Abstract
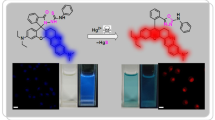
The detection of cyanide anion (CN−), a highly toxic pollutant, has attracted growing attention in the past years. In this work, a nanosensor composed of hyperbranched polyethyleneimine (hPEI)-assisted dual-emissive gold nanoclusters (DE-Au NCs) is proposed for ratiometric detection of CN− based on surface valence state-driving etch. The ratiometric color change of fluorescence is based on a fact that the red-emissive Au NCs with a high content of surface Au(I) can be easily etched by CN−, while the blue-emissive Au NCs with nearly neutral character can resist CN−. Because of the specific gold-CN− chemistry and electrostatic attraction between the positively charged hPEI protecting layer and the negatively charged CN−, the DE-Au NC-based nanosensor provides high selectivity toward CN− over other anions with a limit of detection of 10 nM. Practical application of the proposed DE-Au NC nanosensor is verified by satisfying recoveries of CN− determination in river water and urine samples.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen L-Y, Wang C-W, Yuan Z, Chang H-T. Fluorescent gold nanoclusters: recent advances in sensing and imaging. Anal Chem. 2015;87:216–29.
Chakraborty I, Pradeep T. Atomically precise clusters of noble metals: emerging link between atoms and nanoparticles. Chem Rev. 2017;117:8208–71.
Hesari M, Ding Z. A grand avenue to Au nanocluster electrochemiluminescence. Acc Chem Res. 2017;50:218–30.
Xu WW, Zeng XC, Gao Y. Application of electronic counting rules for ligand-protected gold nanoclusters. Acc Chem Res. 2018;51:2739–47.
Higaki T, Li Y, Zhao S, Li Q, Li S, Du X-S, et al. Atomically tailored gold nanoclusters for catalytic application. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58:8291–302.
Kwak K, Lee D. Electrochemistry of atomically precise metal nanoclusters. Acc Chem Res. 2019;52:12–22.
Jin R. Atomically precise metal nanoclusters: stable sizes and optical properties. Nanoscale. 2015;7:1549–65.
Yang H, Lu F, Sun Y, Yuan Z, Lu C. Fluorescent gold nanocluster-based sensor array for nitrophenol isomer discrimination via an integration of host–guest interaction and inner filter effect. Anal Chem. 2018;90:12846–53.
Yuan Z, Peng M, He Y, Yeung ES. Functionalized fluorescent gold nanodots: synthesis and application for Pb2+ sensing. Chem Commun. 2011;47:11981–3.
Tseng Y-T, Yuan Z, Yang Y-Y, Huang C-C, Chang H-T. Photoluminescent gold nanodots: role of the accessing ligands. RSC Adv. 2014;4:33629–35.
Lu F, Yang H, Yuan Z, Nakanishi T, Lu C, He Y. Highly fluorescent polyethyleneimine protected Au8 nanoclusters: one-pot synthesis and application in hemoglobin detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2019;291:170–6.
Tao Y, Li M, Ren J, Qu X. Metal nanoclusters: novel probes for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:8636–63.
Lee MH, Kim JS, Sessler JL. Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:4185–91.
Li Z, Guo S, Yuan Z, Lu C. Carbon quantum dot-gold nanocluster nanosatellite for ratiometric fluorescence probe and imaging for hydrogen peroxide in living cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;241:821–7.
Liu H, Jia L, Wang Y, Wang M, Gao Z, Ren X. Ratiometric fluorescent sensor for visual determination of copper ions and alkaline phosphatase based on carbon quantum dots and gold nanoclusters. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:2531–43.
Hu X, Shi J, Shi Y, Li W, Arslan M, Zhang W, et al. A ratiometric fluorescence sensor for ultra-sensitive detection of trypsin inhibitor in soybean flour using gold nanocluster@carbon nitride quantum dots. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:3341–51.
Jensen P, Wilson MT, Aasa R, Malmstrom BG. Cyanide inhibition of cytochrome-c oxidase - a rapid-freeze electron-paramagnetic-res investigation. Biochem J. 1984;224:829–37.
Baltrunas G, Pakalniene E, Popkirov GS, Schindler RN. The surface roughness of a silver electrode during electrocrystallization in cyanide electroplating bath. Z Phys Chem. 2002;216:791–802.
Dini JW. Cyanide and gold mining. Plat Surf Finish. 2004;91:17–8.
Jo J, Lee D. Turn-on fluorescence detection of cyanide in water: activation of latent fluorophores through remote hydrogen bonds that mimic peptide beta-turn motif. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:16283–91.
Xu Z, Chen X, Kim HN, Yoon J. Sensors for the optical detection of cyanide ion. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39:127–37.
Huang MF, Chang HT. Detection of carbohydrates using surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry with HgTe nanostructures. Chem Sci. 2012;3:2147–52.
Jackson R, Oda RP, Bhandari RK, Mahon SB, Brenner M, Rockwood GA, et al. Development of a fluorescence-based sensor for rapid diagnosis of cyanide exposure. Anal Chem. 2014;86:1845–52.
Wang F, Wang L, Chen X, Yoon J. Recent progress in the development of fluorometric and colorimetric chemosensors for detection of cyanide ions. Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43:4312–24.
Dong Z-Z, Yang C, Vellaisamy K, Li G, Leung C-H, Ma D-L. Construction of a nano biosensor for cyanide anion detection and its application in environmental and biological systems. ACS Sens. 2017;2:1517–22.
