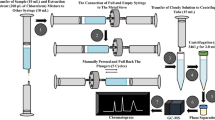
Abstract
A new UHPLC-UV method has been developed for the simultaneous analysis of seven alkaloids [ajmaline (1), yohimbine (2), corynanthine (3), ajmalicine (4), serpentine (5), serpentinine (6), and reserpine (7)] from the root samples of Rauwolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz. The chromatographic separation was achieved using a reversed phase C18 column with a mobile phase of water and acetonitrile, both containing 0.05 % formic acid. The seven compounds were completely separated within 8 min at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min with a 2-μL injection volume. The method is validated for linearity, accuracy, repeatability, limits of detection (LOD), and limits of quantification (LOQ). Seven plant samples and 21 dietary supplements claiming to contain Rauwolfia roots were analyzed and content of total alkaloids (1–7) varied, namely, 1.57–12.1 mg/g dry plant material and 0.0–4.5 mg/day, respectively. The results indicated that commercial products are of variable quality. The developed analytical method is simple, economic, fast, and suitable for quality control analysis of Rauwolfia samples and commercial products. The UHPLC-QToF-mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization (ESI) interface method is described for the confirmation and characterization of alkaloids from plant samples. This method involved the detection of [M + H]+ or M+ ions in the positive mode.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
(1999) WHO monographs on selected medicinal plants. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland Vol 1, pp. 221–230
Plummer AJ, Earl A, Schneider JA, Trapold J, Barrett W (1954) Pharmacology of Rauwolfia alkaloids, including reserpine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 59:8–21. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1954.tb45914.x
Wilkins RW, Judson WE (1953) The use of Rauwolfia serpentina in hypertensive patients. N Engl J Med 248(2):48–53
Bhatia BB (1942) On the use of Rauwolfia serpentina in high blood pressure. J Indian Med Assoc XI9, p. 262
Vakil RJ (1949) A clinical trial of Rauwolfia serpentina in essential hypertension. Br Heart J 11(4):350–355
Phillips DD, Chadha MS (1955) The alkaloids of Rauwolfia serpentina Benth. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc (Baltim) 44(9):553–567
Mehrotra S, Goel M, Srivastava V, Rahman L (2015) Hairy root biotechnology of Rauwolfia serpentina: a potent approach for the production of pharmaceutically important terpenoid indole alkaloids. Biotechnol Lett 37(2):253–263. doi:10.1007/s10529-014-1695-y
Bein HJ (1956) The pharmacology of Rauwolfia. Pharmacol Rev 8(3):435–483
Lucas RA (1963) The chemistry and pharmacology of the Rauwolfia alkaloids. In: Ellis GP, West GB (eds) Progress in medicinal chemistry, vol Volume 3. Elsevier, pp 146–186. doi:10.1016/S0079-6468(08)70118-8
Iwu MM, Court WE (1982) Stem bark alkaloids of Rauwolfia vomitoria. Planta Med 45(06):105–111. doi:10.1055/s-2007-971256
Schlitter E (1965) The alkaloids-chemistry and physiology, vol VIII. Academic Press, New York, pp 287–334
Robinson JW (1977) Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Rauwolfia alkaloids by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) utilizing the fluorescence detector. EDRO SARAP Res Tech Rep 2:23–61
Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (1985) Goodman and Gilman's, The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 7th edn. Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., New York, p 209
Court WE, Habib MS (1973) Separation of Rauwolfia alkaloids by thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr A 80. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)85354-1
Le Xuan P, Munier RL, Meunier S (1980) Two-dimensional separations and behaviour of Rauwolfia, Corynanthe and Pseudocinchona alkaloids on unmodified silica gel. Chromatographia 13(11):693–697. doi:10.1007/BF02303439
Klyushnichenko VE, Yakimov SA, Tuzova TP, Syagailo YV, Kuzovkina IN, Wulfson AN, Miroshnikov AI (1995) Determination of indole alkaloids from R. serpentina and R. vomitoria by high-performance liquid chromatography and high-performance thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr A 704(2):357–362. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(95)00082-X
Panwar GS, Guru SK (2011) Alkaloid profiling and estimation of reserpine in Rauwolfia serpentina plant by TLC, HP-TLC and HPLC. Asian J Plant Sci 10(8):393–400. doi:10.3923/ajps.2011.393.400
