Abstract
Rationale
Methamphetamine addiction is a persistent and intractable pathological learning and memory, whereas no approved therapeutics is available. However, few attentions have been paid to how associative learning participates in the formation of intractable memory related to drug addiction
Objectives and methods
To investigate the role of associative learning in methamphetamine addiction and the underlying neurobiological mechanism, methamphetamine self-administration, oral sucrose self-administration, chemogenetic neuromanipulation, and fiber photometry in mice were performed in this study.
Results
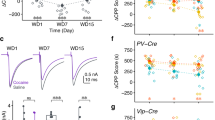
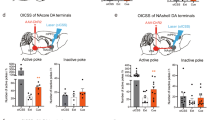
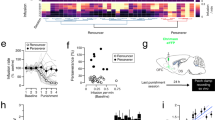
We reported that associative learning increased methamphetamine-induced self-administration, but not oral sucrose self-administration. In addition, the enhancement of methamphetamine-induced self-administration was independent of more methamphetamine consumption, and remained with higher drug-taking and motivation in the absence of visual cues, suggesting the direct effects of the associative learning that enhanced methamphetamine-induced self-administration. Moreover, chemogenetic inactivation of the secondary visual cortex (V2) reduced the enhancement of the drug-taking induced by associative learning but did not alter sucrose-taking. Further fiber photometry of V2 neurons demonstrated that methamphetamine-associative learning elicits V2 neuron excitation, and sucrose-associative learning elicits V2 neuron inhibition.
Conclusions
Therefore, this study reveals the neurobiological mechanism of V2 excitability underlying how associative learning participates in the formation of intractable memory related to drug addiction, and gives evidence to support V2 as a promising target for stimulation therapy for methamphetamine addiction.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets from this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
References
Alarcón DE, Delamater AR (2019) Outcome-specific Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer (PIT) with alcohol cues and its extinction. Alcohol 76:131–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.09.003
Amodeo LR, Jennings SD, Mulholland PJ, Ehlers CL (2021) Chronic intermittent ethanol during adolescence and adulthood alters dendritic spines in the primary motor and visual cortex in rats. Alcohol 97:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2021.09.032
Bakin JS, Nakayama K, Gilbert CD (2000) Visual responses in monkey areas V1 and V2 to three-dimensional surface configurations. J Neurosci 20:8188–98. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.20-21-08188.2000
Bender BN, Torregrossa MM (2020) Molecular and circuit mechanisms regulating cocaine memory. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:3745–3768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03498-8
Caprioli D, Venniro M, Zhang M, Bossert JM, Warren BL, Hope BT, Shaham Y (2017) Role of Dorsomedial Striatum Neuronal Ensembles in Incubation of Methamphetamine Craving after Voluntary Abstinence. J Neurosci 37:1014–1027. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3091-16.2016
Chen Y, Wang G, Zhang W, Han Y, Zhang L, Xu H, Meng S, Lu L, Xue Y, Shi J (2022) An orbitofrontal cortex-anterior insular cortex circuit gates compulsive cocaine use. Sci Adv 8:eabq5745 https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abq5745
Degni LAE, Dalbagno D, Starita F, Benassi M, di Pellegrino G, Garofalo S (2022) General Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer in humans: Evidence from Bayesian inference. Front Behav Neurosci 16:945503. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2022.945503
Depoortere RY, Li DH, Lane JD, Emmett-Oglesby MW (1993) Parameters of self-administration of cocaine in rats under a progressive-ratio schedule. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45:539–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(93)90503-l
Fuchs RA, Evans KA, Parker MP, See RE (2004) Differential involvement of orbitofrontal cortex subregions in conditioned cue-induced and cocaine-primed reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. J Neurosci 24:6600–10. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1924-04.2004
Gao Z, Chen L, Fan R, Lu W, Wang D, Cui S, Huang L, Zhao S, Guan S, Zhu Y, Wang JH (2016) Associations of Unilateral Whisker and Olfactory Signals Induce Synapse Formation and Memory Cell Recruitment in Bilateral Barrel Cortices: Cellular Mechanism for Unilateral Training Toward Bilateral Memory. Front Cell Neurosci. 10:285. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00285
