Abstract
Rationale
Neuropsychiatric disorders encompass a broad category of medical conditions that include both neurology as well as psychiatry such as major depressive disorder, autism spectrum disorder, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia as well as psychosis.
Objective
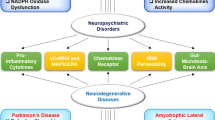
NADPH-oxidase (NOX), which is the free radical generator, plays a substantial part in oxidative stress in neuropsychiatric disorders. It is thought that elevated oxidative stress as well as neuroinflammation plays a part in the emergence of neuropsychiatric disorders. Including two linked with membranes and four with subunits of cytosol, NOX is a complex of multiple subunits. NOX has been linked to a significant source of reactive oxygen species in the brain. NOX has been shown to control memory processing and neural signaling. However, excessive NOX production has been linked to cardiovascular disorders, CNS degeneration, and neurotoxicity. The increase in NOX leads to the progression of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Result
Our review mainly emphasized the characteristics of NOX and its various mechanisms, the modulation of NOX in various neuropsychiatric disorders, and various studies supporting the fact that NOX might be the potential therapeutic target for neuropsychiatric disorders.
Conclusion
Here, we summarizes various pharmacological studies involving NOX inhibitors in neuropsychiatric disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad SF, Zoheir KM, Ansari MA, Nadeem A, Bakheet SA, Al-Ayadhi LY, Alzahrani MZ, Al-Shabanah OA, Al-Harbi MM, Attia SM (2017) Dysregulation of Th1, Th2, Th17, and T regulatory cell-related transcription factor signaling in children with autism. Mol Neurobiol 54:4390–4400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9977-0
Akyol O, Zoroglu SS, Armutcu F, Sahin S, Gurel A (2004) Nitric oxide as a physiopathological factor in neuropsychiatric disorders. In Vivo 18(3):377–390
Alokam R, Singhal S, Srivathsav GS, Garigipati S, Puppala S, Sriram D, Perumal Y (2015) Design of dual inhibitors of ROCK-I and NOX2 as potential leads for the treatment of neuroinflammation associated with various neurological disorders including autism spectrum disorder. Mol BioSyst 11(2):607–617. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MB00570H
Altenhöfer S, Radermacher KA, Kleikers PW, Wingler K, Schmidt HH (2015) Evolution of NADPH oxidase inhibitors: selectivity and mechanisms for target engagement. Antioxid Redox Signal 23(5):406–427. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5814
Andreazza AC, Wang JF, Salmasi F, Shao L, Young LT (2013) Specific subcellular changes in oxidative stress in prefrontal cortex from patients with bipolar disorder. J Neurochem 127(4):552–561. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12316
Anrather J, Racchumi G, Iadecola C (2006) NF-κB regulates phagocytic NADPH oxidase by inducing the expression of gp91phox. J Biol Chem 281(9):5657–5667. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M506172200
Atkins CM, Sweatt JD (1999) Reactive oxygen species mediate activity-dependent neuron–glia signaling in output fibers of the hippocampus. J Neurosci 19(17):7241–7248. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-07241.1999
Avramopoulos D (2018) Recent advances in the genetics of schizophrenia. Complex Psychiatry 4(1):35–51. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488679
Barbieri SS, Sandrini L, Musazzi L, Popoli M, Ieraci A (2021) Apocynin prevents anxiety-like behavior and histone deacetylases overexpression induced by sub-chronic stress in mice. Biomolecules 11(6):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11060885
Beasley C, Cotter D, Khan N, Pollard C, Sheppard P, Varndell I, Lovestone S, Anderton B, Everall I (2001) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β immunoreactivity is reduced in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 302(2-3):117–20
Beck K, Hindley G, Borgan F, Ginestet C, McCutcheon R, Brugger S, Driesen N, Ranganathan M, D'Souza DC, Taylor M, Krystal JH, Howes OD (2020) Association of ketamine with psychiatric symptoms and implications for its therapeutic use and for understanding schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 3(5):e204693. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.4693
Behl T, Kaur D, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Zengin G, Andronie-Cioara FL, Toma MM, Bungau S, Bumbu AG (2021a) Role of monoamine oxidase activity in Alzheimer’s disease: an insight into the therapeutic potential of inhibitors. Molecules 26(12):3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26123724
