Abstract
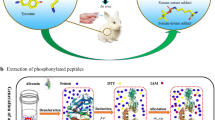
Organophosphorus nerve agents (OPNAs) covalently bind to tyrosine 411 of human serum albumin (HSA) and the formed adducts are stable biomarkers of OPNA exposure. The detection of these adducts has been limited to mass spectrometry techniques combined with protein digestion. Here, we developed indirect competitive ELISA (icELISA) methods to verify OPNA exposure by the detection of OPNA-phosphonylated adducts at tyrosine 411 residue (OPNA-HSA adducts), in which monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against phosphonylation sites at tyrosine 411 were introduced. The two mAbs were prepared by the fourth generation of rabbit mAb technology using the phosphonylated peptides of LVRY(GD or VX)TKKVPQC as the haptens. These mAbs were screened using our developed competitive ELISA method and then selected based on their individual affinity and selectivity. As a result, we obtained two mAbs that recognized the HSA Tyr 411 adduct of GD (mAb-5G2) or VX (mAb-12B9), respectively. They shared the highest affinity exhibiting a Kd value of about 10−6 mol/L of the OPNA exposure concentration. They also had remarkable selectivity, which could especially recognize their individual OPNA-HSA adducts in a native state but did not recognize other OPNA-HSAs and unadducted HSAs. Especially for mAb-12B9, it could clearly distinguish VX-HSA and GB-HSA between which there was only one alkyl difference in their phosphonyl portion of the adducted sites. The two mAbs were then used to build the icELISA method for analysis of the serum samples exposed to OPNA. It was found that the detectable lowest GD- and VX-exposed concentrations in serum samples were respectively 1.0 × 10−6 mol/L and 10.0 × 10−6 mol/L. This study provides one novel approach and strategy for the retrospective detection of OPNA exposure, and the two mAbs have great potential to be extended for point-of-care testing of OPNA intoxication.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellison DH. Handbook of chemical and biological warfare agents. CRC press, 2007.
Wiener SW, Hoffman RS. Nerve agents: a comprehensive review. J Intensive Care Med. 2004;19(1):22–37.
Amend N, Niessen K, Seeger T, Wille T, Worek F, Thiermann H. Diagnostics and treatment of nerve agent poisoning-current status and future developments. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020;1479(1):13–28.
Mirbabaei F, Mohammad-Khah A, Babri M, Naseri MT. Verification of exposure to sarin nerve agent through the chemical analysis of red blood cell samples. Microchem J. 2020;158:8.
John H, van der Schans MJ, Koller M, Spruit HET, Worek F, Thiermann H, et al. Fatal sarin poisoning in Syria 2013: forensic verification within an international laboratory network. Forensic Toxicol. 2018;36(1):61–71.
Hulse EJ, Haslam JD, Emmett SR, Woolley T. Organophosphorus nerve agent poisoning: managing the poisoned patient. Br J Anaesth. 2019;123(4):457–63.
Holmstedt B. Pharmacology of organophosphorus cholinesterase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev. 1959;11(11):567.
Black RM. History and perspectives of bioanalytical methods for chemical warfare agent detection. J Chromatogr B. 2010;878(17–18):1207–15.
Worek F, Koller M, Thiermann H, Szinicz L. Diagnostic aspects of organophosphate poisoning. Toxicology. 2005;214(3):182–9.
Ashani Y, Shapira S, Levy D, Wolfe AD, Doctor BP, Raveh L. Butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase prophylaxis against soman poisoning in mice. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991;41(1):37–41.
Fidder A, Hulst AG, Noort D, de Ruiter R, van der Schans MJ, Benschop HP, et al. Retrospective detection of exposure to organophosphorus anti-cholinesterases: mass spectrometric analysis of phosphylated human butyrylcholinesterase. Chem Res Toxicol. 2002;15(4):582–90.
Wille T, Djordjević S, Worek F, Thiermann H, Vučinić S. Early diagnosis of nerve agent exposure with a mobile test kit and implications for medical countermeasures: a trigger to react. BMJ military health. 2020;166(2):99–102.
Hofmann JN, Carden A, Fenske RA, Ruark HE, Keifer MC. Evaluation of a clinic-based cholinesterase test kit for the Washington State Cholinesterase Monitoring Program. Am J Ind Med. 2008;51(7):532–8.
Worek F, Schilha M, Neumaier K, Aurbek N, Wille T, Thiermann H, et al. On-site analysis of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activity with the ChE check mobile test kit-determination of reference values and their relevance for diagnosis of exposure to organophosphorus compounds. Toxicol Lett. 2016;249:22–8.