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND (2002) Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry 159:1642–52. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.159.10.1642
Hanlon CA, Dowdle LT, Naselaris T, Canterberry M, Cortese BM (2014) Visual cortex activation to drug cues: a meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging papers in addiction and substance abuse literature. Drug Alcohol Depend 143:206–12
Hirokawa J, Bosch M, Sakata S, Sakurai Y, Yamamori T (2008) Functional role of the secondary visual cortex in multisensory facilitation in rats. Neuroscience 153:1402–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.01.011
Huang S, Zhang Z, Dai Y, Zhang C, Yang C, Fan L, Liu J, Hao W, Chen H (2018) Craving Responses to Methamphetamine and Sexual Visual Cues in Individuals With Methamphetamine Use Disorder After Long-Term Drug Rehabilitation. Front Psychiatry 9:145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00145
Huang Y, Ceceli AO, Kronberg G, King S, Malaker P, Parvaz MA, Alia-Klein N, Garland EL, Goldstein RZ (2023) Association of Cortico-Striatal Engagement During Cue Reactivity, Reappraisal, and Savoring of Drug and Non-Drug Stimuli With Craving in Heroin Addiction. Am J Psychiatry appiajp20220759. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.20220759
Jasinska AJ, Stein EA, Kaiser J, Naumer MJ, Yalachkov Y (2014) Factors modulating neural reactivity to drug cues in addiction: a survey of human neuroimaging studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 38:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.10.013
Kane L, Venniro M, Quintana-Feliciano R, Madangopal R, Rubio FJ, Bossert JM, Caprioli D, Shaham Y, Hope BT, Warren BL (2021) Fos-expressing neuronal ensemble in rat ventromedial prefrontal cortex encodes cocaine seeking but not food seeking in rats. Addict Biol 26:e12943. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12943
Keiflin R, Janak PH (2015) Dopamine Prediction Errors in Reward Learning and Addiction: From Theory to Neural Circuitry. Neuron 88:247–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.08.037
Kober H, Lacadie CM, Wexler BE, Malison RT, Sinha R, Potenza MN (2016) Brain Activity During Cocaine Craving and Gambling Urges: An fMRI Study. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:628–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2015.193
Lamb RJ, Schindler CW, Pinkston JW (2016) Conditioned stimuli’s role in relapse: preclinical research on Pavlovian-Instrumental-Transfer. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 233:1933–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4216-y
LeBlanc KH, Ostlund SB, Maidment NT (2012) Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer in cocaine seeking rats. Behav Neurosci 126:681–9. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029534
Li Q, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li W, Yang W, Zhu J, Wu N, Chang H, Zheng Y, Qin W, Zhao L, Yuan K, Liu J, Wang W, Tian J (2012) Craving correlates with mesolimbic responses to heroin-related cues in short-term abstinence from heroin: an event-related fMRI study. Brain Res 1469:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.06.024
Liu D, Deng J, Zhang Z, Zhang ZY, Sun YG, Yang T, Yao H (2020) Orbitofrontal control of visual cortex gain promotes visual associative learning. Nat Commun 11:2784. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16609-7
Lu J, Zhang Z, Yin X, Tang Y, Ji R, Chen H, Guang Y, Gong X, He Y, Zhou W, Wang H, Cheng K, Wang Y, Chen X, Xie P, Guo ZV (2022) An entorhinal-visual cortical circuit regulates depression-like behaviors. Mol Psychiatry 27:3807–3820. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01540-8
Moorman DE, Aston-Jones G (2015) Prefrontal neurons encode context-based response execution and inhibition in reward seeking and extinction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:9472–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1507611112
Nagy AJ, Takeuchi Y, Berényi A (2018) Coding of self-motion-induced and self-independent visual motion in the rat dorsomedial striatum. PLoS Biol 16:e2004712. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2004712
Palmatier MI, Evans-Martin FF, Hoffman A, Caggiula AR, Chaudhri N, Donny EC, Liu X, Booth S, Gharib M, Craven L, Sved AF (2006) Dissociating the primary reinforcing and reinforcement-enhancing effects of nicotine using a rat self-administration paradigm with concurrently available drug and environmental reinforcers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0183-4
