Abstract
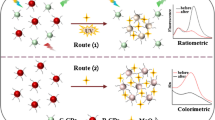
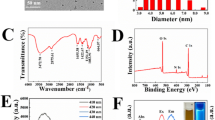
Ratiometric assays, which can effectively surmount external interference, have attracted extensive research interests. Herein, a novel ratiometric sensing platform for Hg2+ is designed based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) with two different optical signals. Under a single excitation, N-CDs have two emission peaks around 668 nm and 412 nm, which are second-order scattering and fluorescence, respectively. Upon the addition of Hg2+, the weak scattering emission at 668 nm can be increased apparently, while the strong fluorescence intensity at 412 nm is weakened. Moreover, the ratio of scattering intensity to fluorescence intensity is linearly dependent on Hg2+ concentration (0.1–10 μM and 10–30 μM, respectively), and the detection limit is 66 nM. In addition, the ratiometric sensing mechanism is investigated in detail, which is due to the combined effect of aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching and scattering enhancement. Furthermore, the developed sensing approach holds a promising application for Hg2+ detection in actual samples.

Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker SN, Baker GA. Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49(38):6726–44.
Liu HP, Ye T, Mao CD. Fluorescent carbon nanoparticles derived from candle soot. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2007;46(34):6473–5.
Huang H, Li CG, Zhu SJ, Wang HL, Chen CL, Wang ZR, et al. Histidine-derived nontoxic nitrogen-doped carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging applications. Langmuir. 2014;30(45):13542–8.
Gao ZH, Lin ZH, Chen XM, Lai ZZ, Huang ZY. Carbon dots-based fluorescent probe for trace Hg2+ detection in water sample. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;222:965–71.
Yan FY, Shi DC, Zheng TC, Yun KY, Zhou XG, Chen L. Carbon dots as nanosensor for sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ and L-cysteine by means of fluorescence “off-on” switching. Sens. Actuators, B. 2016;224:926–35.
Zhang RZ, Chen W. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;55:83–90.
Li W, Zhang HR, Zheng YJ, Chen S, Liu YL, Zhuang JL, et al. Multifunctional carbon dots for highly luminescent orange-emissive cellulose based composite phosphor construction and plant tissue imaging. Nanoscale. 2017;9(35):12976–83.
Zhu XH, Zhao TB, Nie Z, Miao Z, Liu Y, Yao SZ. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticle modulated turn-on fluorescent probes for histidine detection and its imaging in living cells. Nanoscale. 2016;8(4):2205–11.
Lu WJ, Gao YF, Jiao Y, Shuang SM, Li CZ, Dong C. Carbon nano-dots as a fluorescent and colorimetric dual-readout probe for the detection of arginine and Cu2+ and its logic gate operation. Nanoscale. 2017;9(32):11545–52.
Loo AH, Sofer Z, Bousa D, Ulbrich P, Bonanni A, Pumera M. Carboxylic carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for DNA detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2016;8(3):1951–7.
Gao XH, Cui YY, Levenson RM, Chung LWR, Nie SM. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;22:969–76.
Li HT, He XD, Kang ZH, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu JL, et al. Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49(26):4430–4.
Dong YQ, Wang RX, Li GL, Chen CQ, Chi YW, Chen GN. Polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for selective and sensitive detection of copper ions. Anal Chem. 2012;84:6220–4.
Li N, Liu SG, Fan YZ, Ju YJ, Xiao N, Luo HQ, et al. Adenosine-derived doped carbon dots: from an insight into effect of N/P co-doping on emission to highly sensitive picric acid sensing. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1013:63–70.
Qian ZS, Chai LJ, Tang C, Huang YY, Chen JR, Feng H. Carbon quantum dots-based recyclable real-time fluorescence assay for alkaline phosphatase with adenosine triphosphate as substrate. Anal Chem. 2015;87:2966–73.
Kundu A, Layek RK, Kuila A, Nandi AK. Highly fluorescent graphene oxide-poly (vinyl alcohol) hybrid: an effective material for specific Au3+ ion sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(10):5576–82.
