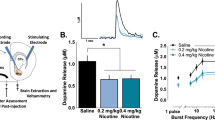
Abstract
Rationale
The behavioral effects of the nicotine metabolites nornicotine and cotinine have not been investigated extensively.
Objectives
To evaluate the effects of nicotine, cotinine, and nornicotine, given alone or in combination, on locomotor activity and emission of ultrasonic vocalizations in male adult rats.
Methods
Rats were first given home cage nicotine injections to make them tolerant to the drug’s locomotor depressant effects. On subsequent days, locomotor activity (LMA) and ultrasonic vocalizations were recorded in an open field, for 60 min after challenge injection, using repeated measures designs. In single-drug experiments, subjects were tested with nicotine 0.05–0.4 mg/kg, cotinine 0.03–3 mg/kg, or nornicotine 0.1–10 mg/kg. In drug-combination experiments, saline or nicotine 0.2 mg/kg challenge was preceded by cotinine (0, 0.3, 3 mg/kg) or nornicotine (0, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3 mg/kg) injection.
Results
High doses of nornicotine increased LMA and blunted the locomotor stimulant effect of nicotine. Less consistently, nicotine and high doses of nornicotine decreased the 50-kHz call rate, with no clear evidence of a nornicotine × nicotine interaction. Cotinine, given alone or before nicotine injection, altered neither LMA nor the call rate. No drug altered the relative prevalence of flat vs. trill 50-kHz call subtypes, except that the highest dose of nornicotine promoted flat calls over trills. No drug evoked 22-kHz calls.
Conclusion
Nornicotine can exert an acute anti-nicotine effect in vivo, as previously reported in vitro. The finding that nicotine did not detectably alter the 50-kHz call profile appears consistent with this drug’s mild subjective effects in human subjects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardo MT, Green TA, Crooks PA, Dwoskin LP (1999) Nornicotine is self-administered intravenously by rats. Psychopharmacology 146:290–296
Benowitz NL, Jacob P III (1994) Metabolism of nicotine to cotinine studied by a dual stable isotope method. Clin Pharmacol Ther 56:483–493
Benowitz NL, Jacob P III, Fong I, Gupta S (1994) Nicotine metabolic profile in man: comparison of cigarette smoking and transdermal nicotine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:296–303
Benowitz NL, Kuyt F, Jacob P, Jones RT, Osman AL (1983) Cotinine disposition and effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 34:604–611
Best LM, Zhao LL, Scardochio T, Clarke PB (2017) Effects of repeated morphine on ultrasonic vocalizations in adult rats: increased 50-kHz call rate and altered subtype profile. Psychopharmacology 234:155–165
Briggs CA, McKenna DG (1998) Activation and inhibition of the human a7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by agonists. Neuropharmacology 37:1095–1102
Brudzynski SM (2015) Pharmacology of ultrasonic vocalizations in adult rats: significance, call classification and neural substrate. Curr Neuropharmacol 13:180–192
Buccafusco JJ, Terry AV (2003) The potential role of cotinine in the cognitive and neuroprotective actions of nicotine. Life Sci 72:2931–2942
Burke CJ, Kisko TM, Swiftwolfe H, Pellis SM, Euston DR (2017) Specific 50-kHz vocalizations are tightly linked to particular types of behavior in juvenile rats anticipating play. PLoS One 12:e0175841
Caine SB, Collins GT, Thomsen M, Wright C, Lanier RK, Mello NK (2014) Nicotine-like behavioral effects of the minor tobacco alkaloids nornicotine, anabasine, and anatabine in male rodents. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 22:9–22
Clarke PBS, Kumar R (1983a) Characterization of the locomotor stimulant action of nicotine in tolerant rats. Br J Pharmacol 80:587–594
Clarke PBS, Kumar R (1983b) The effects of nicotine on locomotor activity in non-tolerant and tolerant rats. Br J Pharmacol 78:329–337
Clemens KJ, Caille S, Stinus L, Cador M (2009) The addition of five minor tobacco alkaloids increases nicotine-induced hyperactivity, sensitization and intravenous self-administration in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:1–12
Constantin A, Clarke PBS (2018) Reinforcement enhancement by nicotine in adult rats: behavioral selectivity and relation to mode of delivery and blood nicotine levels. Psychopharmacology 235:641–650
Craig EL, Zhao B, Cui JZ, Novalen M, Miksys S, Tyndale RF (2014) Nicotine pharmacokinetics in rats is altered as a function of age, impacting the interpretation of animal model data. Drug Metab Dispos 42:1447–1455
