357.
Feng D, Li L, Fang X, Han X, Zhang Y. Dual signal amplification of horseradish peroxidase functionalized nanocomposite as trace label for the electrochemical detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Electrochim Acta. 2014;127:334–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.02.072.
Si Y, Lee HJ. Carbon nanomaterials and metallic nanoparticles-incorporated electrochemical sensors for small metabolites: detection methodologies and applications. Curr Opin Electrochem. 2020;22:234–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2020.08.007.
Cho I-H, Kim DH, Park S. Electrochemical biosensors: perspective on functional nanomaterials for on-site analysis. Biomaterials research. 2020;24(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-019-0181-y.
Zhang H, He R, Niu Y, Han F, Li J, Zhang X, et al. Graphene-enabled wearable sensors for healthcare monitoring. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2022;197:113777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113777
Tian L, Jiang M, Su M, Cao X, Jiang Q, Liu Q, et al. Sweat cortisol determination utilizing MXene and multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite functionalized immunosensor. Microchemical Journal. 2022:108172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.108172
Manickam P, Fernandez RE, Umasankar Y, Gurusamy M, Arizaleta F, Urizar G, et al. Salivary cortisol analysis using metalloporphyrins and multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite functionalized electrodes. Sens Actuators, B Chem. 2018;274:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.133.
Kaushik A, Vasudev A, Arya SK, Bhansali S. Mediator and label free estimation of stress biomarker using electrophoretically deposited Ag@AgO–polyaniline hybrid nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;50:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.06.012.
Vabbina PK, Kaushik A, Pokhrel N, Bhansali S, Pala N. Electrochemical cortisol immunosensors based on sonochemically synthesized zinc oxide 1D nanorods and 2D nanoflakes. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;63:124–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.026.
Arya SK, Dey A, Bhansali S. Polyaniline protected gold nanoparticles based mediator and label free electrochemical cortisol biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011;28(1):166–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.07.015.
Munje RD, Muthukumar S, Panneer Selvam A, Prasad S. Flexible nanoporous tunable electrical double layer biosensors for sweat diagnostics. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):14586. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14586.
Kim KS, Lim SR, Kim S-E, Lee JY, Chung C-H, Choe W-S, et al. Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical cortisol sensor using bifunctional protein interlayer-modified graphene electrodes. Sens Actuators, B Chem. 2017;242:1121–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.135.
Vasudev A, Kaushik A, Tomizawa Y, Norena N, Bhansali S. An LTCC-based microfluidic system for label-free, electrochemical detection of cortisol. Sens Actuators, B Chem. 2013;182:139–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.02.096.
Moreno-Guzmán M, Eguílaz M, Campuzano S, González-Cortés A, Yáñez-Sedeño P, Pingarrón JM. Disposable immunosensor for cortisol using functionalized magnetic particles. Analyst. 2010;135(8):1926–33. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0AN00206B.
Pasha SK, Kaushik A, Vasudev A, Snipes SA, Bhansali S. Electrochemical immunosensing of saliva cortisol. J Electrochem Soc. 2014;161(2):B3077. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.017402jes.
Tuteja SK, Ormsby C, Neethirajan S. Noninvasive label-free detection of cortisol and lactate using graphene embedded screen-printed electrode. Nano-Micro Letters. 2018;10(3):41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-018-0193-5.
Demuru S, Kim J, El Chazli M, Bruce S, Dupertuis M, Binz P-A, et al. Antibody-coated wearable organic electrochemical transistors for cortisol detection in human sweat. ACS Sensors. 2022;7(9):2721–31. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.2c01250.
Rice P, Upasham S, Jagannath B, Manuel R, Pali M, Prasad S. CortiWatch: watch-based cortisol tracker. Future Science OA. 2019;5(9):FSO416. https://doi.org/10.2144/fsoa-2019-0061
Shajari S, Salahandish R, Zare A, Hassani M, Moossavi S, Munro E, et al. MicroSweat: a wearable microfluidic patch for noninvasive and reliable sweat collection enables human stress monitoring. Advanced Science. 2022;n/a(n/a):2204171. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202204171
Jiang C, Wang G, Hein R, Liu N, Luo X, Davis JJ. Antifouling strategies for selective in vitro and in vivo sensing. Chem Rev. 2020;120(8):3852–89. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00739.
