Abstract
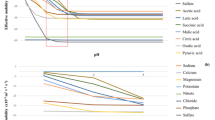
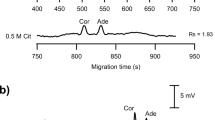
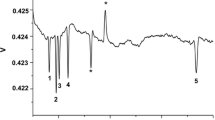
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is excellent at separating all the ions in a sample but is rarely used as a result of its detection issue and easy loss of very fast ions by common one-end injection methods. Herein we propose a newly developed method aimed at simultaneous determination of positive and negative ions with a home-made CE device, featuring bi-end injection and contactless conductivity detection at the middle. By simply using 2.5 M acetic acid as a running buffer, the method can separate 37 ions (3 inorganic anions, 8 inorganic cations, 10 biogenic amines, and 16 amino acids) per run, with linearity between 10 and 2000 μM (R2 > 0.99), limit of detection of 1.0–16.6 μM, and limit of quantification of 2.3–31.7 μM. The recovery measured by spiking standards into samples at high, middle, and low levels was between 73% and 110%. The intra- and interday repeatability of the 37 analytes ranged from 0.69% to 8.97% and from 0.68% to 11.04%, respectively. The proposed method was evaluated by analysis of 21 beers and, in addition to acquiring the concentration information, the brands of the tested beers were distinguished. This method is of high throughput, fast, and cost-effective. It could be a promising tool for ionomic analysis.

ᅟ




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nord LI, Vaag P, Duus JØ. Quantification of organic and amino acids in beer by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2004;76(16):4790–8.
Cortacero-Ramı́Rez S, Segura-Carretero A, Cruces-Blanco C, Fernández-Gutiérrez A. Analysis of beer components by capillary electrophoretic methods. Trends Analyt Chem. 2003;22(7):440–55.
Grosse Y, Baan R, Straif K, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Cogliano V. Carcinogenicity of nitrate, nitrite, and cyanobacterial peptide toxins. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(8):628–9.
Sindelar JJ, Milkowski AL. Human safety controversies surrounding nitrate and nitrite in the diet. Nitric Oxide. 2012;26(4):259–66.
Redruello B, Ladero V, Del Rio B, Fernández M, Martín MC, Alvarez MA. A UHPLC method for the simultaneous analysis of biogenic amines, amino acids and ammonium ions in beer. Food Chem. 2017;217:117–24.
Redruello B, Ladero V, Cuesta I, Álvarez-Buylla JR, Martín MC, Fernández M, et al. A fast, reliable, ultra high performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of amino acids, biogenic amines and ammonium ions in cheese, using diethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate as a derivatising agent. Food Chem. 2013;139(1–4):1029–35.
Gómez-Alonso S, Hermosín-Gutiérrez I, García-Romero E. Simultaneous HPLC analysis of biogenic amines, amino acids, and ammonium ion as aminoenone derivatives in wine and beer samples. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55(3):608–13.
Pereira V, Pontes M, Câmara JS, Marques JC. Simultaneous analysis of free amino acids and biogenic amines in honey and wine samples using in loop orthophthalaldeyde derivatization procedure. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1189(1–2):435–43.
Parente E, Martuscelli M, Gardini F, Grieco S, Crudele M, Suzzi G. Evolution of microbial populations and biogenic amine production in dry sausages produced in southern Italy. J Appl Microbiol. 2001;90(6):882–91.
Eerola S, Sagués A-XR, Lilleberg L, Aalto H. Biogenic amines in dry sausages during shelf-life storage. Z Lebensm Forsch A. 1997;205(5):351–5.
Hernández-Jover T, Izquierdo-Pulido M, Veciana-Nogués MT, Mariné-Font A, Vidal-Carou MC. Biogenic amine and polyamine contents in meat and meat products. J Agric Food Chem. 1997;45(6):2098–102.
Bisson A, Anslyn E. Optical sensing of inorganic anions employing a synthetic receptor and ionic colorimetric dyes. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1999;2(6):1111–4.
Cui L, Wu J, Ju H. Electrochemical sensing of heavy metal ions with inorganic, organic and bio-materials. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;63:276–86.
Arienzo M, Capasso R. Analysis of metal cations and inorganic anions in olive oil mill waste waters by atomic absorption spectroscopy and ion chromatography. Detection of metals bound mainly to the organic polymeric fraction. J Agric Food Chem. 2000;48(4):1405–10.
