Abstract
A human insulin (hINS) certified reference material (CRM) was developed by the National Institute of Metrology (NIM). Three milligrams of purified solid hINS was packed into a brown sealed tube. The candidate material was identified by de novo sequence using mass spectrometry and Edman degradation methods. The content of insulin-related impurities, aggregation, moisture, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), anions, and ignition residues was also determined. Both mass balance (MB) and amino acid analysis-based isotope dilution mass spectrometry (AAA-IDMS) were used for the certified value assessment, which was determined to be (0.857 ± 0.024) g/g. The certified value was validated by liquid chromatography-circular dichroism spectroscopy (LC-CD) and quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance (qNMR) methods, which were in good agreement. No inhomogeneity was observed during a homogeneity examination. A stability examination showed that the CRM was stable for at least 12 months when stored at − 70 °C, and for 7 days when stored at 4, 25, or 40 °C. The CRM is expected to be used as a primary calibrator for matrix insulin CRM development and for quality control in biopharmaceutical production and clinical diagnostics.
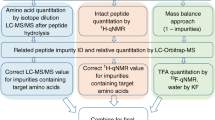
Graphical abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
All the numbers that follow “ ± ” are expanded uncertainties with a coverage factor of 2 except “110.0 ± 0.5 °C” that appears later, which means the maximum permitted bias.
References
ISO 17511:2020 In vitro diagnostic medical devices — requirements for establishing metrological traceability of values assigned to calibrators, trueness control materials and human samples.
JJF 1752–2019. Calibration specification for automatic enclosed luminescence immunoassay analyzer.
Westwood S, Choteau T, Daireaux A, et al. Mass balance method for the SI value assignment of the purity of organic compounds. Anal Chem. 2013;85(6):3118–26.
Stoppacher N, Josephs RD, Daireaux A, et al. Accurate quantification of impurities in pure peptide material – angiotensin I: comparison of calibration requirements and method performance characteristics of liquid chromatography coupled to hybrid tandem mass spectrometry and linear ion trap high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Sp. 2015;29(18):1651–60.
Melanson JE, Thibeault M-P, Stocks BB, et al. Purity assignment for peptide certified reference materials by combining qNMR and LC-MS/MS amino acid analysis results: application to angiotensin II. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(26):6719–31.
Josephs RD, Stoppacher N, Daireaux A, et al. State-of-the-art and trends for the SI traceable value assignment of the purity of peptides using the model compound angiotensin I. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. 2018;101:108–19.
Villanueva J, Carrascal M, Abian J. Isotope dilution mass spectrometry for absolute quantification in proteomics: concepts and strategies. J Proteomics. 2014;96:184–99.
Öztürk Er E, Özbek B, Bakırdere S. Determination of seventeen free amino acids in human urine and plasma samples using quadruple isotope dilution mass spectrometry combined with hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography – tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2021;1641:461970.
Kato M, Takatsu A. Amino acid analysis by hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled with isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2030:111–8.
Yang R, Dong J, Guo H, et al. Rapid and precise measurement of serum branched-chain and aromatic amino acids by isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Plos One. 2013;8(12):e81144.
Kim J, Tran TTH, Hong S-P, et al. A reference measurement procedure for amino acids in blood using isotope dilution ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2017;1055–1056:72–80.
Heiss M, Reichle VF, Kellner S. Observing the fate of tRNA and its modifications by nucleic acid isotope labeling mass spectrometry: NAIL-MS. RNA Biol. 2017;14(9):1260–8.
Shibayama S, Fujii S-I, Inagaki K, et al. Formic acid hydrolysis/liquid chromatography isotope dilution mass spectrometry: an accurate method for large DNA quantification. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1468:109–15.
Kung AW, Kilby PM, Portwood DE, et al. Quantification of dsRNA using stable isotope labeling dilution liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Sp. 2018;32(7):590–6.
Chen Q, Hu Y, Fang Z, et al. Elevated levels of oxidative nucleic acid modification markers in urine from gastric cancer patients: quantitative analysis by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Fron Chem, 2020, 8(1187)
Pritchard C, Torma FA, Hopley C, et al. Investigating microwave hydrolysis for the traceable quantification of peptide standards using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 2011;412(1):40–6.
