Abstract
Background
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) delivered to the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) induces antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like responses in various animal models. Electrophysiology and neurochemical studies suggest that these effects may be dependent, at least in part, on the serotonergic system. In rodents, vmPFC DBS reduces raphe cell firing and increases serotonin (5-HT) release and the expression of serotonergic receptors in different brain regions.
Methods
We examined whether the behavioural responses of chronic vmPFC DBS are mediated by 5-HT1A or 5-HT1B receptors through a series of experiments. First, we delivered stimulation to mice undergoing chronic social defeat stress (CSDS), followed by a battery of behavioural tests. Second, we measured the expression of 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors in different brain regions with western blot. Finally, we conducted pharmacological experiments to mitigate the behavioural effects of DBS using the 5-HT1A antagonist, WAY-100635, or the 5-HT1B antagonist, GR-127935.
Results
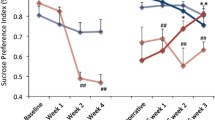
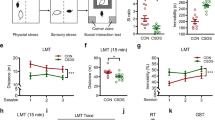
We found that chronic DBS delivered to stressed animals reduced the latency to feed in the novelty suppressed feeding test (NSF) and immobility in the forced swim test (FST). Though no significant changes were observed in receptor expression, 5-HT1B levels in DBS-treated animals were found to be non-significantly increased in the vmPFC, hippocampus, and nucleus accumbens and reduced in the raphe compared to non-stimulated controls. Finally, while animals given vmPFC stimulation along with WAY-100635 still presented significant responses in the NSF and FST, these were mitigated following GR-127935 administration.
Conclusions
The antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects of DBS in rodents may be partially mediated by 5-HT1B receptors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggleton JP, Nelson AJD (2020) Distributed interactive brain circuits for object-in-place memory: a place for time? Brain Neurosci Adv 4:2398212820933471. https://doi.org/10.1177/2398212820933471
Anthony JP, Sexton TJ, Neumaier JF (2000) Antidepressant-induced regulation of 5-HT(1b) mRNA in rat dorsal raphe nucleus reverses rapidly after drug discontinuation. J Neurosci Res 61:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-4547(20000701)61:1<82::AID-JNR10>3.0.CO;2-E
Antoniuk S, Bijata M, Ponimaskin E, Wlodarczyk J (2019) Chronic unpredictable mild stress for modeling depression in rodents: meta-analysis of model reliability. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 99:101–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.12.002
Awan NR, Lozano A, Hamani C (2009) Deep brain stimulation: current and future perspectives. Neurosurg Focus 27:E2. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.4.FOCUS0982
Bagdy E, Kiraly I, Harsing LG Jr (2000) Reciprocal innervation between serotonergic and GABAergic neurons in raphe nuclei of the rat. Neurochem Res 25:1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007672008297
Bambico FR, Bregman T, Diwan M, Li J, Darvish-Ghane S, Li Z, Laver B, Amorim BO, Covolan L, Nobrega JN, Hamani C (2015) Neuroplasticity-dependent and -independent mechanisms of chronic deep brain stimulation in stressed rats. Transl Psychiatry 5:e674. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2015.166
Bambico FR, Comai S, Diwan M, Hasan SMN, Conway JD, Darvish-Ghane S, Hamani C, Gobbi G, Nobrega JN (2018) High frequency stimulation of the anterior vermis modulates behavioural response to chronic stress: involvement of the prefrontal cortex and dorsal raphe? Neurobiol Dis 116:166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.03.011
Bannai M, Fish EW, Faccidomo S, Miczek KA (2007) Anti-aggressive effects of agonists at 5-HT1B receptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus of mice. Psychopharmacology 193:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0780-5
Bartolomucci A, Palanza P, Gaspani L, Limiroli E, Panerai AE, Ceresini G, Poli MD, Parmigiani S (2001) Social status in mice: behavioral, endocrine and immune changes are context dependent. Physiol Behav 73:401–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9384(01)00453-x
Bergfeld IO, Mantione M, Hoogendoorn ML, Ruhe HG, Notten P, van Laarhoven J, Visser I, Figee M, de Kwaasteniet BP, Horst F, Schene AH, van den Munckhof P, Beute G, Schuurman R, Denys D (2016) Deep brain stimulation of the ventral anterior lof the internal capsule for treatment-resistant depression: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiat 73:456–464. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0152