Behl T, Kaur G, Sehgal A, Bhardwaj S, Singh S, Buhas C, Judea-Pusta C, Uivarosan D, Munteanu MA, Bungau S (2021b) Multifaceted role of matrix metalloproteinases in neurodegenerative diseases: pathophysiological and therapeutic perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 22(3):1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031413
Berk M, Kapczinski F, Andreazza AC, Dean OM, Giorlando F, Maes M, Yücel M, Gama CS, Dodd S, Dean B, Magalhães PV (2011) Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35(3):804–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.001
Berton O, McClung CA, DiLeone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Graham D, Tsankova NM, Bolanos CA, Rios M, Monteggia LM (2006) Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 311(5762):864–868. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1120972
Bitanihirwe BK, Woo TU (2011) Oxidative stress in schizophrenia: an integrated approach. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35(3):878–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.10.008
Bozkurt NM, Unal G (2023) Vortioxetine improved negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia in subchronic MK-801 model in rats. Behav Brain Res 27(444):114365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114365
Brandes RP (2003) Role of NADPH oxidases in the control of vascular gene expression. Antioxid Redox Signal 5(6):803–811. https://doi.org/10.1089/152308603770380115
Bray NJ, O’Donovan MC (2018) The genetics of neuropsychiatric disorders. Brain Neurosci Adv 2:2398212818799271. https://doi.org/10.1177/2398212818799271
Britvic D, Maric N, Doknic M, Pekic S, Andric S, Jasovic-Gasic M, Popovic V (2013) Metabolic issues in psychotic disorders with the focus on first-episode patients: a review. Psychiatr Danub 25(4):415
Brown JR, Goldblatt D, Buddle J, Morton L, Thrasher AJ (2003) Diminished production of anti-inflammatory mediators during neutrophil apoptosis and macrophage phagocytosis in chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). J Leukoc Biol 73(5):591–599. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1202599
Cameron D, Blake DJ, Bray NJ, Hill MJ (2019) Transcriptional changes following cellular knockdown of the schizophrenia risk gene SETD1A are enriched for common variant association with the disorder. Complex Psychiatry 5(2):109–114. https://doi.org/10.1159/000497181
Carlen M, Meletis K, Siegle JH, Cardin JA, Futai K, Vierling-Claassen D, Ruehlmann C, Jones SR, Deisseroth K, Sheng MI, Moore CI (2012) A critical role for NMDA receptors in parvalbumin interneurons for gamma rhythm induction and behavior. Mol Psychiatry 17(5):537–548. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2011.31
Chen H, Kim GS, Okami N, Narasimhan P, Chan PH (2011) NADPH oxidase is involved in post-ischemic brain inflammation. Neurobiol Dis 42(3):341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.01.027
Cheng G, Cao Z, Xu X, Van Meir EG, Lambeth JD (2001) Homologs of gp91phox: cloning and tissue expression of Nox3, Nox4, and Nox5. Gene 269(1-2):131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00449-8
Clement HW, Vazquez JF, Sommer O, Heiser P, Morawietz H, Hopt U, Schulz E, von Dobschütz E (2010) Lipopolysaccharide-induced radical formation in the striatum is abolished in Nox2 gp91phox-deficient mice. J Neural Transm 117:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0327-5
Coccurello R, Moles A (2010) A murine model of atypical antipsychotic-induced weight gain and metabolic dysregulation. Curr Protoc Neurosci 52(1):9–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142301.ns0933s52
Colaianna M, Schiavone S, Zotti M, Tucci P, Morgese MG, Bäckdahl L, Holmdahl R, Krause KH, Cuomo V, Trabace L (2013) Neuroendocrine profile in a rat model of psychosocial stress: relation to oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(12):1385–1399. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4569
Cooney SJ, Bermudez-Sabogal SL, Byrnes KR (2013) Cellular and temporal expression of NADPH oxidase (NOX) isotypes after brain injury. J Neuroinflammation 10:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-10-155
Dantzler HA, Matott MP, Martinez D, Kline DD (2019) Hydrogen peroxide inhibits neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus via potassium channel activation. Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys 317(1):R121–R133. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00054.2019
Dikalov S (2011) Cross talk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidases. Free Radic Biol Med 51(7):1289–1301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.033