Harwood JJ, Wen S. Analysis of organic and inorganic selenium anions by ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. J Chromatogr A. 1997;788(1–2):105–11.
Haddad PR, Jackson PE, Shaw MJ. Developments in suppressor technology for inorganic ion analysis by ion chromatography using conductivity detection. J Chromatogr A. 2003;1000(1–2):725–42.
Meng H-B, Wang T-R, Guo B-Y, Hashi Y, Guo C-X, Lin J-M. Simultaneous determination of inorganic anions and cations in explosive residues by ion chromatography. Talanta. 2008;76(2):241–5.
Ding M-Y, Suzuki Y, Koizumi H. Simultaneous determination of organic acids, inorganic anions and cations in beverages by ion chromatography with a mixed-bed stationary phase of anion and cation exchangers. Analyst. 1995;120(6):1773–7.
Sarazin C, Delaunay N, Varenne A, Vial J, Costanza C, Eudes V, et al. Identification and determination of inorganic anions in real extracts from pre-and post-blast residues by capillary electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217(44):6971–8.
Kutlán D, Molnár-Perl I. New aspects of the simultaneous analysis of amino acids and amines as their o-phthaldialdehyde derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography: analysis of wine, beer and vinegar. J Chromatogr A. 2003;987(1–2):311–22.
Rovio S, Sirén K, Sirén H. Application of capillary electrophoresis to determine metal cations, anions, organic acids, and carbohydrates in some Pinot Noir red wines. Food Chem. 2011;124(3):1194–200.
Unterholzner V, Macka M, Haddad PR, Zemann A. Simultaneous separation of inorganic anions and cations using capillary electrophoresis with a movable contactless conductivity detector. Analyst. 2002;127(6):715–8.
Sáiz J, Duc MT, Koenka IJ, Martín-Alberca C, Hauser PC, García-Ruiz C. Concurrent determination of anions and cations in consumer fireworks with a portable dual-capillary electrophoresis system. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1372:245–52.
Mai TD, Hauser PC. Simultaneous separations of cations and anions by capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection employing a sequential injection analysis manifold for flexible manipulation of sample plugs. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1267:266–72.
Agra-Gutiérrez C, Hardcastle JL, Ball JC, Compton RG. Anodic stripping voltammetry of copper at insonated glassy carbon-based electrodes: application to the determination of copper in beer. Analyst. 1999;124(7):1053–7.
Mayer H, Marconi O, Floridi S, Montanari L, Fantozzi P. Determination of Cu(II) in beer by derivative potentiometric stripping analysis. J Inst Brew. 2003;109(4):332–6.
Llobat-Estelles M, Mauri-Aucejo A, Marin-Saez R. Detection of bias errors in ETAAS: determination of copper in beer and wine samples. Talanta. 2006;68(5):1640–7.
Huang K-J, Jin C-X, Song S-L, Wei C-Y, Liu Y-M, Li J. Development of an ionic liquid-based ultrasonic-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction method for sensitive determination of biogenic amines: application to the analysis of octopamine, tyramine and phenethylamine in beer samples. J Chromatogr B. 2011;879(9–10):579–84.
Torrea D, Ancín C. Content of biogenic amines in a Chardonnay wine obtained through spontaneous and inoculated fermentations. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50(17):4895–9.
He L, Xu Z, Hirokawa T, Shen L. Simultaneous determination of aliphatic, aromatic and heterocyclic biogenic amines without derivatization by capillary electrophoresis and application in beer analysis. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1482:109–14.
Izquierdo-Pulido M, Hernández-Jover T, Mariné-Font A, Vidal-Carou MC. Biogenic amines in European beers. J Agric Food Chem. 1996;44(10):3159–63.
Charalambous G. Involatile constituents of beer. Brewing Sci. 1981;2:167–254.
Klampfl CW. Analysis of organic acids and inorganic anions in different types of beer using capillary zone electrophoresis. J Agric Food Chem. 1999;47(3):987–90.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21727809, 21475136, 21235007 & 21621062) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-SLH034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is no conflict of interest in this article.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection New Insights into Analytical Science in China with guest editors Lihua Zhang, Hua Cui, and Qiankun Zhuang.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 333 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Guo, Z. & Chen, Y. A bi-end injection capillary electrophoresis method for simultaneous determination of 37 cations and anions in beers. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 4113–4121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1507-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1507-7