Berton O, Durand M, Aguerre S, Mormede P, Chaouloff F (1999) Behavioral, neuroendocrine and serotonergic consequences of single social defeat and repeated fluoxetine pretreatment in the Lewis rat strain. Neuroscience 92:327–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00742-8
Berton O, McClung CA, Dileone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Graham D, Tsankova NM, Bolanos CA, Rios M, Monteggia LM, Self DW, Nestler EJ (2006) Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 311:864–868. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1120972
Blier P, Pineyro G, el Mansari M, Bergeron R, de Montigny C (1998) Role of somatodendritic 5-HT autoreceptors in modulating 5-HT neurotransmission. Ann N Y Acad Sci 861:204–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10192.x
Bregman T, Nona C, Volle J, Diwan M, Raymond R, Fletcher PJ, Nobrega JN, Hamani C (2018) Deep brain stimulation induces antidepressant-like effects in serotonin transporter knockout mice. Brain Stimul 11:423–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2017.11.008
Brown EC, Clark DL, Forkert ND, Molnar CP, Kiss ZHT, Ramasubbu R (2020) Metabolic activity in subcallosal cingulate predicts response to deep brain stimulation for depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 45:1681–1688. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-0745-5
Bruchim-Samuel M, Lax E, Gazit T, Friedman A, Ahdoot H, Bairachnaya M, Pinhasov A, Yadid G (2016) Electrical stimulation of the vmPFC serves as a remote control to affect VTA activity and improve depressive-like behavior. Exp Neurol 283:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.05.016
Casquero-Veiga M, Garcia-Garcia D, Desco M, Soto-Montenegro ML (2018) Understanding deep brain stimulation: in vivo metabolic consequences of the electrode insertional effect. Biomed Res Int 2018:8560232. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8560232
Castro E, Diaz A, Rodriguez-Gaztelumendi A, Del Olmo E, Pazos A (2008) WAY100635 prevents the changes induced by fluoxetine upon the 5-HT1A receptor functionality. Neuropharmacology 55:1391–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.038
Chakravarty MM, Hamani C, Martinez-Canabal A, Ellegood J, Laliberte C, Nobrega JN, Sankar T, Lozano AM, Frankland PW, Lerch JP (2016) Deep brain stimulation of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex causes reorganization of neuronal processes and vasculature. Neuroimage 125:422–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.049
Chao OY, de Souza Silva MA, Yang YM, Huston JP (2020) The medial prefrontal cortex - hippocampus circuit that integrates information of object, place and time to construct episodic memory in rodents: behavioral, anatomical and neurochemical properties. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 113:373–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.04.007
Chenu F, David DJ, Leroux-Nicollet I, Le Maitre E, Gardier AM, Bourin M (2008) Serotonin1B heteroreceptor activation induces an antidepressant-like effect in mice with an alteration of the serotonergic system. J Psychiatry Neurosci 33:541–550
Christoffel DJ, Golden SA, Russo SJ (2011) Structural and synaptic plasticity in stress-related disorders. Rev Neurosci 22:535–549. https://doi.org/10.1515/RNS.2011.044
Coenen VA, Schlaepfer TE, Bewernick B, Kilian H, Kaller CP, Urbach H, Li M, Reisert M (2019) Frontal white matter architecture predicts efficacy of deep brain stimulation in major depression. Transl Psychiatry 9:197. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0540-4
Coenen VA, Schlaepfer TE, Sajonz B, Dobrossy M, Kaller CP, Urbach H, Reisert M (2020) Tractographic description of major subcortical projection pathways passing the anterior limb of the internal capsule. Corticopetal organization of networks relevant for psychiatric disorders. Neuroimage Clin 25:102165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102165
Cryan JF, Markou A, Lucki I (2002) Assessing antidepressant activity in rodents: recent developments and future needs. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:238–245
Cryan JF, Page ME, Lucki I (2005a) Differential behavioral effects of the antidepressants reboxetine, fluoxetine, and moclobemide in a modified forced swim test following chronic treatment. Psychopharmacology 182:335–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0093-5
Cryan JF, Valentino RJ, Lucki I (2005b) Assessing substrates underlying the behavioral effects of antidepressants using the modified rat forced swimming test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:547–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.03.008
Dallman MF, Akana SF, Bhatnagar S, Bell ME, Strack AM (2000) Bottomed out: metabolic significance of the circadian trough in glucocorticoid concentrations. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24(Suppl 2):S40–S46. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801276