Edens WA, Sharling L, Cheng G, Shapira R, Kinkade JM, Lee T, Edens HA, Tang X, Sullards C, Flaherty DB, Benian GM (2001) Tyrosine cross-linking of extracellular matrix is catalyzed by Duox, a multidomain oxidase/peroxidase with homology to the phagocyte oxidase subunit gp91 phox. J Cell Biol 154(4):879–892. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200103132
Eising E, Carrion-Castillo A, Vino A, Strand EA, Jakielski KJ, Scerri TS, Hildebrand MS, Webster R, Ma A, Mazoyer B, Francks C (2019) A set of regulatory genes co-expressed in embryonic human brain is implicated in disrupted speech development. Mol Psychiatry 24(7):1065–1078. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0020-x
El-Ansary A, Al-Ayadhi L (2012) Neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorders. J Neuroinflammation 9:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-265
Ershova ES, Shmarina GV, Martynov AV, Zakharova NV, Veiko RV, Umriukhin PE, Kostyuk GP, Kutsev SI, Veiko NN, Kostyuk SV (2022) NADPH-oxidase 4 gene over-expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes of the schizophrenia patients. PLoS One 17(6):e0269130. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0269130
Farber NB (2003) The NMDA receptor hypofunction model of psychosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003(1):119–130. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1300.008
Feil R, Fraga MF (2012) Epigenetics and the environment: emerging patterns and implications. Nat Rev Genet 13(2):97–109. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3142
Frick LR, Williams K, Pittenger C (2013) Microglial dysregulation in psychiatric disease. Clin Dev Immunol 2013. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/608654
Guilmatre A, Huguet G, Delorme R, Bourgeron T (2014) The emerging role of SHANK genes in neuropsychiatric disorders. Dev Neurobiol 74(2):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.22128
Ha H, Lee HB (2005) Reactive oxygen species amplify glucose signalling in renal cells cultured under high glucose and in diabetic kidney. Nephrology 10:S7–S10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2005.00448.x
Hampton MB, Fadeel B, Orrenius S (1998) Redox regulation of the caspases during apoptosis a. Ann N Y Acad Sci 854(1):328–335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09913.x
Helfinger V, Henke N, Harenkamp S, Walter M, Epah J, Penski C, Mittelbronn M, Schröder K (2016) The NADPH Oxidase Nox4 mediates tumour angiogenesis. Acta Physiol 216(4):435–446. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12625
Hovatta I, Tennant RS, Helton R, Marr RA, Singer O, Redwine JM, Ellison JA, Schadt EE, Verma IM, Lockhart DJ, Barlow C (2005) Glyoxalase 1 and glutathione reductase 1 regulate anxiety in mice. Nature 438:662–666
Iadarola ND, Niciu MJ, Richards EM, Vande Voort JL, Ballard ED, Lundin NB, Nugent AC, Machado-Vieira R, Zarate CA Jr (2015) Ketamine and other N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in the treatment of depression: a perspective review. Ther Adv Chronic Dis 6(3):97–114. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622315579059
Ibi M, Katsuyama M, Fan C, Iwata K, Nishinaka T, Yokoyama T, Yabe-Nishimura C (2006) NOX1/NADPH oxidase negatively regulates nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth. Free Radic Biol Med 40(10):1785–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.01.009
Ibi M, Liu J, Arakawa N, Kitaoka S, Kawaji A, Matsuda KI, Iwata K, Matsumoto M, Katsuyama M, Zhu K, Teramukai S (2017) Depressive-like behaviors are regulated by NOX1/NADPH oxidase by redox modification of NMDA receptor 1. J Neurosci 37(15):4200. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2988-16.2017
Jiang CC, Lin LS, Long S, Ke XY, Fukunaga K, Lu YM, Han F (2022) Signalling pathways in autism spectrum disorder: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1):229. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01081-0
Jiang L, Wu X, Wang S, Chen SH, Zhou H, Wilson B, Jin CY, Lu RB, Xie K, Wang Q, Hong JS (2016) Clozapine metabolites protect dopaminergic neurons through inhibition of microglial NADPH oxidase. J Neuroinflammation 13:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0573-z
Kalra P, Khan H, Kaur A, Singh TG (2022) Mechanistic insight on autophagy modulated molecular pathways in cerebral ischemic injury: from preclinical to clinical perspective. Neurochem Res 1:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03500-0