Goud KY, Reddy KK, Khorshed A, Kumar VS, Mishra RK, Oraby M, et al. Electrochemical diagnostics of infectious viral diseases: trends and challenges. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2021;180:113112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113112
Liu N, Xu Z, Morrin A, Luo X. Low fouling strategies for electrochemical biosensors targeting disease biomarkers. Anal Methods. 2019;11(6):702–11. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY02674B.
Bandodkar AJ, Choi J, Lee SP, Jeang WJ, Agyare P, Gutruf P, et al. Soft, Skin-interfaced microfluidic systems with passive galvanic stopwatches for precise chronometric sampling of sweat. Adv Mater. 2019;31(32):1902109. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201902109.
Saha T, Songkakul T, Knisely CT, Yokus MA, Daniele MA, Dickey MD, et al. Wireless wearable electrochemical sensing platform with zero-power osmotic sweat extraction for continuous lactate monitoring. ACS Sensors. 2022;7(7):2037–48. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.2c00830.
Zhang H, Zhang D-Z, Wang D-Y, Xu Z-Y, Yang Y, Zhang B. Flexible single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator with MWCNT/PDMS composite film for environmental energy harvesting and human motion monitoring. Rare Met. 2022;41(9):3117–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02031-z.
Maji D, Das D, Wala J, Das S. Buckling assisted and lithographically micropatterned fully flexible sensors for conformal integration applications. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):17776. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17776.
Özmen EN, Kartal E, Turan MB, Yazıcıoğlu A, Niazi JH, Qureshi A. Graphene and carbon nanotubes interfaced electrochemical nanobiosensors for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and other respiratory viral infections: a review. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2021;129:112356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112356
Abu Nayem SM, Shaheen Shah S, Sultana N, Aziz MA, Saleh Ahammad AJ. Electrochemical sensing platforms of dihydroxybenzene: Part 1 – Carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their derivatives. Chem Rec. 2021;21(5):1039–72. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202100043.
Ahirwar R. Recent advances in nanomaterials-based electrochemical immunosensors and aptasensors for HER2 assessment in breast cancer. Microchim Acta. 2021;188(10):317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04963-2.
Sun X, Zhao C, Li H, Yu H, Zhang J, Qiu H, et al. Wearable near-field communication sensors for healthcare: materials, fabrication and application. Micromachines. 2022;13(5):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050784.
Olenik S, Lee HS, Güder F. The future of near-field communication-based wireless sensing. Nat Rev Mater. 2021;6(4):286–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-021-00299-8.
Wu Y, Mechael SS, Carmichael TB. Wearable E-textiles using a textile-centric design approach. Acc Chem Res. 2021;54(21):4051–64. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00433.
Choudhry NA, Arnold L, Rasheed A, Khan IA, Wang L. Textronics—a review of textile-based wearable electronics. Adv Eng Mater. 2021;23(12):2100469. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202100469.
Xia J, Khaliliazar S, Hamedi MM, Sonkusale S. Thread-based wearable devices. MRS Bull. 2021;46(6):502–11. https://doi.org/10.1557/s43577-021-00116-1.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Talent Management Project of Prince of Songkla University and the Center of Excellence for Innovation in Chemistry (PERCH-CIC), Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research, and Innovation (MHESI).
Funding
I.J. received support from the National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT, Grant No. N41A640129), Prince of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Published in the topical collection Young Investigators in (Bio-)Analytical Chemistry 2023 with guest editors Zhi-Yuan Gu, Beatriz Jurado-Sánchez, Thomas H. Linz, Leandro Wang Hantao, Nongnoot Wongkaew, and Peng Wu.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khumngern, S., Jeerapan, I. Advances in wearable electrochemical antibody-based sensors for cortisol sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 3863–3877 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04577-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04577-y