Perry CJ, Zbukvic I, Kim JH, Lawrence AJ (2014) Role of cues and contexts on drug-seeking behaviour. Br J Pharmacol 171:4636–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12735
Peters J, LaLumiere RT, Kalivas PW (2008) Infralimbic prefrontal cortex is responsible for inhibiting cocaine seeking in extinguished rats. J Neurosci 28:6046–53. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1045-08.2008
Prévost C, Liljeholm M, Tyszka JM, O’Doherty JP (2012) Neural correlates of specific and general Pavlovian-to-Instrumental Transfer within human amygdalar subregions: a high-resolution fMRI study. J Neurosci 32:8383–90. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.6237-11.2012
Rosen LG, Sun N, Rushlow W, Laviolette SR (2015) Molecular and neuronal plasticity mechanisms in the amygdala-prefrontal cortical circuit: implications for opiate addiction memory formation. Front Neurosci 9:399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2015.00399
Schiffino FL, Holland PC (2016) Secondary visual cortex is critical to the expression of surprise-induced enhancements in cue associability in rats. Eur J Neurosci 44:1870–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13286
Song R, Yang RF, Wu N, Su RB, Li J, Peng XQ, Li X, Gaál J, Xi ZX, Gardner EL (2012) YQA14: a novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonist that inhibits cocaine self-administration in rats and mice, but not in D3 receptor-knockout mice. Addict Biol 17:259–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1369-1600.2011.00317.x
Torregrossa MM, Gordon J, Taylor JR (2013) Double dissociation between the anterior cingulate cortex and nucleus accumbens core in encoding the context versus the content of pavlovian cocaine cue extinction. J Neurosci 33:8370–7. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0489-13.2013
Van Eden CG, Lamme VA, Uylings HB (1992) Heterotopic Cortical Afferents to the Medial Prefrontal Cortex in the Rat. A Combined Retrograde and Anterograde Tracer Study. Eur J Neurosci 4:77–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00111.x
Wang D, Zhao J, Gao Z, Chen N, Wen B, Lu W, Lei Z, Chen C, Liu Y, Feng J, Wang JH (2015) Neurons in the barrel cortex turn into processing whisker and odor signals: a cellular mechanism for the storage and retrieval of associative signals. Front Cell Neurosci 9:320. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00320
Weible AP, Posner MI, Niell CM (2019) Differential Involvement of Three Brain Regions during Mouse Skill Learning. eNeuro 6 https://doi.org/10.1523/eneuro.0143-19.2019
Yuan Z, Qi Z, Wang R, Cui Y, An S, Wu G, Feng Q, Lin R, Dai R, Li A, Gong H, Luo Q, Fu L, Luo M (2023) A corticoamygdalar pathway controls reward devaluation and depression using dynamic inhibition code. Neuron 111:3837-3853.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.022
Zhang S, Xu M, Kamigaki T, Hoang Do JP, Chang WC, Jenvay S, Miyamichi K, Luo L, Dan Y (2014) Selective attention. Long-range and local circuits for top-down modulation of visual cortex processing. Science 345:660–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254126
Zhao X, Huang L, Guo R, Liu Y, Zhao S, Guan S, Ge R, Cui S, Wang S, Wang JH (2017) Coordinated Plasticity among Glutamatergic and GABAergic Neurons and Synapses in the Barrel Cortex Is Correlated to Learning Efficiency. Front Cell Neurosci 11:221. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00221
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFC3304201), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7232106) and Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by BAST (No. BYESS2023230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dan-ni Cao, Ning Wu and Jin Li initiated this project and designed the study. Cai-ling Wang conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. Cai-ling Wang and Dan-ni Cao wrote and revised the manuscript. Ying-jie Zhu provided technical support.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee under permission No. IACUC-2022-001W and were performed in strict accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Cl., Cao, Dn., Wu, N. et al. The secondary visual cortex mediated the enhancement of associative learning on methamphetamine self-administration behaviors. Psychopharmacology (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-024-06597-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-024-06597-7