Munro NB, Talmage SS, Griffin GD, Waters LC, Watson AP, King JF, et al. The sources, fate, and toxicity of chemical warfare agent degradation products. Environ Health Perspect. 1999;107(12):933–74.
Lin Y, Chen J, Yan L, Guo L, Wu B, Li C, et al. Determination of nerve agent metabolites in human urine by isotope-dilution gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after solid phase supported derivatization. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(21):5213–20.
Blanca M, Shifrovitch A, Dachir S, Lazar S, Elgarisi M, Marder D, et al. Highly sensitive retrospective determination of organophosphorous nerve agent biomarkers in human urine implemented in vivo in rabbit. Arch Toxicol. 2020;94(9):3033–44.
Baygildiev T, Vokuev M, Ogorodnikov R, Braun A, Rybalchenko I, Rodin I. Simultaneous determination of organophosphorus nerve agent markers in urine by LC-MS/MS using anion-exchange solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr B. 2019;1132:121815.
Liu CC, Huang GL, Xi HL, Liu SL, Liu JQ, Yu HL, et al. Simultaneous quantification of soman and VX adducts to butyrylcholinesterase, their aged methylphosphonic acid adduct and butyrylcholinesterase in plasma using an off-column procainamide-gel separation method combined with UHPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B. 2016;1036:57–65.
Peeples ES, Schopfer LM, Duysen EG, Spaulding R, Voelker T, Thompson CM, et al. Albumin, a new biomarker of organophosphorus toxicant exposure, identified by mass spectrometry. Toxicol Sci. 2005;83(2):303–12.
Bonichon M, Valbi V, Combès A, Desoubries C, Bossée A, Pichon V. Online coupling of immunoextraction, digestion, and microliquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of sarin and soman-butyrylcholinesterase adducts in human plasma. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410(3):1039–51.
Worek F, Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer P. Kinetic analysis of interactions between human acetylcholinesterase, structurally different organophosphorus compounds and oximes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68(11):2237–48.
Graham LA, Johnson D, Carter MD, Stout EG, Erol HA, Isenberg SL, et al. A high-throughput UHPLC-MS/MS method for the quantification of five aged butyrylcholinesterase biomarkers from human exposure to organophosphorus nerve agents. Biomed Chromatogr. 2017;31(4):e3830.
Rybal’chenko IV, Baigil’diev TM, Rodin IA. Chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis for the determination of the markers and biomarkers of chemical warfare agents. J Anal Chem. 2021;76(1):26–40.
Langenberg JP, van der Schans MJ, Noort D. Assessment of nerve agent exposure: existing and emerging methods. Bioanalysis. 2009;1(4):729–39.
Hua X, Eremin SA, Liu F, Wang M. Antibody developments and immunoassays for organophosphorus chemicals: a review. Curr Org Chem. 2017;21(26):2640–52.
Johnson JK, Cerasoli DM, Lenz DE. Role of immunogen design in induction of soman-specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Lett. 2005;96(1):121–7.
Sathe M, Merwyn S, Ghorpade R, Agarwal GS, Rao MK, Rai GP, et al. Design and synthesis of immunoconjugates and development of competition inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (CIEIA) for the detection of O-isopropyl methylphosphonofluoridate (sarin): an organophosphorous toxicant. J Hazard Mater. 2011;192(3):1720–8.
Yao J, Wang Z, Guo L, Xu X, Liu L, Xu L, et al. Advances in immunoassays for organophosphorus and pyrethroid pesticides. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2020;131:116022.
Belabassi Y, Chao CK, Holly R, George KM, Nagy JO, Thompson CM. Preparation and characterization of diethoxy- and monoethoxy phosphylated (‘aged’) serine haptens and use in the production of monoclonal antibodies. Chem Biol Interact. 2014;223:134–40.
Wang H, Wang J, Timchalk C, Lin Y. Magnetic electrochemical immunoassays with quantum dot labels for detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase in plasma. Anal Chem. 2008;80(22):8477–84.
Liu G, Wang J, Barry R, Petersen C, Timchalk C, Gassman PL, et al. Nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase: an exposure biomarker of organophosphate pesticides and nerve agents. Chemistry. 2008;14(32):9951–9.
Wang L, Du D, Lu D, Lin CT, Smith JN, Timchalk C, et al. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of organophosphorylated butyrylcholinesterase: a biomarker of exposure to organophosphate agents. Anal Chim Acta. 2011;693(1–2):1–6.