Dandekar MP, Fenoy AJ, Carvalho AF, Soares JC, Quevedo J (2018) Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: an integrative review of preclinical and clinical findings and translational implications. Mol Psychiatry 23:1094–1112. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2018.2
Dandekar MP, Saxena A, Scaini G, Shin JH, Migut A, Giridharan VV, Zhou Y, Barichello T, Soares JC, Quevedo J, Fenoy AJ (2019) Medial forebrain bundle deep brain stimulation reverses anhedonic-like behavior in a chronic model of depression: importance of BDNF and inflammatory cytokines. Mol Neurobiol 56:4364–4380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1381-5
Davidson C, Stamford JA (1995) Evidence that 5-hydroxytryptamine release in rat dorsal raphe nucleus is controlled by 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D autoreceptors. Br J Pharmacol 114:1107–1109. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13321.x
Davidson B, Suresh H, Goubran M, Rabin JS, Meng Y, Mithani K, Pople CB, Giacobbe P, Hamani C, Lipsman N (2020) Predicting response to psychiatric surgery: a systematic review of neuroimaging findings. J Psychiatry Neurosci 45:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.190208
de Almeida RM, Nikulina EM, Faccidomo S, Fish EW, Miczek KA (2001) Zolmitriptan–a 5-HT1B/D agonist, alcohol, and aggression in mice. Psychopharmacology 157:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100778
Detke MJ, Rickels M, Lucki I (1995) Active behaviors in the rat forced swimming test differentially produced by serotonergic and noradrenergic antidepressants. Psychopharmacology 121:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245592
Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, Carpenter LL, Howland RH, Bhati MT, O’Reardon JP, Eskandar EN, Baltuch GH, Machado AD, Kondziolka D, Cusin C, Evans KC, Price LH, Jacobs K, Pandya M, Denko T, Tyrka AR, Brelje T, Deckersbach T, Kubu C, Malone DA Jr (2015) A randomized sham-controlled trial of deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for chronic treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 78:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.11.023
Edemann-Callesen H, Voget M, Empl L, Vogel M, Wieske F, Rummel J, Heinz A, Mathe AA, Hadar R, Winter C (2015) Medial forebrain bundle deep brain stimulation has symptom-specific anti-depressant effects in rats and as opposed to ventromedial prefrontal cortex stimulation interacts with the reward system. Brain Stimul 8:714–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2015.02.009
Fenoy AJ, Schulz PE, Selvaraj S, Burrows CL, Zunta-Soares G, Durkin K, Zanotti-Fregonara P, Quevedo J, Soares JC (2018) A longitudinal study on deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle for treatment-resistant depression. Transl Psychiatry 8:111. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0160-4
Frank AC, Scangos KW, Larson PS, Norbu T, Lee AT, Lee AM (2021) Identification of a personalized intracranial biomarker of depression and response to DBS therapy. Brain Stimul 14:1002–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2021.06.009
Furlanetti LL, Coenen VA, Aranda IA, Dobrossy MD (2015) Chronic deep brain stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle reverses depressive-like behavior in a hemiparkinsonian rodent model. Exp Brain Res 233:3073–3085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4375-9
Gabbott PL, Warner TA, Jays PR, Bacon SJ (2003) Areal and synaptic interconnectivity of prelimbic (area 32), infralimbic (area 25) and insular cortices in the rat. Brain Res 993:59–71
Gardier AM, Malagie I, Trillat AC, Jacquot C, Artigas F (1996) Role of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in the mechanism of action of serotoninergic antidepressant drugs: recent findings from in vivo microdialysis studies. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 10:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.1996.tb00145.x
Gersner R, Toth E, Isserles M, Zangen A (2010) Site-specific antidepressant effects of repeated subconvulsive electrical stimulation: potential role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Biol Psychiatry 67:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.015
Gidyk DC, Diwan M, Gouveia FV, Giacobbe P, Lipsman N, Hamani C (2021) Investigating the role of CB1 endocannabinoid transmission in the anti-fear and anxiolytic-like effects of ventromedial prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation. J Psychiatr Res 135:264–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.01.029
Golden SA, Covington HE 3rd, Berton O, Russo SJ (2011) A standardized protocol for repeated social defeat stress in mice. Nat Protoc 6:1183–1191. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.361
