Abstract
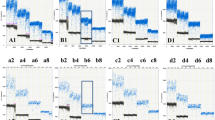
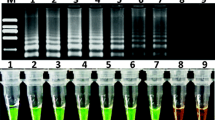
Reference materials are important in accurate analysis of genetically modified organism (GMO) contents in food/feeds, and development of novel reference plasmid is a new trend in the research of GMO reference materials. Herein, we constructed a novel multi-targeting plasmid, pSOY, which contained seven event-specific sequences of five GM soybeans (MON89788-5', A2704-12-3', A5547-127-3', DP356043-5', DP305423-3', A2704-12-5', and A5547-127-5') and sequence of soybean endogenous reference gene Lectin. We evaluated the specificity, limit of detection and quantification, and applicability of pSOY in both qualitative and quantitative PCR analyses. The limit of detection (LOD) was as low as 20 copies in qualitative PCR, and the limit of quantification (LOQ) in quantitative PCR was 10 copies. In quantitative real-time PCR analysis, the PCR efficiencies of all event-specific and Lectin assays were higher than 90 %, and the squared regression coefficients (R2) were more than 0.999. The quantification bias varied from 0.21 % to 19.29 %, and the relative standard deviations were from 1.08 % to 9.84 % in simulated samples analysis. All the results demonstrated that the developed multi-targeting plasmid, pSOY, was a credible substitute of matrix reference materials, and could be used as a reliable reference calibrator in the identification and quantification of multiple GM soybean events.

One multi-targets plasmid, pSOY, that can be used as calibrator in the detection of the five GM soybean Events




Similar content being viewed by others
References
James C (2013) Global status of commercialize biotech/GM crops: 2013. ISAAA Briefs 46/ Available at; http://www.isaaa.org/resources/publications/briefs/46/. Accessed 20 Nov 2014
Kamle S, Ali S (2013) Genetically modified crops: detection strategies and biosafety issues. Gene 522(2):123–132
Takabatake R, Onishi M, Koiwa T, Futo S, Minegishi Y, Akiyama H, Teshima R, Furui S, Kitta K (2010) Establishment and evaluation of event-specific quantitative PCR method for genetically modified soybean MON89788. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 51(5):242–246
European Commission Regulation (EC) 1829/2003 and 1830/2003. Official J Eur Communities: Legislation 268:1–28
Carter CA, Gruere GP (2003) International approaches to the labeling of genetically modified foods. Choices 18(2):1–4
Order 10 (2002) Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing
James D, Schmidt A, Wall E, Green M, Masri S (2003) Reliable detection and identification of genetically modified maize, soybean, and canola by multiplex PCR analysis. J Agric Food Chem 51(20):5829–5834
Ciabatti I, Froiio A, Gatto F, Amaddeo D, Marchesi U (2005) In-house validation and quality control of real-time PCR methods for GMO detection: a practical approach. Dev Biol (Basel) 126:79–86
Kiddle G, Hardinge P, Buttigieg N, Gandelman O, Pereira C, McElqunn CJ, Rizzoli M, Jackson R, Appleton N, Moore C, Tisi LC, Murray JA (2012) GMO detection using a bioluminescent real time reporter (BART) of loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) suitable for field use. BMC Biotechnol 12:15
Prins TW, Van Dijk JP, Beenen HG, Van H, Voorhuijzen MM, Schoen CD, Aarts HJ, Kok EJ (2008) Optimized padlock probe ligation and microarray detection of multiple (non-authorized) GMOs in a single reaction. BMC Genomics 9:584
Fantozzi A, Ermolli M, Marini M, Scotti D, Balla B, Querci M, Lanqrell SR, Van den Eede G (2007) First application of a microsphere-based immunoassay to the detection of genetically modified organisms (GMOs): quantification of Cry1Ab protein in genetically modified maize. J Agric Food Chem 55(4):1071–1076
Ahmed FE (2002) Detection of genetically modified organisms in foods. Trends Biotechnol 20(5):215–223
Wang R, Minunni M, Tombelli S, Mascini M (2004) A new approach for the detection of DNA sequences in amplified nucleic acids by a surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 20(3):598–605