Wee SS, Ng YH, Ng SM. Synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots via simple acid hydrolysis of bovine serum albumin and its potential as sensitive sensing probe for lead (II) ions. Talanta. 2013;116:71–6.
Zhang LB, Zhu JB, Ai J, Zhou ZX, Jia XF, Wang EK. Label-free G-quadruplex-specific fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of copper(II) ion. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;39:268–73.
Sivaraman G, Sathiyaraja V, Chellappa D. Turn-on fluorogenic and chromogenic detection of Fe(III) and its application in living cell imaging. J Lumin. 2014;145:480–5.
Nolan EM, Lippard SJ. Tools and tactics for the optical detection of mercuric ion. Chem Rev. 2008;108(9):3443–80.
Zahir F, Rizwi SJ, Haq SK, Khan RH. Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005;20(2):351–60.
Lai C, Liu SY, Zhang C, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Qin L, et al. Electrochemical aptasensor based on sulfur–nitrogen codoped ordered mesoporous carbon and thymine-Hg2+-thymine mismatch structure for Hg2+ detection. ACS Sens. 2018;3(12):2566–73.
Huang DW, Niu CG, Ruan M, Wang XY, Zeng GM, Deng CH. Highly sensitive strategy for Hg2+ detection in environmental water samples using long lifetime fluorescence quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47(9):4392–8.
Huang DL, Xue WJ, Zeng GM, Wan J, Chen GM, Huang C, et al. Immobilization of Cd in river sediments by sodium alginate modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: impact on enzyme activities and microbial community diversity. Water Res. 2016;106:15–25.
Gong XM, Huang DL, Liu YG, Zeng GM, Wang RZ, Wan J, et al. Stabilized nanoscale zerovalent iron mediated cadmium accumulation and oxidative damage of Boehmeria nivea (L.) gaudich cultivated in cadmium contaminated, Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017;51(19):11308–16.
Li J, Tu WW, Li HB, Han M, Lan YQ, Dai ZH, et al. In situ-generated nano-gold plasmon-enhanced photoelectrochemical aptasensing based on carboxylated perylene-functionalized graphene. Anal Chem. 2014;86:1306–12.
Veerakumar P, Chen SM, Madhu P, Veeramani V, Hung CT, Liu SB. Nickel nanoparticle-decorated porous carbons for highly active catalytic reduction of organic dyes and sensitive detection of Hg (II) ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(44):24810–21.
Wei TX, Dong TT, Wang ZY, Bao JC, Tu WW, Dai ZH. Aggregation of individual sensing units for signal accumulation: conversion of liquid-phase colorimetric assay into enhanced surface-tethered electrochemical analysis. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(28):8880–3.
Li JY, Fu WX, Bao JC, Wang ZY, Dai ZH. Fluorescence regulation of copper nanoclusters via DNA template manipulation toward design of a high signal-to-noise ratio biosensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(8):6965–71.
Chauhan K, Singh P, Singhal RK. New chitosan-thiomer: an efficient colorimetric sensor and effective sorbent for mercury at ultralow concentration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(47):26069–78.
Lin SM, Geng S, Li N, Lin NB, Luo HQ. D-penicillamine-templated copper nanoparticles via ascorbic acid reduction as a mercury ion sensor. Talanta. 2016;151:106–13.
Zhao JJ, Huang MJ, Zhang LL, Zou MB, Chen DX, Huang Y, et al. Unique approach to develop carbon dot-based nanohybrid near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent sensor for the detection of mercury ions. Anal Chem. 2017;89:8044–9.
Song W, Duan WX, Liu YH, Ye ZJ, Chen YL, Chen HL, Qi SD, Wu J, Liu D, Xiao LH, Ren CL, Chen XG. Ratiometric detection of intracellular lysine and pH with one-pot synthesized dual emissive carbon dots, Anal. Chem. 2017;89: 13626–33.
Chen JQ, Xue SF, Chen ZH, Zhang SQ, Shi GY, Zhang M. GelRed/[G3T]5/Tb3+ hybrid: a novel label-free ratiometric fluorescent probe for H2O2 and oxidase-based visual biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;100:526–32.