Gomez-Lazaro E, Arregi A, Beitia G, Vegas O, Azpiroz A, Garmendia L (2011) Individual differences in chronically defeated male mice: behavioral, endocrine, immune, and neurotrophic changes as markers of vulnerability to the effects of stress. Stress 14:537–548. https://doi.org/10.3109/10253890.2011.562939
Hamani C, Nobrega JN (2012) Preclinical studies modeling deep brain stimulation for depression. Biol Psychiatry 72:916–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.05.024
Hamani C, Schwalb JM, Rezai AR, Dostrovsky JO, Davis KD, Lozano AM (2006) Deep brain stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain: long-term outcome and the incidence of insertional effect. Pain 125:188–196
Hamani C, Diwan M, Isabella S, Lozano AM, Nobrega JN (2010a) Effects of different stimulation parameters on the antidepressant-like response of medial prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation in rats. J Psychiatr Res 44:683–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2009.12.010
Hamani C, Diwan M, Macedo CE, Brandao ML, Shumake J, Gonzalez-Lima F, Raymond R, Lozano AM, Fletcher PJ, Nobrega JN (2010b) Antidepressant-like effects of medial prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation in rats. Biol Psychiatry 67:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.08.025
Hamani C, Nobrega JN, Lozano AM (2010c) Deep brain stimulation in clinical practice and in animal models. Clin Pharmacol Ther 88:559–562. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.2010.133
Hamani C, Mayberg H, Stone S, Laxton A, Haber S, Lozano AM (2011) The subcallosal cingulate gyrus in the context of major depression. Biol Psychiatry 69:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.034
Hamani C, Giacobbe P, Diwan M, Balbino ES, Tong J, Bridgman A, Lipsman N, Lozano AM, Kennedy SH, Nobrega JN (2012a) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors potentiate the effects of deep brain stimulation. Am J Psychiatry 169:1320–1321. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12060754
Hamani C, Machado DC, Hipolide DC, Dubiela FP, Suchecki D, Macedo CE, Tescarollo F, Martins U, Covolan L, Nobrega JN (2012b) Deep brain stimulation reverses anhedonic-like behavior in a chronic model of depression: role of serotonin and brain derived neurotrophic factor. Biol Psychiatry 71:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.08.025
Hamani C, Amorim BO, Wheeler AL, Diwan M, Driesslein K, Covolan L, Butson CR, Nobrega JN (2014) Deep brain stimulation in rats: different targets induce similar antidepressant-like effects but influence different circuits. Neurobiol Dis 71:205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.08.007
Hamani C, Fonoff ET, Parravano DC, Silva VA, Galhardoni R, Monaco B, Navarro J, Yeng LT, Teixeira MJ, Ciampi de Andrade D (2021) Motor cortex stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain: results of a double-blind randomized study. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awab189
Hamani C, Temel Y (2012) Deep brain stimulation for psychiatric disease: contributions and validity of animal models. Sci Transl Med 4:142rv8. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3003722
Hammels C, Pishva E, De Vry J, van den Hove DL, Prickaerts J, van Winkel R, Selten JP, Lesch KP, Daskalakis NP, Steinbusch HW, van Os J, Kenis G, Rutten BP (2015) Defeat stress in rodents: from behavior to molecules. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 59:111–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.10.006
Hogg S, Dalvi A (2004) Acceleration of onset of action in schedule-induced polydipsia: combinations of SSRI and 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptor antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2003.09.020
Holtzheimer PE, Kelley ME, Gross RE, Filkowski MM, Garlow SJ, Barrocas A, Wint D, Craighead MC, Kozarsky J, Chismar R, Moreines JL, Mewes K, Posse PR, Gutman DA, Mayberg HS (2012) Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant unipolar and bipolar depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1456
Holtzheimer PE, Husain MM, Lisanby SH, Taylor SF, Whitworth LA, McClintock S, Slavin KV, Berman J, McKhann GM, Patil PG, Rittberg BR, Abosch A, Pandurangi AK, Holloway KL, Lam RW, Honey CR, Neimat JS, Henderson JM, DeBattista C, Rothschild AJ, Pilitsis JG, Espinoza RT, Petrides G, Mogilner AY, Matthews K, Peichel D, Gross RE, Hamani C, Lozano AM, Mayberg HS (2017) Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a multisite, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet Psychiatry 4:839–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(17)30371-1
