Abstract
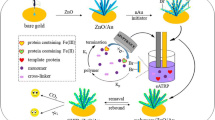
Using the surface molecular imprinting technique, a thermo-sensitive molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor was constructed for bovine hemoglobin (BHb) detection with the silanized carbon dots (CD@SiO2) as fluorescent signal, N-isopropylacrylamide as monomer sensitive to temperature, and BHb as template. The silanized carbon dots coated by the molecularly imprinted polymer (CD@SiO2@MIP) were characterized by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and fluorescence spectroscopy. Owing to the combination of the strong fluorescence sensitivity of CDs and the high selectivity of the molecular imprinting shell, the prepared sensor showed good recognition and detection performance to the target protein BHb, with a linear range of 0.31–1.55 μM and a detection limit of 1.55 μM. Furthermore, the sensor was utilized to detect the content of BHb in real urine with a recovery of 98.6–100.5%. The CD@SiO2@MIP sensors present a high potential for applications in the detection of BHb in biological systems.

Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duan L, He Q, Yan XH, Cui Y, Wang KW, Li JB. Hemoglobin protein hollow shells fabricated through covalent layer-by-layer technique. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;354:357–62.
Duan HM, Wang XJ, Wang YH, Li JB, Luo CN. Bioreceptor multi-walled carbon nanotubes@Fe3O4@SiO2-surface molecular imprinted polymer in an ultrasensitive chemiluminescent biosensor for bovine hemoglobin. RSC Adv. 2015;5:88492–9.
Wang YQ, Zhang HM, Zhou QH. Studies on the interaction of caffeine with bovine hemoglobin. Eur J Med Chem. 2009;44:2100–5.
Chen LX, Xu SF, Li JH. Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:2922–42.
Chen LX, Wang XY, Lu WH, Wu XQ, Li JH. Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2016;45:2137–211.
Wu Q, Li MN, Huang Z, Shao YM, Bai L, Zhou LC. Well-defined nanostructured core-shell magnetic surface imprinted polymers (Fe3O4@SiO2@MIPs) for effective extraction of trace tetrabromobisphenol A from water. J Ind Eng Chem. 2018;60:268–78.
Gao DM, Zhang ZP, Wu MH, Xie CG, Guan GJ, Wang DP. A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:7859–66.
Ge L, Wang SSM, Yu JH, Li NQ, Ge SG, Yan M. Molecularly imprinted polymer grafted porous Au-paper electrode for an microfluidic electro-analytical origami device. Adv Funct Mater. 2013;23:3115–23.
Ma Y, Pan PGQ, Zhang Y, Guo XZ, Zhang HQ. Narrowly dispersed hydrophilic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for efficient molecular recognition in real aqueous samples including river water, milk, and bovine serum. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2013;52:1511–4.
Xu SF, Lu HZ, Li JH, Song XL, Wang AX, Chen LX, et al. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers-capped CdTe quantum dots for the fluorescent sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:8146–54.
Saylan Y, Yilmaz F, Ozgur E, Derazshamshir A, Yavuz H, Denizli A. Molecular imprinting of macromolecules for sensor applications. Sensors. 2017;17:898–928.
Li DY, He XW, Chen Y, Li WY, Zhang YK. Novel hybrid structure silica/CdTe/molecularly imprinted polymer: synthesis, specific recognition, and quantitative fluorescence detection of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:12609–16.
Wang XY, Yu SM, Liu W, Fu LW, Wang YQ, Li JH, et al. A molecular imprinting based hybrid ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the visual determination of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Sens. 2018;3:378–85.
Yang YQ, He XW, Wang YZ, Li WY, Zhang YK. Epitope imprinted polymer coating CdTe quantum dots for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of the target protein bovine serum albumin. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;54:266–72.
Li DY, Zhang XM, Yan YJ, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK. Thermo-sensitive imprinted polymer embedded carbon dots using epitope approach. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016;79:187–92.
Zhang Z, Li JH, Wang XY, Shen DZ, Chen LX. Quantum dots based mesoporous structured imprinting microspheres for the sensitive fluorescent detection of phycocyanin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:9118–27.
Li W, Sun Y, Yang CC, Yan XM, Guo H, Fu GQ. Fabrication of surface protein-imprinted nanoparticles using a metal chelating monomer via aqueous precipitation polymerization. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:27188–96.
Bereli N, Andac M, Baydemir G, Say R, Galaev IY, Denizli A. Protein recognition via ion-coordinated molecularly imprinted supermacroporous cryogels. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1190:18–26.