Wu L, Yang B, Bi J, et al. Development of bovine serum albumin certified reference material. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;400(10):3443–9.
Josephs RD, Li M, Song D, et al. Key comparison study on peptide purity—synthetic human C-peptide. Metrologia. 2017;54(1A):08007.
Tran TTH, Lim J, Kim J, et al. Fully international system of units-traceable glycated hemoglobin quantification using two stages of isotope-dilution high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1513:183–93.
Liu H, Wong L, Yong S, et al. Achieving comparability with IFCC reference method for the measurement of hemoglobin A1c by use of an improved isotope-dilution mass spectrometry method. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(25):7579–87.
Burkitt WI, Pritchard C, Arsene C, et al. Toward Système International d’Unité-traceable protein quantification: from amino acids to proteins. Anal Biochem. 2008;376(2):242–51.
Muñoz A, Kral R, Schimmel H. Quantification of protein calibrants by amino acid analysis using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem. 2011;408(1):124–31.
Yim J-H, Yoon I, Yang H-J, et al. Quantification of recombinant human erythropoietin by amino acid analysis using isotope dilution liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(18):4401–9.
Wu L, Takatsu A, Park S-R, et al. Development and co-validation of porcine insulin certified reference material by high-performance liquid chromatography–isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(11):3125–35.
Yang W, Liqing W, Fei D, et al. Development of an SI-traceable HPLC–isotope dilution mass spectrometry method to quantify β-lactoglobulin in milk powders. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62(14):3073–80.
Li J, Wu L, Jin Y, et al. A universal SI-traceable isotope dilution mass spectrometry method for protein quantitation in a matrix by tandem mass tag technology. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408(13):3485–93.
Pierce-Ruiz C, Santana WI, Sutton WJH, et al. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins using isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Vaccine. 2021;39(36):5106–15.
Chou D Hary A, Sharma R J, Singh I P. Determination of Major Sesquiterpene Lactones in Essential Oil of Inula racemosa and Saussurea lappa using qNMR. J Essent Oil Bear Pl, 2016.
Chen XL, Qi J, Yu BY. Quantitative analysis of salvianolic acids, ginsenosides and borneols using 1H qNMR for quality control of compound Danshen dripping pills. Anal Methods. 2017;9(38):5580–5.
Dunn PJH, Malinovsky D, Achtar E, et al. Systematic comparison of post-column isotope dilution using LC-CO-IRMS with qNMR for amino acid purity determination. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411(27):7207–20.
Tsirivakou A, Melliou E, Magiatis P. A Method for the rapid measurement of alkylresorcinols in flour, bread and related products based on 1H qNMR. Foods. 2020;9(8):1025.
Huang T, Zhang W, Dai X, et al. Precise measurement for the purity of amino acid and peptide using quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance. Talanta. 2014;125:94–101.
Zhang W, Huang T, Li H, et al. Purity measurement of human C-peptide by high performance liquid chromatography and quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2018;24(3):391–6.
Weber M, Hellriegel C, Rück A, et al. Using high-performance quantitative NMR (HP-qNMR®) for certifying traceable and highly accurate purity values of organic reference materials with uncertainties <0.1 %. Accredit Qual Assur, 2013, 18(2): 91-8.
Luo Y, Wu L, Yang B, et al. A novel potential primary method for quantification of enantiomers by high performance liquid chromatography-circular dichroism. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7390.
Chinese Pharmacopoeia. 2020.
GB/T 606–2003. General method for the determination of moisture in chemical reagents Karl Fischer method.
Varongchayakul N, Song J, Meller A, et al. Single-molecule protein sensing in a nanopore: a tutorial. Chem Soc Rev. 2018;47(23):8512–24.
General and statistical principles for characterization of reference materials. 2012.
Heaton AL, Armentrout PB. Thermodynamics and mechanism of protonated asparagine decomposition. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009;20(5):852–66.
Ma R, Huang T, Zhang W, et al. High performance liquid chromatography - quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance - high performance liquid chromatography for purity measurement of human insulin. J Liq Chromatogr R T. 2018;41(4):1–10.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the projects AKYZD1907, AKY1959, and 2018B02020707. Victoria Muir, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn/), edited the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wu, L., Huang, Y. et al. Development of a human insulin certified reference material with SI-traceable purity. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 3443–3457 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03965-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03965-0