Karam CS, Ballon JS, Bivens NM, Freyberg Z, Girgis RR, Lizardi-Ortiz JE, Markx S, Lieberman JA, Javitch JA (2010) Signaling pathways in schizophrenia: emerging targets and therapeutic strategies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 31(8):381–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2010.05.004
Katsuyama M, Matsuno K, Yabe-Nishimura C (2011) Physiological roles of NOX/NADPH oxidase, the superoxide-generating enzyme. J Clin Biochem Nutr 50(1):9–22. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.11-06SR
Khan H, Bangar A, Grewal AK, Bansal P, Singh TG (2022a) Caspase-mediated regulation of the distinct signaling pathways and mechanisms in neuronal survival. Int Immunopharmacol 1(110):108951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108951
Khan H, Garg N, Singh TG, Kaur A, Thapa K (2022b) Calpain inhibitors as potential therapeutic modulators in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Res 47(5):1125–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03521-9
Khan H, Grewal AK, Singh TG (2022c) Mitochondrial dynamics related neurovascular approaches in cerebral ischemic injury. Mitochondrion 5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2022.08.001
Khan H, Grewal AK, Singh TG (2022d) Pharmacological postconditioning by protocatechuic acid attenuates brain injury in ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) mice model: implications of nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor pathway. Neuroscience. 21(491):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.016
Khan H, Gupta A, Singh TG, Kaur A (2021) Mechanistic insight on the role of leukotriene receptors in ischemic–reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Rep 73:1240–1254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43440-021-00258-8
Khan H, Kaur P, Singh TG, Grewal AK, Sood S (2022e) Adenosine as a key mediator of neuronal survival in cerebral ischemic injury. Neurochem Res 30:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03737-3
Khan H, Tiwari C, Grewal AK, Singh TG, Chauhan S, Batiha GE (2022f) Pharmacological modulation of phosphodiesterase-7 as a novel strategy for neurodegenerative disorders. Inflammopharmacology 22:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01072-1
Khan MM, Evans DR, Gunna V, Scheffer RE, Parikh VV, Mahadik SP (2002) Reduced erythrocyte membrane essential fatty acids and increased lipid peroxides in schizophrenia at the never-medicated first-episode of psychosis and after years of treatment with antipsychotics. Schizophr Res 58(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-9964(01)00334-6
Kim SH, Won SJ, Sohn S, Kwon HJ, Lee JY, Park JH, Gwag BJ (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor can act as a pronecrotic factor through transcriptional and translational activation of NADPH oxidase. J Cell Biol 159(5):821–831. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200112131
Kishida KT, Hoeffer CA, Hu D, Pao M, Holland SM, Klann E (2006) Synaptic plasticity deficits and mild memory impairments in mouse models of chronic granulomatous disease. Mol Cell Biol 26(15):5908–5920. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00269-06
Kishida KT, Pao M, Holland SM, Klann E (2005) NADPH oxidase is required for NMDA receptor-dependent activation of ERK in hippocampal area CA1. J Neurochem 94(2):299–306. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03189.x
Kiyohara T, Miyano K, Kamakura S, Hayase J, Chishiki K, Kohda A, Sumimoto H (2018) Differential cell surface recruitment of the superoxide-producing NADPH oxidases Nox1, Nox2 and Nox5: the role of the small GTPase Sar1. Genes Cells 23(6):480–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/gtc.12590
Krause KH (2004) Tissue distribution and putative physiological function of NOX family NADPH oxidases. Jpn J Infect Dis 57(5):S28–S29
Kuehner JN, Bruggeman EC, Wen Z, Yao B (2019) Epigenetic regulations in neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Genet 4(10):268. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00268
Kulak A, Steullet P, Cabungcal JH, Werge T, Ingason A, Cuenod M, Do KQ (2013) Redox dysregulation in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: insights from animal models. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(12):1428–1443. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4858
Kunz M, Gama CS, Andreazza AC, Salvador M, Ceresér KM, Gomes FA, Belmonte-de-Abreu PS, Berk M, Kapczinski F (2008) Elevated serum superoxide dismutase and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances in different phases of bipolar disorder and in schizophrenia. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32(7):1677–1681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.07.001