Iniguez SD, Riggs LM, Nieto SJ, Dayrit G, Zamora NN, Shawhan KL, Cruz B, Warren BL (2014) Social defeat stress induces a depression-like phenotype in adolescent male c57BL/6 mice. Stress 17:247–255. https://doi.org/10.3109/10253890.2014.910650
Jimenez-Sanchez L, Castane A, Perez-Caballero L, Grifoll-Escoda M, Lopez-Gil X, Campa L, Galofre M, Berrocoso E, Adell A (2016a) Activation of AMPA receptors mediates the antidepressant action of deep brain stimulation of the infralimbic prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 26:2778–2789. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhv133
Jimenez-Sanchez L, Linge R, Campa L, Valdizan EM, Pazos A, Diaz A, Adell A (2016b) Behavioral, neurochemical and molecular changes after acute deep brain stimulation of the infralimbic prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 108:91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.04.020
Kaster MP, Santos AR, Rodrigues AL (2005) Involvement of 5-HT1A receptors in the antidepressant-like effect of adenosine in the mouse forced swimming test. Brain Res Bull 67:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2005.05.025
Krishnan V, Nestler EJ (2011) Animal models of depression: molecular perspectives. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 7:121–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/7854_2010_108
Krishnan V, Han MH, Graham DL, Berton O, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Laplant Q, Graham A, Lutter M, Lagace DC, Ghose S, Reister R, Tannous P, Green TA, Neve RL, Chakravarty S, Kumar A, Eisch AJ, Self DW, Lee FS, Tamminga CA, Cooper DC, Gershenfeld HK, Nestler EJ (2007) Molecular adaptations underlying susceptibility and resistance to social defeat in brain reward regions. Cell 131:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.09.018
Kronfeld-Schor N, Einat H (2012) Circadian rhythms and depression: human psychopathology and animal models. Neuropharmacology 62:101–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.08.020
Kudryavtseva NN, Bakshtanovskaya IV, Koryakina LA (1991) Social model of depression in mice of C57BL/6J strain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:315–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(91)90284-9
Lagace DC, Donovan MH, DeCarolis NA, Farnbauch LA, Malhotra S, Berton O, Nestler EJ, Krishnan V, Eisch AJ (2010) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is functionally important for stress-induced social avoidance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:4436–4441. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0910072107
Lesch KP (1991) 5-HT1A receptor responsivity in anxiety disorders and depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 15:723–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-5846(91)90001-h
Lim SN, Lee ST, Tsai YT, Chen IA, Tu PH, Chen JL, Chang HW, Su YC, Wu T (2007) Electrical stimulation of the anterior nucleus of the thalamus for intractable epilepsy: a long-term follow-up study. Epilepsia 48:342–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00898.x
Lim LW, Janssen ML, Kocabicak E, Temel Y (2015a) The antidepressant effects of ventromedial prefrontal cortex stimulation is associated with neural activation in the medial part of the subthalamic nucleus. Behav Brain Res 279:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.11.008
Lim LW, Prickaerts J, Huguet G, Kadar E, Hartung H, Sharp T, Temel Y (2015b) Electrical stimulation alleviates depressive-like behaviors of rats: investigation of brain targets and potential mechanisms. Transl Psychiatry 5:e535. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2015.24
Lopez-Mendoza D, Aguilar-Bravo H, Swanson HH (1998) Combined effects of Gepirone and (+)WAY 100135 on territorial aggression in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-3057(97)00563-7
Lozano AM, Giacobbe P, Hamani C, Rizvi SJ, Kennedy SH, Kolivakis TT, Debonnel G, Sadikot AF, Lam RW, Howard AK, Ilcewicz-Klimek M, Honey CR, Mayberg HS (2012) A multicenter pilot study of subcallosal cingulate area deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. J Neurosurg 116:315–322. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.10.JNS102122
Lucki I (1996) Serotonin receptor specificity in anxiety disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 57(Suppl 6):5–10
Lucki I, Singh A, Kreiss DS (1994) Antidepressant-like behavioral effects of serotonin receptor agonists. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 18:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0149-7634(94)90039-6
Lueptow LM (2017) Novel object recognition test for the investigation of learning and memory in mice. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/55718
Malone DA Jr, Dougherty DD, Rezai AR, Carpenter LL, Friehs GM, Eskandar EN, Rauch SL, Rasmussen SA, Machado AG, Kubu CS, Tyrka AR, Price LH, Stypulkowski PH, Giftakis JE, Rise MT, Malloy PF, Salloway SP, Greenberg BD (2009) Deep brain stimulation of the ventral capsule/ventral striatum for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 65:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.08.029
