Abstract
Rationale
Job stress can lead to job burnout, and BDNF polymorphism has been found to be involved in its psychopathological mechanism. Research needs a better understanding of the important role of gene × environment (i.e., BDNF polymorphism × job stress) interaction on job burnout.
Objective
This study aimed to explore how BDNF rs6265 polymorphism may moderate the relationship between job stress and job burnout.
Methods
Three hundred forty-one healthy participants (187 males and 154 females) from a Chinese university were included. The present study used a standardized questionnaire including demographic characteristics, job stress assessed by the House and Rizzo’s Work Stress Scale, and job burnout assessed by the Maslach Burnout Inventory-General Survey. The BDNF rs6265 polymorphism was genotyped.
Results
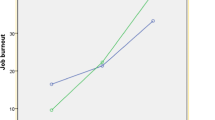
Job stress showed a positive correlation with emotional exhaustion (p < 0.001), cynicism (p < 0.001), and reduced personal accomplishment (p < 0.01). The main effects of BDNF rs6265 polymorphism on emotional exhaustion and cynicism were significant [F(1,333) = 5.136, p = 0.024; F(1,333) = 4.175, p = 0.042, respectively]. The interaction between job stress and BDNF rs6265 on cynicism was significant (△ R2 = 0.013, p = 0.014) after controlling for age, sex, education, and position, indicating that individuals with BDNF rs6265 TT genotype showed higher level of cynicism when in high job stress.
Conclusions
The results provided evidence for the association of BDNF gene rs6265 polymorphism, job stress, and their interaction with job burnout. Individuals with TT genotype in BDNF rs6265 might be susceptible to stressful situations, which would lead to cynicism.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera M, Arias B, Wichers M, Barrantes-Vidal N, Moya J, Villa H, van Os J, Ibáñez MI, Ruipérez MA, Ortet G, Fañanás L (2009) Early adversity and 5-HTT/BDNF genes: new evidence of gene-environment interactions on depressive symptoms in a general population. Psychol Med 39:1425–1432
Bakusic J, Ghosh M, Polli A, Bekaert B, Schaufeli W, Claes S, Godderis L (2020) Epigenetic perspective on the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in burnout. Transl Psychiatry 10:354
Belsky J, Jonassaint C, Pluess M, Stanton M, Brummett B, Williams R (2009) Vulnerability genes or plasticity genes? Mol Psychiatry 14:746–754
Belsky J, Pluess M (2009) Beyond diathesis stress: differential susceptibility to environmental influences. Psychol Bull 135:885–908
Benjamin DJ, Cesarini D, van der Loos MJ, Dawes CT, Koellinger PD, Magnusson PK, Chabris CF, Conley D, Laibson D, Johannesson M, Visscher PM (2012) The genetic architecture of economic and political preferences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:8026–8031
Blom V, Bergström G, Hallsten L, Bodin L, Svedberg P (2012) Genetic susceptibility to burnout in a Swedish twin cohort. Eur J Epidemiol 27:225–231
Bodenmann G, Meuwly N, Bradbury TN, Gmelch S, Ledermann T (2010) Stress, anger, and verbal aggression in intimate relationships: moderating effects of individual and dyadic coping. J Soc Pers Relat 27:408–424
Brotheridge CM, Grandey AA (2002) Emotional labor and burnout: comparing two perspectives of “People work.” J Vocat Behav 60:17–39
Brown GW, Craig TK, Harris TO, Herbert J, Hodgson K, Tansey KE, Uher R (2014) Functional polymorphism in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene interacts with stressful life events but not childhood maltreatment in the etiology of depression. Depress Anxiety 31:326–334
Carlson BC, Thompson JA (1995) Job burnout and job leaving in public school teachers: Implications for stress management. Int J Stress Manag 2:15–29
Chan DW (1998) Stress, coping strategies, and psychological distress among secondary school teachers in hong kong. Am Educ Res J 35:145–163
Chen J, Li X, McGue M (2012) Interacting effect of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and stressful life events on adolescent depression. Genes Brain Behav 11:958–965
Czira ME, Wersching H, Baune BT, Berger K (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene polymorphisms, neurotransmitter levels, and depressive symptoms in an elderly population. Age (dordr) 34:1529–1541
Dias VV, Brissos S, Frey BN, Andreazza AC, Cardoso C, Kapczinski F (2009) Cognitive function and serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 11:663–671
Dragano N, He Y, Moebus S, Jöckel KH, Erbel R, Siegrist J (2008) Two models of job stress and depressive symptoms. Results from a population-based study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 43:72–78
Dyrbye LN, Massie FS Jr, Eacker A, Harper W, Power D, Durning SJ, Thomas MR, Moutier C, Satele D, Sloan J, Shanafelt TD (2010) Relationship between burnout and professional conduct and attitudes among US medical students. JAMA 304:1173–1180