Gupta MM, Srivastava A, Tripathi AK, Misra H, Verma RK (2006) Use of HPTLC, HPLC, and densitometry for qualitative separation of indole alkaloids from Rauvolfia serpentina roots. J Planar Chromatogr-Mod TLC 19(110):282–287. doi:10.1556/JPC.19.2006.4.5
Srivastava A, Tripathi AK, Pandey R, Verma RK, Gupta MM (2006) Quantitative determination of reserpine, ajmaline, and ajmalicine in Rauvolfia serpentina by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr Sci 44(9):557–560. doi:10.1093/chromsci/44.9.557
Cieri UR (1998) Determination of reserpine and rescinnamine in Rauwolfia serpentina powders and tablets: collaborative study. J AOAC Int 81(2):373–380
Gerasimenko I, Sheludko Y, Unger M, Stockigt J (2001) Development of an efficient system for the separation of indole alkaloids by high performance liquid chromatography and its applications. Phytochem Anal 12(2):96–103. doi:10.1002/pca.567
Stockigt D, Unger M, Belder D, Stockigt J (1997) Analysis of Rauwolfia alkaloids employing capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Nat Prod Lett 9(4):265–272. doi:10.1080/10575639708043638
Madhusudanan KP, Banerjee S, Khanuja SPS, Chattopadhyay SK (2008) Analysis of hairy root culture of Rauvolfia serpentina using direct analysis in real time mass spectrometric technique. Biomed Chromatogr 22(6):596–600. doi:10.1002/bmc.974
Hong B, Li W, Song A, Zhao C (2013) Determination of indole alkaloids and highly volatile compounds in Rauvolfia verticillata by HPLC-UV and GC-MS. J Chromatogr Sci 51(10):926–930. doi:10.1093/chromsci/bms191
Hong B, Cheng W, Wu J, Zhao C (2010) Screening and identification of many of the compounds present in Rauvolfia verticillata by use of high-pressure LC and quadrupole TOF MS. Chromatographia 72(9–10):841–847. doi:10.1365/s10337-010-1760-1
Habib MS, Court WE (1974) Separation and identification of microquantities of Rauwolfia alkaloids. Planta Med 25(4):331–341. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1097952
Singh DK, Srivastava B, Sahu A (2004) Spectrophotometric determination of Rauwolfia alkaloids: estimation of reserpine in pharmaceuticals. Anal Sci 20(3):571–573. doi:10.2116/analsci.20.571
Gupta S, Shanker K, Srivastava SK (2012) HPTLC method for the simultaneous determination of four indole alkaloids in Rauwolfia tetraphylla: a study of organic/green solvent and continuous/pulse sonication. J Pharm Biomed Anal 66:33–39. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2012.02.018
Verma RK, Gupta S, Gupta MM, Srivastava SK (2012) A simple isocratic HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of antipsychotic indole alkaloids in Rauwolfia tetraphylla. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 35(7):937–950. doi:10.1080/10826076.2011.615086
Kumar S, Bajpai V, Singh A, Bindu S, Srivastava M, Rameshkumar KB, Kumar B (2015) Rapid fingerprinting of Rauwolfia species using direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry combined with principal component analysis for their discrimination. Anal Methods 7(14):6021–6026. doi:10.1039/C5AY01249J
Karioti A, Giocaliere E, Guccione C, Pieraccini G, Gallo E, Vannacci A, Bilia AR (2014) Combined HPLC-DAD–MS, HPLC–MSn and NMR spectroscopy for quality control of plant extracts: The case of a commercial blend sold as dietary supplement. J Pharm Biomed Anal 88:7–15. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.040
ICH (2005) Validation of analytical procedures: text and methodology, ICH harmonized tripartite guidelines
Iwu MM, Court WE (1977) Root alkaloids of Rauwolfia vomitoria afz. Planta Med 32(1):88–99
Acknowledgments
This research is supported in part by “Science Based Authentication of Dietary Supplements” funded by the Food and Drug Administration grant number 1U01FD004246-3 and the US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Specific Cooperative Agreement No. 58-6408-02-1-603-04. The authors would like to thank Dr. Jon Parcher, Research Professor Emeritus at The University of Mississippi for providing support and valuable suggestions in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sagi, S., Avula, B., Wang, YH. et al. Quantification and characterization of alkaloids from roots of Rauwolfia serpentina using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 177–190 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9093-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9093-4