Maluach AM, Misquitta KA, Prevot TD, Fee C, Sibille E, Banasr M, Andreazza AC (2017) Increased neuronal DNA/RNA oxidation in the frontal cortex of mice subjected to unpredictable chronic mild stress. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks) 1.https://doi.org/10.1177/2470547017724744
Maura G, Raiteri M (1986) Cholinergic terminals in rat hippocampus possess 5-HT1B receptors mediating inhibition of acetylcholine release. Eur J Pharmacol 129:333–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(86)90443-7
Mayberg HS, Lozano AM, Voon V, McNeely HE, Seminowicz D, Hamani C, Schwalb JM, Kennedy SH (2005) Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Neuron 45:651–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.02.014
Mayorga AJ, Dalvi A, Page ME, Zimov-Levinson S, Hen R, Lucki I (2001) Antidepressant-like behavioral effects in 5-hydroxytryptamine(1A) and 5-hydroxytryptamine(1B) receptor mutant mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:1101–1107
Medrihan L, Sagi Y, Inde Z, Krupa O, Daniels C, Peyrache A, Greengard P (2017) Initiation of behavioral response to antidepressants by cholecystokinin neurons of the dentate gyrus. Neuron 95(564–576):e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.06.044
Moore P, Landolt HP, Seifritz E, Clark C, Bhatti T, Kelsoe J, Rapaport M, Gillin JC (2000) Clinical and physiological consequences of rapid tryptophan depletion. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:601–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00161-5
Moshe H, Gal R, Barnea-Ygael N, Gulevsky T, Alyagon U, Zangen A (2016) Prelimbic stimulation ameliorates depressive-like behaviors and increases regional BDNF expression in a novel drug-resistant animal model of depression. Brain Stimul 9:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2015.10.009
Muscat R, Towell A, Willner P (1988) Changes in dopamine autoreceptor sensitivity in an animal model of depression. Psychopharmacology 94:545–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00212853
Nautiyal KM, Tritschler L, Ahmari SE, David DJ, Gardier AM, Hen R (2016) A lack of serotonin 1B autoreceptors results in decreased anxiety and depression-related behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:2941–2950. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2016.109
Neumaier JF, Root DC, Hamblin MW (1996) Chronic fluoxetine reduces serotonin transporter mRNA and 5-HT1B mRNA in a sequential manner in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(96)00095-4
O’Neill MF, Conway MW (2001) Role of 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(1B) receptors in the mediation of behavior in the forced swim test in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:391–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00196-2
O’Neill MF, Fernandez AG, Palacios JM (1996) GR 127935 blocks the locomotor and antidepressant-like effects of RU 24969 and the action of antidepressants in the mouse tail suspension test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:535–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(95)02047-0
Papp M, Gruca P, Lason M, Tota-Glowczyk K, Niemczyk M, Litwa E, Willner P (2018) Rapid antidepressant effects of deep brain stimulation of the pre-frontal cortex in an animal model of treatment-resistant depression. J Psychopharmacol 32:1133–1140. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881118791737
Papp M, Gruca P, Lason M, Niemczyk M, Willner P (2019) The role of prefrontal cortex dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in the mechanism of action of venlafaxine and deep brain stimulation in animal models of treatment-responsive and treatment-resistant depression. J Psychopharmacol 33:748–756. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881119827889
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2012) Paxinos and Franklin’s the mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic Press
Perez-Caballero L, Perez-Egea R, Romero-Grimaldi C, Puigdemont D, Molet J, Caso JR, Mico JA, Perez V, Leza JC, Berrocoso E (2014) Early responses to deep brain stimulation in depression are modulated by anti-inflammatory drugs. Mol Psychiatry 19:607–614. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2013.63
Perez-Caballero L, Soto-Montenegro ML, Hidalgo-Figueroa M, Mico JA, Desco M, Berrocoso E (2018) Deep brain stimulation electrode insertion and depression: patterns of activity and modulation by analgesics. Brain Stimul 11:1348–1355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2018.06.010