Qin L, He XW, Zhang W, Li WY, Zhang YK. Macroporous thermosensitive imprinted hydrogel for recognition of protein by metal coordinate interaction. Anal Chem. 2009;81:7206–16.
Stobiecka M, Chalupa A. Modulation of plasmon-enhanced resonance energy transfer to gold nanoparticles by protein survivin channeled-shell gating. J Phys Chem B. 2015;119:13227–35.
Stobiecka M. Novel plasmonic field-enhanced nanoassay for trace detection of proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014;55:379–85.
Li H, Shao FQ, Zou SY, Yang QJ, Huang H, Feng JJ, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of N,P-doped carbon dots for fluorescent cell imaging. Microchim. Acta. 2016;183:821–6.
Wang WP, Lu YC, Huang H, Feng JJ, Chen JR, Wang AJ. Facile synthesis of water-soluble and biocompatible fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for cell imaging. Analyst. 2014;139:1692–6.
Huang H, Lv JJ, Zhou DL, Bao N. One-pot green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles as fluorescent probes for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2013;3:21691–6.
Baker SN, Baker GA. Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:6726–44.
Mao Y, Bao Y, Han DX, Li FH, Niu L. Efficient one-pot synthesis of molecularly imprinted silica nanospheres embedded carbon dots for fluorescent dopamine optosensing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2012;38:55–60.
Wang H, Yi JH, Velado D, Yu YY, Zhou SQ. Immobilization of carbon dots in molecularly imprinted microgels for optical sensing of glucose at physiological pH. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015;7:15735–45.
Zhou Y, Qu ZB, Zeng YB, Zhou TS, Shi GY. A novel composite of graphene quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer for fluorescent detection of paranitrophenol. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;52:317–23.
Liu HC, Ding L, Chen LG, Chen YH, Zhou TY, Li HY, et al. A facile, green synthesis of biomass carbon dots coupled with molecularly imprinted polymers for highly selective detection of oxytetracycline. J Ind Eng Chem. 2019;69:455–63.
Fang MY, Zhuo KL, Chen YJ, Zhao YJ, Wang JJ. Fluorescent probe based on carbon dots/silica/molecularly imprinted polymer for lysozyme detection and cell imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019;411:5799–807.
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H, et al. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2013;52:3953–7.
Stöber W, Fink A. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1968;26:62–9.
Zhang X, Yang S, Sun LQ, Luo AQ. Surface-imprinted polymer coating L-cysteine-capped ZnS quantum dots for target protein specific recognition. J Mater Sci. 2016;51:6075–85.
Yang YH, Gao MY. Preparation of fluorescent SiO2 particles with single CdTe nanocrystal cores by the reverse microemulsion method. Adv Mater. 2005;17:2354–7.
Lutz JF, Akdemir O, Hoth A. Point by point comparison of two thermosensitive polymers exhibiting a similar LCST: is the age of poly (NIPAM) over. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:13046–7.
Chen YF, Rosenzweig Z. Luminescent CdS quantum dots as selective ion probes. Anal Chem. 2002;74:5132–8.
Guo T, Deng QL, Fang GZ, Gu DH, Yang YK, Wang S. Upconversion fluorescence metal-organic frameworks thermo-sensitive imprinted polymer for enrichment and sensing protein. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;79:341–6.
Zhang W, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK. Thermo-sensitive imprinted polymer coating CdTe quantum dots for target protein specific recognition. Chem Commun. 2012;48:1757–9.
Wang XY, Yu JL, Li JH, Kang Q, Shen DZ, Chen LX. Quantum dots based imprinting fluorescent nanosensor for the selective and sensitive detection of phycocyanin: a general imprinting strategy toward proteins. Sens Actuat B-Chem. 2018;255:268–74.
Lv PP, Xie DD, Zhang ZH. Magnetic carbon dots based molecularly imprinted polymers for fluorescent detection of bovine hemoglobin. Talanta. 2018;188:145–51.
Tan L, Kang CC, Xu SY, Tang YW. Selective room temperature phosphorescence sensing of target protein using Mn-doped ZnS QDs-embedded molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013;48:216–23.
Funding
This study received financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21873026, 21573058, 21773059, 21303044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The informed consent was obtained from the healthy volunteer who provide urine sample for this study. All experiments in this study were approved by the Academic Ethics Committee of Henan Normal University, China, and have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 427 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Chen, Y., Fang, M. et al. Silanized carbon dot-based thermo-sensitive molecularly imprinted fluorescent sensor for bovine hemoglobin detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 5811–5817 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02803-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02803-5