Karmakar A, Joarder B, Mallick A, Samanta P, Desai AV, Basu S, et al. Aqueous phase sensing of cyanide ions using a hydrolytically stable metal–organic framework. Chem Commun. 2017;53:1253–6.
Long L, Huang M, Wang N, Wu Y, Wang K, Gong A, et al. A mitochondria-specific fluorescent probe for visualizing endogenous hydrogen cyanide fluctuations in neurons. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140:1870–5.
Cang J, Wang C-W, Chen P-C, Lin Y-J, Li Y-C, Chang H-T. Control of pH for separated quantitation of nitrite and cyanide ions using photoluminescent copper nanoclusters. Anal Methods. 2017;9:5254–9.
Wang C-W, Chen Y-N, Wu B-Y, Lee C-K, Chen Y-C, Huang Y-H, et al. Sensitive detection of cyanide using bovine serum albumin-stabilized cerium/gold nanoclusters. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:287–94.
Wang X-B, Wang Y-L, Yang J, Xing X-P, Li J, Wang L-S. Evidence of significant covalent bonding in Au(CN)2−. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:16368–70.
Senapati D, Dasary SSR, Singh AK, Senapati T, Yu H, Ray PC. A label-free gold-nanoparticle-based SERS assay for direct cyanide detection at the parts-per-trillion level. Chem-Eur J. 2011;17:8445–51.
Liu YL, Ai KL, Cheng XL, Huo LH, Lu LH. Gold-nanocluster-based fluorescent sensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of cyanide in water. Adv Funct Mater. 2010;20:951–6.
Shang L, Jin LH, Dong SJ. Sensitive turn-on fluorescent detection of cyanide based on the dissolution of fluorophore functionalized gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun. 2009:3077–9.
Zhang G, Qiao Y, Xu T, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Shi L, et al. Highly selective and sensitive nanoprobes for cyanide based on gold nanoclusters with red fluorescence emission. Nanoscale. 2015;7:12666–72.
Yuan Z, Du Y, He Y. Hyperbranched polyamine assisted synthesis of dual-luminescent gold composite with pH responsive character. Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2017;5:014011.
Yuan Z, Lu F, Peng M, Wang C-W, Tseng Y-T, Du Y, et al. Selective colorimetric detection of hydrogen sulfide based on primary amine-active ester cross-linking of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2015;87:7267–73.
Yuan Z, Hu C-C, Chang H-T, Lu C. Gold nanoparticles as sensitive optical probes. Analyst. 2016;141:1611–26.
White-Morris RL, Olmstead MM, Balch AL. Aurophilic interactions in cationic gold complexes with two isocyanide ligands. Polymorphic yellow and colorless forms of [(cyclohexyl isocyanide)2AuI](PF6) with distinct luminescence. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:1033–40.
Chen T-H, Tseng W-L. (Lysozyme type VI)-stabilized Au8 clusters: synthesis mechanism and application for sensing of glutathione in a single drop of blood. Small. 2012;8:1912–9.
Du Y, Yuan Z, Xu D, Cai N, He Y, Yeung ES. Polyethyleneimine solubilized luminescent Au(I)-thiolate complexes for highly sensitive and selective cyanide anion sensing. J Chin Chem Soc. 2013;60:1347–52.
Yuan Z, Cai N, Du Y, He Y, Yeung ES. Sensitive and selective detection of copper ions with highly stable polyethyleneimine-protected silver nanoclusters. Anal Chem. 2014;86:419–26.
Xu D, Wang Q, Yang T, Cao J, Lin Q, Yuan Z, et al. Polyethyleneimine capped silver nanoclusters as efficient antibacterial agents. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016;13:334.
Shojaeifard Z, Hemmateenejad B, Shamsipur M. Efficient on–off ratiometric fluorescence probe for cyanide ion based on perturbation of the interaction between gold nanoclusters and a copper(II)-phthalocyanine complex. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8:15177–86.
Zong C, Zheng LR, He W, Ren X, Jiang C, Lu L. In situ formation of phosphorescent molecular gold(I) cluster in a macroporous polymer film to achieve colorimetric cyanide sensing. Anal Chem. 2014;86:1687–92.
Lu D, Liu L, Li F, Shuang S, Li Y, Choi MMF, et al. Lysozyme-stabilized gold nanoclusters as a novel fluorescence probe for cyanide recognition. Spectrochim Acta, Part A. 2014;121:77–80.
Cheng C, Chen H-Y, Wu C-S, Meena JS, Simon T, Ko F-H. A highly sensitive and selective cyanide detection using a gold nanoparticle-based dual fluorescence–colorimetric sensor with a wide concentration range. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;227:283–90.
Rajamanikandan R, Ilanchelian M. β-Cyclodextrin protected gold nanoparticle based cotton swabs as an effective candidate for specific sensing of trace levels of cyanide. Anal Methods. 2019;11:97–104.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (2202038), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21605003 and 51877205), the State Key Laboratory of NBC Protection for Civilian (JH05-2019-02), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (buctrc201619).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All biological experiments were performed with the approval of the Human Ethics Committee, Beijing University of Chemical Technology. Informed consent was obtained from the participant included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Yang, Y., Liu, S. et al. Ratiometric and sensitive cyanide sensing using dual-emissive gold nanoclusters. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 5819–5826 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02806-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02806-2