Lavigne MC, Malech HL, Holland SM, Leto TL (2001) Genetic requirement of p47 phox for superoxide production by murine microglia. FASEB J 15(2):285–287. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.00-0608fje
Le Belle JE, Sperry J, Ngo A, Ghochani Y, Laks DR, López-Aranda M, Silva AJ, Kornblum HI (2014) Maternal inflammation contributes to brain overgrowth and autism-associated behaviors through altered redox signaling in stem and progenitor cells. Stem Cell Rep 3(5):725–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.09.004
Lelkes PI, Hahn KL, Sukovich DA, Karmiol S, Schmidt DH (1998) On the possible role of reactive oxygen species in angiogenesis. Oxygen Transp Tissue XX:295–310
Liu Q, Kang JH, Zheng RL (2005) NADPH oxidase produces reactive oxygen species and maintains survival of rat astrocytes. Cell Biochem Funct 23(2):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.1171
Lyle AN, Deshpande NN, Taniyama Y, Seidel-Rogol B, Pounkova L, Du P, Papaharalambus C, Lassègue B, Griendling KK (2009) Poldip2, a novel regulator of Nox4 and cytoskeletal integrity in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 105(3):249–259. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.193722
Ma MW, Wang J, Zhang Q, Wang R, Dhandapani KM, Vadlamudi RK, Brann DW (2017) NADPH oxidase in brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurodegener 12:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0150-7
Maes M, Landucci Bonifacio K, Morelli NR, Vargas HO, Barbosa DS, Carvalho AF, Nunes SO (2019) Major differences in neurooxidative and neuronitrosative stress pathways between major depressive disorder and types I and II bipolar disorder. Mol Neurobiol 56:141–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1051-7
Masood A, Nadeem A, Mustafa SJ, O'Donnell JM (2008) Reversal of oxidative stress-induced anxiety by inhibition of phosphodiesterase-2 in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326(2):369–379. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.137208
Mathew SJ, Manji HK, Charney DS (2008) Novel drugs and therapeutic targets for severe mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(9):2080–2092. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301652
Meitzler JL, de Montellano PR (2009) Caenorhabditis elegans and human dual oxidase 1 (DUOX1)“peroxidase” domains: insights into heme binding and catalytic activity. J Biol Chem 284(28):18634–18643. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.013581
Moreira AP, Vizuete AF, Zin LE, de Marques CO, Pacheco RF, Leal MB, Gonçalves CA (2022) The methylglyoxal/RAGE/NOX-2 pathway is persistently activated in the hippocampus of rats with STZ-induced sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox Res 40(2):395–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00476-9
Moreno JC, Bikker H, Kempers MJ, Van Trotsenburg AP, Baas F, de Vijlder JJ, Vulsma T, Ris-Stalpers C (2002) Inactivating mutations in the gene for thyroid oxidase 2 (THOX2) and congenital hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 347(2):95–102. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa012752
Morris G, Berk M (2015) The many roads to mitochondrial dysfunction in neuroimmune and neuropsychiatric disorders. BMC Med 13:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-015-0310-y
Morris G, Puri BK, Walker AJ, Maes M, Carvalho AF, Bortolasci CC, Walder K, Berk M (2019) Shared pathways for neuroprogression and somatoprogression in neuropsychiatric disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1(107):862–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.09.025
Nadeem A, Ahmad SF, Bakheet SA, Al-Harbi NO, Al-Ayadhi LY, Attia SM, Zoheir KM (2017) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling is associated with upregulated NADPH oxidase expression in peripheral T cells of children with autism. Brain Behav Immun 1(61):146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.12.024
Nersesyan Y, Demirkhanyan L, Cabezas-Bratesco D, Oakes V, Kusuda R, Dawson T, Sun X, Cao C, Cohen AM, Chelluboina B, Veeravalli KK (2017) Oxytocin modulates nociception as an agonist of pain-sensing TRPV1. Cell Rep 21(6):1681–1691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.063
Okada M, Kawano Y, Fukuyama K, Motomura E, Shiroyama T (2020) Candidate strategies for development of a rapid-acting antidepressant class that does not result in neuropsychiatric adverse effects: prevention of ketamine-induced neuropsychiatric adverse reactions. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):7951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217951