Popova NK, Naumenko VS (2013) 5-HT1A receptor as a key player in the brain 5-HT system. Rev Neurosci 24:191–204. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2012-0082
Prevot TD, Misquitta KA, Fee C, Newton DF, Chatterjee D, Nikolova YS, Sibille E, Banasr M (2019) Residual avoidance: a new, consistent and repeatable readout of chronic stress-induced conflict anxiety reversible by antidepressant treatment. Neuropharmacology 153:98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.005
Puigdemont D, Portella M, Perez-Egea R, Molet J, Gironell A, de Diego-Adelino J, Martin A, Rodriguez R, Alvarez E, Artigas F, Perez V (2015) A randomized double-blind crossover trial of deep brain stimulation of the subcallosal cingulate gyrus in patients with treatment-resistant depression: a pilot study of relapse prevention. J Psychiatry Neurosci 40:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.130295
Raab A, Dantzer R, Michaud B, Mormede P, Taghzouti K, Simon H, Le Moal M (1986) Behavioural, physiological and immunological consequences of social status and aggression in chronically coexisting resident-intruder dyads of male rats. Physiol Behav 36:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(86)90007-7
Reznikov R, Binko M, Nobrega JN, Hamani C (2016) Deep brain stimulation in animal models of fear, anxiety, and posttraumatic stress disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:2810–2817. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2016.34
Riva-Posse P, Choi KS, Holtzheimer PE, McIntyre CC, Gross RE, Chaturvedi A, Crowell AL, Garlow SJ, Rajendra JK, Mayberg HS (2014) Defining critical white matter pathways mediating successful subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 76:963–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.03.029
Riva-Posse P, Choi KS, Holtzheimer PE, Crowell AL, Garlow SJ, Rajendra JK, McIntyre CC, Gross RE, Mayberg HS (2018) A connectomic approach for subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation surgery: prospective targeting in treatment-resistant depression. Mol Psychiatry 23:843–849. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.59
Rogoz Z, Kabzinski M, Sadaj W, Rachwalska P, Gadek-Michalska A (2012) Effect of co-treatment with fluoxetine or mirtazapine and risperidone on the active behaviors and plasma corticosterone concentration in rats subjected to the forced swim test. Pharmacol Rep 64:1391–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1734-1140(12)70936-2
Rummel J, Voget M, Hadar R, Ewing S, Sohr R, Klein J, Sartorius A, Heinz A, Mathe AA, Vollmayr B, Winter C (2016) Testing different paradigms to optimize antidepressant deep brain stimulation in different rat models of depression. J Psychiatr Res 81:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.06.016
Sankar T, Chakravarty MM, Jawa N, Li SX, Giacobbe P, Kennedy SH, Rizvi SJ, Mayberg HS, Hamani C, Lozano AM (2020) Neuroanatomical predictors of response to subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. J Psychiatry Neurosci 45:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.180207
Sari Y (2004) Serotonin1B receptors: from protein to physiological function and behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:565–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2004.08.008
Schlaepfer TE, Cohen MX, Frick C, Kosel M, Brodesser D, Axmacher N, Joe AY, Kreft M, Lenartz D, Sturm V (2008) Deep brain stimulation to reward circuitry alleviates anhedonia in refractory major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1301408
Schlaepfer TE, Bewernick BH, Kayser S, Madler B, Coenen VA (2013) Rapid effects of deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant major depression. Biol Psychiatry 73:1204–1212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.01.034
Srejic LR, Hamani C, Hutchison WD (2015) High-frequency stimulation of the medial prefrontal cortex decreases cellular firing in the dorsal raphe. Eur J Neurosci 41:1219–1226. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12856
Takagishi M, Chiba T (1991) Efferent projections of the infralimbic (area 25) region of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tracer PHA-L study. Brain Res 566:26–39
Takahashi K, Kitamura Y, Ushio S, Sendo T (2020) Immobility-reducing effects of ketamine during the forced swim test on 5-HT1A receptor activity in the medial prefrontal cortex in an intractable depression model. Acta Med Okayama 74:301–306. https://doi.org/10.18926/AMO/60368
Tao R, Ma Z, Auerbach SB (1996) Differential regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release by GABAA and GABAB receptors in midbrain raphe nuclei and forebrain of rats. Br J Pharmacol 119:1375–1384. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb16049.x
Tasker RR (1998) Deep brain stimulation is preferable to thalamotomy for tremor suppression. Surg Neurol 49: 145–53; discussion 153–4.