Ren W, Zhang Y, Chen HG, Gao ZF, Li NB, Luo HQ. Ultrasensitive label-free resonance Rayleigh scattering aptasensor for Hg2+ using Hg2+-triggered exonuclease III-assisted target recycling and growth of G-wires for signal amplification. Anal Chem. 2016;88:1385–90.
Huang CZ, Li KA, Tong SY. Determination of nucleic acids by a resonance light-scattering technique with alpha, beta, gamma, delta-tetrakis[4-(trimothylammoniumyl)phenyl]porphine. Anal Chem. 1996;68(13):2259–63.
Zhang WJ, Liu SG, Han L, Luo HQ, Li NB. A ratiometric fluorescent and colorimetric dual-signal sensing platform based on N-doped carbon dots for selective and sensitive detection of copper (II) and pyrophosphate ion. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2019;283:215–21.
Wang C, Ling L, Yao YG, Song QJ. One-step synthesis of fluorescent smart thermoresponsive copper clusters: a potential nanothermometer in living cells. Nano Res. 2015;8(6):1975–86.
Xu JG, Wang ZB. Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, third edition, 2006 75–77.
Bourlinos AB, Trivizas G, Karakassides MA, Baikousi M, Kouloumpis A, Gournis D, et al. Green and simple route toward boron doped carbon dots with significantly enhanced non-linear optical properties. Carbon. 2015;83:173–9.
Gong PW, Yang ZG, Wei H, Wang ZF, Hou KM, Wang JG, et al. To lose is to gain: effective synthesis of water-soluble graphene fluoroxide quantum dots by sacrificing certain fluorine atoms from exfoliated fluorinated graphene. Carbon. 2015;83:152–61.
Shi BF, Su YB, Zhang LL, Huang MJ, Liu RJ, Zhao SL. Nitrogen and phosphorus Codoped carbon nanodots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of Fe3+ in human serum and living cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(17):10717–25.
Zou SY, Hou CJ, Fa HB, Zhang L, Ma Y, Dong L, et al. An efficient fluorescent probe for fluazinam using N, S co-doped carbon dots from L-cysteine. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;239:1033–41.
Yang JS, Wu HX, Yang P, Hou CJ, Huo DQ. A high performance N-doped carbon quantum dots/5,5′-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) fluorescent sensor for biothiols detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;255:3179–86.
Atchudana R, Edisona TNJI, Aseerb KR, Perumal S, Karthika N, Lee YR. Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots derived from Phyllanthus acidus utilized as a fluorescent probe for label-free selective detection of Fe3+ ions, live cell imaging and fluorescent ink. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018;99:303–11.
Du XJ, Jiang D, Liu Q, Zhu GB, Mao HP, Wang K. Fabrication of graphene oxide decorated with nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and its enhanced electrochemiluminescence for ultrasensitive detection of pentachlorophenol. Analyst. 2015;140(4):1253–9.
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA. Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science. 1997;277(5329):1078–81.
Yang X, Yang MX, Pang B, Vara M, Xia YN. Gold nanomaterials at work in biomedicine. Chem Rev. 2015;115(19):10410–88.
Guo LH, Xu Y, Ferhan AR, Chen GN, Kim DH. Oriented gold nanoparticle aggregation for colorimetric sensors with surprisingly high analytical figures of merit. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135(33):12338–45.
Deng RR, Xie XJ, Vendrell M, Chang YT, Liu XG. Intracellular glutathione detection using MnO2-nanosheet-modified upconversion nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(50):20168–71.
Gogoi A, Mukherjee SP, Ramesh A, Das G. Aggregation-induced emission active metal-free chemosensing platform for highly selective turn-on sensing and bioimaging of pyrophosphate anion. Anal Chem. 2015;87:6974–9.
Funding
This work received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21675131) and the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (No. CSTC-2015jcyjB50001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 405 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W.J., Liu, S.G., Zhang, X.Y. et al. Ratiometric assay of mercury ion based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots with two different optical signals: second-order scattering and fluorescence. Anal Bioanal Chem 412, 4375–4382 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02676-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02676-8