George KM, Schule T, Sandoval LE, Jennings LL, Taylor P, Thompson CM. Differentiation between acetylcholinesterase and the organophosphate-inhibited form using antibodies and the correlation of antibody recognition with reactivation mechanism and rate. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(46):45512–8.
Park SJ, Kim DH, Yoo J, Hwang EY, Shin MS, Lee NT, et al. Detection of organophosphate bound butyrylcholinesterase using a monoclonal antibody. Appl Biol Chem. 2017;60(3):1–8.
Chen S, Zhang J, Lumley L, Cashman JR. Immunodetection of serum albumin adducts as biomarkers for organophosphorus exposure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013;344(2):531–41.
Li B, Duysen EG, Froment MT, Masson P, Nachon F, Jiang W, et al. Polyclonal antibody to soman-tyrosine. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013;26(4):584–92.
VanDine R, Babu UM, Condon P, Mendez A, Sambursky R. A 10-minute point-of-care assay for detection of blood protein adducts resulting from low level exposure to organophosphate nerve agents. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;203(1):108–12.
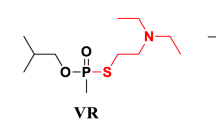
Crow BS, Pantazides BG, Quinones-Gonzalez J, Garton JW, Carter MD, Perez JW, et al. Simultaneous measurement of tabun, sarin, soman, cyclosarin, VR, VX, and VM adducts to tyrosine in blood products by isotope dilution UHPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem. 2014;86(20):10397–405.
Guo Y, Werbel T, Wan S, Wu H, Li Y, Clare-Salzler M, et al. Potent antigen-specific immune response induced by infusion of spleen cells coupled with succinimidyl-4-(N-maleimidomethyl cyclohexane)-1-carboxylate (SMCC) conjugated antigens. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016;31:158–68.
Kivi G, Teesalu K, Parik J, Kontkar E, Ustav M Jr, Noodla L, et al. HybriFree: a robust and rapid method for the development of monoclonal antibodies from different host species. BMC Biotechnol. 2016;16:2.
Starkie DO, Compson JE, Rapecki S, Lightwood DJ. Generation of recombinant monoclonal antibodies from immunised mice and rabbits via flow cytometry and sorting of antigen-specific IgG+ memory B Cells. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0152282.
Weber J, Peng H, Rader C. From rabbit antibody repertoires to rabbit monoclonal antibodies. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(3):e305.
Babcook JS, Leslie KB, Olsen OA, Salmon RA, Schrader JW. A novel strategy for generating monoclonal antibodies from single, isolated lymphocytes producing antibodies of defined specificities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(15):7843–8.
Li B, Nachon F, Froment MT, Verdier L, Debouzy JC, Brasme B, et al. Binding and hydrolysis of soman by human serum albumin. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008;21(2):421–31.
Li B, Ricordel I, Schopfer LM, Baud F, Mégarbane B, Nachon F, et al. Detection of adduct on tyrosine 411 of albumin in humans poisoned by dichlorvos. Toxicol Sci. 2010;116(1):23–31.
Li B, Schopfer LM, Hinrichs SH, Masson P, Lockridge O. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry assay for organophosphorus toxicants bound to human albumin at Tyr411. Anal Biochem. 2007;361(2):263–72.
Ding SJ, Carr J, Carlson JE, Tong L, Xue W, Li Y, et al. Five tyrosines and two serines in human albumin are labeled by the organophosphorus agent FP-biotin. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008;21(9):1787–94.
Fu F, Sun F, Lu X, Song T, Ding J, Gao R, et al. A novel potential biomarker on Y263 site in human serum albumin poisoned by six nerve agents. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2019;1104:168–75.
Schopfer LM, Grigoryan H, Li B, Nachon F, Masson P, Lockridge O. Mass spectral characterization of organophosphate-labeled, tyrosine-containing peptides: characteristic mass fragments and a new binding motif for organophosphates. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010;878(17–18):1297–311.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the State Key Laboratory of NBC Protection for Civilians.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The animal experiments were performed in compliance with the ethical guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The welfare of experimental animals was guaranteed. All procedures followed internationally recognized guidelines.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Q., Yu, HL., Yang, Y. et al. Screening of monoclonal antibodies against specific phosphonylation sites and analysis of serum samples exposed to soman and VX using an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 414, 2713–2724 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03914-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-022-03914-x