Tatarczynska E, Klodzinska A, Chojnacka-Wojcik E (2002) Effects of combined administration of 5-HT1A and/or 5-HT1B receptor antagonists and paroxetine or fluoxetine in the forced swimming test in rats. Pol J Pharmacol 54:615–623
Tatarczynska E, Klodzinska A, Stachowicz K, Chojnacka-Wojcik E (2004) Effects of a selective 5-HT1B receptor agonist and antagonists in animal models of anxiety and depression. Behav Pharmacol 15:523–534. https://doi.org/10.1097/00008877-200412000-00001
Thiele S, Furlanetti L, Pfeiffer LM, Coenen VA, Dobrossy MD (2018) The effects of bilateral, continuous, and chronic Deep Brain Stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle in a rodent model of depression. Exp Neurol 303:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.02.002
Tiger M, Varnas K, Okubo Y, Lundberg J (2018) The 5-HT1B receptor - a potential target for antidepressant treatment. Psychopharmacology 235:1317–1334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4872-1
Torres-Sanchez S, Perez-Caballero L, Berrocoso E (2017) Cellular and molecular mechanisms triggered by Deep Brain Stimulation in depression: a preclinical and clinical approach. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 73:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.09.005
Torres-Sanchez S, Perez-Caballero L, Mico JA, Celada P, Berrocoso E (2018) Effect of Deep Brain Stimulation of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex on the noradrenergic system in rats. Brain Stimul 11:222–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2017.10.003
Veerakumar A, Challis C, Gupta P, Da J, Upadhyay A, Beck SG, Berton O (2014) Antidepressant-like effects of cortical deep brain stimulation coincide with pro-neuroplastic adaptations of serotonin systems. Biol Psychiatry 76:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.12.009
Volle J, Bregman T, Scott B, Diwan M, Raymond R, Fletcher PJ, Nobrega JN, Hamani C (2018) Deep brain stimulation and fluoxetine exert different long-term changes in the serotonergic system. Neuropharmacology 135:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.005
Warren BL, Vialou VF, Iniguez SD, Alcantara LF, Wright KN, Feng J, Kennedy PJ, Laplant Q, Shen L, Nestler EJ, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2013) Neurobiological sequelae of witnessing stressful events in adult mice. Biol Psychiatry 73:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.06.006
Warren BL, Sial OK, Alcantara LF, Greenwood MA, Brewer JS, Rozofsky JP, Parise EM, Bolanos-Guzman CA (2014) Altered gene expression and spine density in nucleus accumbens of adolescent and adult male mice exposed to emotional and physical stress. Dev Neurosci 36:250–260. https://doi.org/10.1159/000362875
Willner P (2017) The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: history, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol Stress 6:78–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ynstr.2016.08.002
Willner P, Towell A, Sampson D, Sophokleous S, Muscat R (1987) Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology 93:358–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00187257
Willner P, Muscat R, Papp M (1992) Chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia: a realistic animal model of depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 16:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80194-0
Zanelati TV, Biojone C, Moreira FA, Guimaraes FS, Joca SR (2010) Antidepressant-like effects of cannabidiol in mice: possible involvement of 5-HT1A receptors. Br J Pharmacol 159:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00521.x
Funding
This work was supported in part with funds from the Harquail Centre for Neuromodulation and Veteran Affairs Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ES, MD, TR, HK, ACPC, and FVG conducted behavioural and neurochemical experiments. ES and CH analysed the results and wrote the manuscript. PG and NL critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Suppl. Fig 1.
Representative blots showing 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B expression in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) and hippocampus (HPC) of stress exposed mice receiving deep brain stimulation (DBS), sham stimulation or controls with no implanted electrodes. (PNG 795 kb)

Suppl. Fig 2.
Representative blots showing 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B expression in the raphe and nucleus accumbens (NAcc) of stress exposed mice receiving deep brain stimulation (DBS), sham stimulation or controls with no implanted electrodes. (PNG 742 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Silk, E., Diwan, M., Rabelo, T. et al. Serotonin 5-HT1B receptors mediate the antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects of ventromedial prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation in a mouse model of social defeat. Psychopharmacology 239, 3875–3892 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-022-06259-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-022-06259-6