Corbisier P, Broeders S, Charels D, Trapmann S, Vincent S, Emons H (2007) Certification of plasmid DNA containing MON810 maize DNA fragments: Certified reference materials ERM-AD413. EC Certification Report 1–31
Publications Office (2011) Certification of Plasmid DNA Containing NK603 Maize DNA Fragments: Certified Reference Material ERM®-AD415
Charels D, Broeders S, Corbisier P, Trapmann S, Schimmel H, Emons H (2007) Toward metrological traceability for DNA fragment ratios in GM quantification. 3. Suitability of DNA calibrants studied with a MON 810 corn model. J Agric Food Chem 55(9):3268–3274
Trapmann S, Schimmel H, Kramer GN, Van den Eede G, Pauwels J (2002) Production of certified reference materials for the detection of genetically modified organisms. J AOAC Int 85(3):775–779
Toyota A, Akiyama H, Sugimura M, Watanabe T, Kikuchi H, Hino A, Esaka M, Maitani T (2006) Quantification of genetically modified soybeans using a combination of a capillary-type real-time PCR system and a plasmid reference standard. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70(4):821–827
Kuribara H, Shindo Y, Matsuoka T, Takubo K, Futo S, Aoki N, Hirao T, Akiyama H, Goda Y, Toyoda M, Hino A (2002) Novel reference molecules for quantitation of genetically modified maize and soybean. J AOAC Int 85(5):1077–1089
Yang L, Guo J, Pan A, Zhang H, Zhang K, Wang Z, Zhang D (2007) Event-specific quantitative detection of nine genetically modified maizes using one novel standard reference molecule. J Agric Food Chem 55(1):15–24
Wang X, Chen X, Xu J, Wang P, Shen W (2014) Multiplex event-specific qualitative PCR for detecting three transgenic rice lines and application of a standard plasmid as a quantitative reference molecule. Anal Biochem 464:1–8
Liu J, Guo J, Zhang H, Li N, Yang L, Zhang D (2009) Development and in-house validation of the event-specific polymerase chain reaction detection methods for genetically modified soybean MON89788 based on the cloned integration flanking sequence. J Agric Food Chem 57(22):10524–10530
Li X, Pan L, Li J, Zhang Q, Zhang S, Lv R, Yang L (2011) Establishment and application of event-specific polymerase chain reaction methods for two genetically modified soybean events, A2704-12 and A5547-127. J Agric Food Chem 59(24):13188–13194
Xu W, Zhang N, Luo Y, Zhai Z, Shang Y, Yan X, Zheng J, Huang K (2011) Establishment and evaluation of event-specific qualitative and quantitative PCR method for genetically modified soybean DP-356043-5. Eur Food Res Technol 233(4):685–695
Definition of minimum performance requirements for analytical methods of GMO testing; ENGL; Available at: http://gmo-crl.jrc.it/doc/Method%20requirements.pdf. Accessed 20 Nov 2014
Meng Y, Liu X, Wang S, Zhang D, Yang L (2011) Applicability of plasmid calibrant pTC1507 in quantification of TC1507 maize: an interlaboratory study. J Agric Food Chem 60(1):23–28
Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results (1994) International Standard (ISO): 5725. Available at: http://www.iso.org/iso/iso_catalogue/catalogue_tc/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=11833. Accessed 20 Nov 2014
Wang X, Tang Q, Dong L, Dong Y, Su Y, Jia S, Wang Z (2014) Construction of a standard reference plasmid containing seven target genes for the detection of transgenic cotton. Plasmid 74:39–44
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Transgenic Plant Special Fund (2014ZX08012-003 and 2014ZX08012001-007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471670), and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Liqun Pi and Xiang Li contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pi, L., Li, X., Cao, Y. et al. Development and application of a multi-targeting reference plasmid as calibrator for analysis of five genetically modified soybean events. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 2877–2886 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8517-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8517-5