Egan MF, Kojima M, Callicott JH, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Bertolino A, Zaitsev E, Gold B, Goldman D, Dean M, Lu B, Weinberger DR (2003) The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 112:257–269
Elbarazi I, Loney T, Yousef S, Elias A (2017) Prevalence of and factors associated with burnout among health care professionals in Arab countries: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res 17:491
Fang Y, Li Z, Wu S, Wang C, Dong Y, He S (2020) Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphisms moderate the relationship between job stress and general trust in Chinese Han university teachers. J Affect Disord 260:18–23
Folkman S (2013) Stress: Appraisal and Coping. In: Gellman MD, Turner JR (ed) Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine. Springer, New York
Gatt JM, Nemeroff CB, Dobson-Stone C, Paul RH, Bryant RA, Schofield PR, Gordon E, Kemp AH, Williams LM (2009) Interactions between BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and early life stress predict brain and arousal pathways to syndromal depression and anxiety. Mol Psychiatry 14:681–695
He SC, Wu S, Du XD, Jia Q, Wang C, Wu F, Ning Y, Wang D, Wang L, Zhang XY (2019) Interactive effects of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1 gene and work stress on burnout in medical professionals in a Chinese Han population. J Affect Disord 252:1–8
He SC, Wu S, Wang C, Du XD, Yin G, Jia Q, Zhang Y, Wang L, Soares JC, Zhang XY (2018) Interaction between job stress and the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism affects depressive symptoms in Chinese healthcare workers. J Affect Disord 236:157–163
He SC, Wu S, Wang C, Wang DM, Wang J, Xu H, Wang L, Zhang XY (2020) Interaction between job stress, serum BDNF level and the BDNF rs2049046 polymorphism in job burnout. J Affect Disord 266:671–677
He SC, Zhang YY, Zhan JY, Wang C, Du XD, Yin GZ, Cao B, Ning YP, Soares JC, Zhang XY (2017) Burnout and cognitive impairment: associated with serum BDNF in a Chinese Han population. Psychoneuroendocrinology 77:236–243
House RJ, Rizzo JR (1972) Role conflict and ambiguity as critical variables in a model of organizational behavior. Organ Behav Hum Perform 7:467–505
Hyman C, Hofer M, Barde YA, Juhasz M, Yancopoulos GD, Squinto SP, Lindsay RM (1991) BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Nature 350:230–232
Ishaq R, Mahmood A (2017) Relationship between job stress and employee burnout-the moderating role of self-efficacy for university teachers. J Res Reflect Educ 11:100–112
Jiang R, Brummett BH, Babyak MA, Siegler IC, Williams RB (2013) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met and adulthood chronic stress interact to affect depressive symptoms. J Psychiatr Res 47:233–239
Jiang Y, Lian YL, Liu JW (2016) Influence of job burnout on sleep quality of oilfield workers. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 34:86–89
Joffe RT, Gatt JM, Kemp AH, Grieve S, Dobson-Stone C, Kuan SA, Schofield PR, Gordon E, Williams LM (2009) Brain derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism, the five factor model of personality and hippocampal volume: implications for depressive illness. Hum Brain Mapp 30:1246–1256
Khamisa N, Oldenburg B, Peltzer K, Ilic D (2015) Work related stress, burnout, job satisfaction and general health of nurses. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:652–666
Khamisa N, Peltzer K, Oldenburg B (2013) Burnout in relation to specific contributing factors and health outcomes among nurses: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:2214–2240
Kowiański P, Lietzau G, Czuba E, Waśkow M, Steliga A, Moryś J (2018) BDNF: a key factor with multipotent impact on brain signaling and synaptic plasticity. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38:579–593
Kyriacou C (2001) Teacher stress: Directions for future research. Educational Review 53:27–35
Lambert EG, Qureshi H, Frank J, Keena LD, Hogan NL (2016) The relationship of work-family conflict with job stress among Indian police officers: A research note. Police Pract Res 18:37–48
Li CP, Shi K (2003) The influence of distributive justice and procedural justice on job burnout. Acta Psychologica Sinica 35:677–684
Lu ACC, Gursoy D (2016) Impact of job burnout on satisfaction and turnover intention: do generational differences matter? J Hosp Tour Res 40:210–235
Ma J, Liang Y (1997) Structural components of job stress and its relationship with management positions and education levels. Chin J Appl Psychol 3:21–26
Malik SA (2015) Time pressure and challenge appraisal as predictors of job satisfaction: Empirical evidence from Pakistani Universities. SAGE Open 5:1–9