Oliveira J, Debnath M, Etain B, Bennabi M, Hamdani N, Lajnef M, Bengoufa D, Fortier C, Boukouaci W, Bellivier F, Kahn JP (2015) Violent suicidal behaviour in bipolar disorder is associated with nitric oxide synthase 3 gene polymorphism. Acta Psychiatr Scand 132(3):218–225. https://doi.org/10.1111/acps.12433
Pawate S, Shen Q, Fan F, Bhat NR (2004) Redox regulation of glial inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide and interferonγ. J Neurosci Res 77(4):540–551. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20180
Prabhakar NK, Khan H, Grewal AK, Singh TG (2022) Intervention of neuroinflammation in the traumatic brain injury trajectory: in vivo and clinical approaches. Int Immunopharmacol 1(108):108902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108902
Raffa M, Barhoumi S, Atig F, Fendri C, Kerkeni A, Mechri A (2012) Reduced antioxidant defense systems in schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 39(2):371–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.07.013
Rammal H, Bouayed J, Younos C, Soulimani R (2008) Evidence that oxidative stress is linked to anxiety-related behaviour in mice. Brain Behav Immun 22(8):1156–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2008.06.005
Rani R, Kumar A, Jaggi AS, Singh N (2021) Pharmacological investigations on efficacy of Phlorizin a sodium-glucose co-transporter (SGLT) inhibitor in mouse model of intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced dementia of AD type. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 32(6):1057–1064. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2020-0330
Rehni AK, Singh TG, Jaggi AS, Singh N (2008) Pharmacological preconditioning of the brain: a possible interplay between opioid and calcitonin gene related peptide transduction systems. Pharmacol Rep 60(6):904
Reik W (2007) Stability and flexibility of epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature 447(7143):425–432. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05918
Rihal V, Khan H, Kaur A, Singh TG, Abdel-Daim MM (2022) Therapeutic and mechanistic intervention of vitamin D in neuropsychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Res 14:114782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114782
Rossignol DA, Frye RE (2014) Evidence linking oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation in the brain of individuals with autism. Front Physiol 22(5):150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00150
Roth TL, Sweatt JD (2011) Annual research review: epigenetic mechanisms and environmental shaping of the brain during sensitive periods of development. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 52(4):398–408. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02282.x
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Kaur T, Ramkumar V (2012) siRNA-mediated knock-down of NOX3: therapy for hearing loss? Cell Mol Life Sci 69:2429–2434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1016-3
Salim S (2014) Oxidative stress and psychological disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol 12(2):140–147. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X11666131120230309
Sati S, Ghosh S, Jain V, Scaria V, Sengupta S (2012) Genome-wide analysis reveals distinct patterns of epigenetic features in long non-coding RNA loci. Nucleic Acids Res 40(20):10018–10031. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks776
Sauer H, Bekhite MM, Hescheler J, Wartenberg M (2005) Redox control of angiogenic factors and CD31-positive vessel-like structures in mouse embryonic stem cells after direct current electrical field stimulation. Exp Cell Res 304(2):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.11.026
Schiavone S, Camerino GM, Mhillaj E, Zotti M, Colaianna M, De Giorgi A, Trotta A, Cantatore FP, Conte E, Bove M, Tucci P (2017) Visceral fat dysfunctions in the rat social isolation model of psychosis. Front Pharmacol 8(8):787. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00787
Schiavone S, Jaquet V, Sorce S, Dubois-Dauphin M, Hultqvist M, Bäckdahl L, Holmdahl R, Colaianna M, Cuomo V, Trabace L, Krause KH (2012) NADPH oxidase elevations in pyramidal neurons drive psychosocial stress-induced neuropathology. Transl Psychiatry 2(5):e111. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2012.36
Schiavone S, Neri M, Mhillaj E, Morgese MG, Cantatore S, Bove M, Riezzo I, Tucci P, Pomara C, Turillazzi E, Cuomo V (2016) The NADPH oxidase NOX2 as a novel biomarker for suicidality: evidence from human post mortem brain samples. Transl Psychiatry 6(5):e813. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.76
Schiavone S, Sorce S, Dubois-Dauphin M, Jaquet V, Colaianna M, Zotti M, Cuomo V, Trabace L, Krause KH (2009) Involvement of NOX2 in the development of behavioral and pathologic alterations in isolated rats. Biol Psychiatry 66(4):384–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.04.033
Seo JS, Park JY, Choi J, Kim TK, Shin JH, Lee JK, Han PL (2012) NADPH oxidase mediates depressive behavior induced by chronic stress in mice. J Neurosci 32(28):9690–9699. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0794-12.2012
Seo MS, Kim SH, Ahn YM, Kim Y, Jeon WJ, Yoon SC, Roh MS, Juhnn YS, Kim YS (2007) The effects of repeated administrations of MK-801 on ERK and GSK-3β signalling pathways in the rat frontal cortex. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10(3):359–368. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1461145706006869
Seredenina T, Sorce S, Herrmann FR, Ma Mulone XJ, Plastre O, Aguzzi A, Jaquet V, Krause KH (2017) Decreased NOX2 expression in the brain of patients with bipolar disorder: association with valproic acid prescription and substance abuse. Transl Psychiatry 7(8):e1206. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2017.175
Serrano F, Kolluri NS, Wientjes FB, Card JP, Klann E (2003) NADPH oxidase immunoreactivity in the mouse brain. Brain Res 988(1-2):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(03)03364-X
Shao A, Lin D, Wang L, Tu S, Lenahan C, Zhang J (2020) Oxidative stress at the crossroads of aging, stroke and depression. Aging Dis 11(6):1537–1566. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2020.0225
Singh V, Arora S, Kaur R, Shri R (2021) Memory improvement effects of Ganoderma mediosinense in mice via its anticholinergic and antioxidant activities. Alzheimers Dement 17:e050707. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.050707
Sorce S, Krause KH (2009) NOX enzymes in the central nervous system: from signaling to disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 11(10):2481–2504. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.2578
Sorce S, Schiavone S, Tucci P, Colaianna M, Jaquet V, Cuomo V, Dubois-Dauphin M, Trabace L, Krause KH (2010) The NADPH oxidase NOX2 controls glutamate release: a novel mechanism involved in psychosis-like ketamine responses. J Neurosci 30(34):11317–11325. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1491-10.2010
Sullivan MN, Gonzales AL, Pires PW, Bruhl A, Leo MD, Li W, Oulidi A, Boop FA, Feng Y, Jaggar JH, Welsh DG (2015) Localized TRPA1 channel Ca2+ signals stimulated by reactive oxygen species promote cerebral artery dilation. Sci Signal 8(358) ra2-ra2
Sumimoto H (2008) Structure, regulation and evolution of Nox-family NADPH oxidases that produce reactive oxygen species. FEBS J 275(13):3249–3277. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06488.x
Szulwach KE, Li X, Smrt RD, Li Y, Luo Y, Lin L, Santistevan NJ, Li W, Zhao X, Jin P (2010) Cross talk between microRNA and epigenetic regulation in adult neurogenesis. J Cell Biol 189(1):127–141. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200908151
Tang Y, Xu J, Qu W, Peng X, Xin P, Yang X, Ying C, Sun X, Hao L (2012) Resveratrol reduces vascular cell senescence through attenuation of oxidative stress by SIRT1/NADPH oxidase-dependent mechanisms. J Nutr Biochem 23(11):1410–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.08.008
Tavakolizadeh J, Roshanaei K, Salmaninejad A, Yari R, Nahand JS, Sarkarizi HK, Mousavi SM, Salarinia R, Rahmati M, Mousavi SF, Mokhtari R (2018) MicroRNAs and exosomes in depression: potential diagnostic biomarkers. J Cell Biochem 119(5):3783–3797. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26599
Tejada-Simon MV, Serrano F, Villasana LE, Kanterewicz BI, Wu GY, Quinn MT, Klann E (2005) Synaptic localization of a functional NADPH oxidase in the mouse hippocampus. Mol Cell Neurosci 29(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2005.01.007
Thapa K, Khan H, Kanojia N, Singh TG, Kaur A, Kaur G (2022) Therapeutic insights on ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 2:175133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175133
Thiels E, Klann E (2002) Hippocampal memory and plasticity in superoxide dismutase mutant mice. Physiol Behav 77(4-5):601–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9384(02)00900-9
Tiwari P, Khan H, Singh TG, Grewal AK (2022) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase: an overview of mechanistic approaches and therapeutic opportunities in the management of stroke. Neurochem Res 47(7):1830–1852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03595-z