Maslach C, Schaufeli WB, Leiter MP (2001) Job burnout. Annu Rev Psychol 52:397–422
Monroe SM, Simons AD (1991) Diathesis-stress theories in the context of life stress research: implications for the depressive disorders. Psychol Bull 110:406–425
Numakawa T, Suzuki S, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Richards M, Kunugi H (2010) BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol Histopathol 25:237–258
Onen Sertoz O, Tolga Binbay I, Koylu E, Noyan A, Yildirim E, Elbi Mete H (2008) The role of BDNF and HPA axis in the neurobiology of burnout syndrome. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1459–1465
Panatik SAB, Rajab A, Shah IM, Rahman HA, Yusoff RM, Badri SKBZ (2012) Work-family conflict, stress and psychological strain in higher education. International Conference on Education and Management Innovation 30:67–71
Pillai A, Bruno D, Sarreal AS, Hernando RT, Saint-Louis LA, Nierenberg J, Ginsberg SD, Pomara N, Mehta PD, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Buckley PF (2012) Plasma BDNF levels vary in relation to body weight in females. PLoS One 7:e39358
Ribeiro L, Busnello JV, Cantor RM, Whelan F, Whittaker P, Deloukas P, Wong ML, Licinio J (2007) The brain-derived neurotrophic factor rs6265 (Val66Met) polymorphism and depression in Mexican-Americans. Neuroreport 18:1291–1293
Salami SO (2007) Management of stress among trainee-teachers through cognitive-behavioural therapy. Indian J Psychol Sci 4:299–307
Shao D, Zhang HH, Long ZT, Li J, Bai HY, Li JJ, Cao FL (2018) Effect of the interaction between oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) and stressful life events on aggression in Chinese Han adolescents. Psychoneuroendocrinology 96:35–41
Sjors Dahlman A, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Glise K, Jonsdottir IH (2019) Growth factors and neurotrophins in patients with stress-related exhaustion disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 109:104415
Squiers JJ, Lobdell KW, Fann JI, DiMaio JM (2017) Physician burnout: are we treating the symptoms instead of the disease? Ann Thorac Surg 104:1117–1122
Sulkava S, Ollila HM, Ahola K, Partonen T, Viitasalo K, Kettunen J, Lappalainen M, Kivimäki M, Vahtera J, Lindström J, Härmä M, Puttonen S, Salomaa V, Paunio T (2013) Genome-wide scan of job-related exhaustion with three replication studies implicate a susceptibility variant at the UST gene locus. Hum Mol Genet 22:3363–3372
Tapia-Arancibia L, Rage F, Givalois L, Arancibia S (2004) Physiology of BDNF: focus on hypothalamic function. Front Neuroendocrinol 25:77–107
Taylor WD, Züchner S, McQuoid DR, Steffens DC, Speer MC, Krishnan KR (2007) Allelic differences in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism in late-life depression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 15:850–857
van Wingen G, Rijpkema M, Franke B, van Eijndhoven P, Tendolkar I, Verkes RJ, Buitelaar J, Fernández G (2010) The brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism affects memory formation and retrieval of biologically salient stimuli. Neuroimage 50:1212–1218
Verhagen M, van der Meij A, van Deurzen PA, Janzing JG, Arias-Vásquez A, Buitelaar JK, Franke B (2010) Meta-analysis of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in major depressive disorder: effects of gender and ethnicity. Mol Psychiatry 15:260–271
Yamada K, Mizuno M, Nabeshima T (2002) Role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory. Life Sci 70:735–744
Yan Q, Rosenfeld RD, Matheson CR, Hawkins N, Lopez OT, Bennett L, Welcher AA (1997) Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 78:431–448
Yasutake C (2006) Serum BDNF, TNF- α and IL-1β levels in dementia patients. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:406
Zhong J, You J, Gan Y, Zhang Y, Lu C, Wang H (2009) Job stress, burnout, depression symptoms, and physical health among Chinese university teachers. Psychol Rep 105:1248–1254
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the university faculty who participated in the study, and also to the hospital staff who made contributions to the clinical assessments.
Funding
Shu-chang He is currently receiving a grant (grant number 81871060) from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. For the remaining authors, none were declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Haiying Jia and Mingwei He contribute to this study equally. They are considered as joint co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, H., He, M., Zhang, X. et al. The relationship between job stress and job burnout moderated by BDNF rs6265 polymorphism. Psychopharmacology 238, 2963–2971 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05911-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05911-x