Vallet P, Charnay Y, Steger K, Ogier-Denis E, Kovari E, Herrmann F, Michel JP, Szanto I (2005) Neuronal expression of the NADPH oxidase NOX4, and its regulation in mouse experimental brain ischemia. Neuroscience 132(2):233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.12.038
Vargas HO, Nunes SO, Pizzo de Castro M, Bortolasci CC, Sabbatini Barbosa D, Kaminami Morimoto H et al (2013) Oxidative stress and lowered total antioxidant status are associated with a history of suicide attempts. J Affect Disord 150(3):923–930
Vilaplana M, Richard-Devantoy S, Turecki G, Jaafari N, Jollant F (2015) Insight into mental disorders and suicidal behavior: a qualitative and quantitative multimodal investigation. J Clin Psychiatry 76(3):9145
Vilhardt F, Plastre O, Sawada M, Suzuki K, Wiznerowicz M, Kiyokawa E, Trono D, Krause KH (2002) The HIV-1 Nef protein and phagocyte NADPH oxidase activation. J Biol Chem 277(44):42136–42143. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M200862200
Volk DW, Lewis DA (2002) Impaired prefrontal inhibition in schizophrenia: relevance for cognitive dysfunction. Physiol Behav 77(4-5):501–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9384(02)00936-8
Wang X, Pinto-Duarte A, Sejnowski TJ, Behrens MM (2013) How Nox2-containing NADPH oxidase affects cortical circuits in the NMDA receptor antagonist model of schizophrenia. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(12):1444–1462. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4907
Weiner DM, Meltzer HY, Veinbergs I, Donohue EM, Spalding TA, Smith TT, Mohell N, Harvey SC, Lameh J, Nash N, Vanover FKE (2004) The role of M1 muscarinic receptor agonism of N-desmethylclozapine in the unique clinical effects of clozapine. Psychopharmacology 177:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1940-5
Winkelstein JA, Marino MC, Johnston RB Jr, Boyle J, Curnutte J, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Holland SM, Ochs H, Quie P, Buckley RH (2000) Chronic granulomatous disease. Report on a national registry of 368 patients. Medicine 79(3):155–169. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005792-200005000-00003
Wong JL, Créton R, Wessel GM (2004) The oxidative burst at fertilization is dependent upon activation of the dual oxidase Udx1. Dev Cell 7(6):801–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.014
Van Gorp B (2005) Where is the frame? Victims and intruders in the Belgian press coverage of the asylum issue. Eur J Commun 20(4):484–507
Yan J, Huang J, Liu A, Wu J, Fan H, Shen M, Lai X, Ma H, Sun W, Yang J, Xu Y (2021) Atorvastatin improves motor function, anxiety and depression by NOX2-mediated autophagy and oxidative stress in MPTP-lesioned mice. Aging (albany NY) 13(1):831 10.18632%2Faging.202189
Yan J, Liu A, Fan H, Qiao L, Wu J, Shen M, Lai X, Huang J (2020) Simvastatin improves behavioral disorders and hippocampal inflammatory reaction by NMDA-mediated anti-inflammatory function in MPTP-treated mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40:1155–1164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00804-7
Zhang X, Ibi M, Haga R, Iwata K, Matsumoto M, Asaoka N, Liu J, Katsuyama M, Yabe-Nishimura C (2021) NOX1/NADPH oxidase affects the development of autism-like behaviors in a maternal immune activation model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1(534):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.070
Zhu YJ, Fan JJ, Wu FY, Zhang M, Song AQ, Li Y, Li YK, Wu WN (2022) Aging promotes chronic stress-induced depressive-like behavior by activating NLRP1 inflammasome-driven inflammatory signaling in mice. Inflammation 45(6):2172–2185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01683-4
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
The authors are grateful to the Chitkara College of Pharmacy, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Patiala, Punjab, India, for providing the necessary facilities to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and conceived and designed the experiments: Thakur Gurjeet Singh. Analyzed the data: Heena Khan and Thakur Gurjeet Singh. Wrote the manuscript: Parneet Kaur and Heena Khan. Editing of the manuscript: Heena Khan and Amarjot Kaur Grewal. Critically reviewed the article: Thakur Gurjeet Singh.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors read and given their consent for the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, P., Khan, H., Grewal, A.K. et al. Therapeutic potential of NOX inhibitors in neuropsychiatric disorders. Psychopharmacology 240, 1825–1840 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06424-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-023-06424-5