Crooks PA, Dwoskin LP (1997) Contribution of CNS nicotine metabolites to the neuropharmacological effects of nicotine and tobacco smoking. Biochem Pharmacol 54:743–753
Crooks PA, Li M, Dwoskin LP (1997) Metabolites of nicotine in rat brain after peripheral nicotine administration. Cotinine, nornicotine, and norcotinine. Drug Metab Dispos 25:47–54
Dar R, Kaplan R, Shaham L, Frenk H (2007) Euphoriant effects of nicotine in smokers: fact or artifact? Psychopharmacology 191:203–210
Dwoskin LP, Crooks PA, Teng LH, Green TA, Bardo MT (1999a) Acute and chronic effects of nornicotine on locomotor activity in rats: altered response to nicotine. Psychopharmacology 145:442–451
Dwoskin LP, Teng L, Buxton ST, Crooks PA (1999b) (S)-(−)-cotinine, the major brain metabolite of nicotine, stimulates nicotinic receptors to evoke [3H]dopamine release from rat striatal slices in a calcium-dependent manner. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:905–911
Dwoskin LP, Teng L, Buxton ST, Ravard A, Deo N, Crooks PA (1995) Minor alkaloids of tobacco release [3H]dopamine from superfused rat striatal slices. Eur J Pharmacol 276:195–199
Dwoskin LP, Teng LH, Crooks PA (2001) Nornicotine, a nicotine metabolite and tobacco alkaloid: desensitization of nicotinic receptor-stimulated dopamine release from rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol 428:69–79
Earla R, Ande A, McArthur C, Kumar A, Kumar S (2014) Enhanced nicotine metabolism in HIV-1-positive smokers compared with HIV-negative smokers: simultaneous determination of nicotine and its four metabolites in their plasma using a simple and sensitive electrospray ionization liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry technique. Drug Metab Dispos 42:282–293
Engelhardt KA, Fuchs E, Schwarting RK, Wohr M (2017) Effects of amphetamine on pro-social ultrasonic communication in juvenile rats: implications for mania models. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 27:261–273
Fudala PJ, Iwamoto ET (1986) Further studies on nicotine-induced conditioned place preference in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:1041–1049
Ghosheh O, Dwoskin LP, Li WK, Crooks PA (1999) Residence times and half-lives of nicotine metabolites in rat brain after acute peripheral administration of [2′-(14)C]nicotine. Drug Metab Dispos 27:1448–1455
Ghosheh OA, Dwoskin LP, Miller DK, Crooks PA (2001) Accumulation of nicotine and its metabolites in rat brain after intermittent or continuous peripheral administration of [2′- (14)C]nicotine. Drug Metab Dispos 29:645–651
Goldberg SR, Risner ME, Stolerman IP, Reavill C, Garcha HS (1989) Nicotine and some related compounds: effects on schedule-controlled behaviour and discriminative properties in rats. Psychopharmacology 97:295–302
Green TA, Brown RW, Phillips SB, Dwoskin LP, Bardo MT (2002) Locomotor stimulant effects of nornicotine: role of dopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:87–94
Green TA, Crooks PA, Bardo MT, Dwoskin LP (2001) Contributory role for nornicotine in nicotine neuropharmacology: nornicotine-evoked [3H]dopamine overflow from rat nucleus accumbens slices. Biochem Pharmacol 62:1597–1603
Green TA, Phillips SB, Crooks PA, Dwoskin LP, Bardo MT (2000) Nornicotine pretreatment decreases intravenous nicotine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology 152:289–294
Hatsukami D, Pentel PR, Jensen J, Nelson D, Allen SS, Goldman A, Rafael D (1998) Cotinine: effects with and without nicotine. Psychopharmacology 135:141–150
Hukkanen J, Jacob P III, Benowitz NL (2005) Metabolism and disposition kinetics of nicotine. Pharmacol Rev 57:79–115
Kalman D (2002) The subjective effects of nicotine: methodological issues, a review of experimental studies, and recommendations for future research. Nicotine Tob Res 4:25–70
Keenan RM, Hatsukami DK, Pentel PR, Thompson TN, Grillo MA (1994) Pharmacodynamic effects of cotinine in abstinent cigarette smokers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 55:581–590
Kyerematen GA, Morgan M, Warner G, Martin LF, Vesell ES (1990a) Metabolism of nicotine by hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 40:1747–1756
Kyerematen GA, Morgan ML, Chattopadhyay B, DeBethizy JD, Vesell ES (1990b) Disposition of nicotine and eight metabolites in smokers and nonsmokers: identification in smokers of two metabolites that are longer lived than cotinine. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 48:641–651
Kyerematen GA, Vesell ES (1991) Metabolism of nicotine. Drug Metab Rev 23:3–41
Laplagne DA, Elias CM (2016) Rats synchronise locomotion with ultrasonic vocalizations at the subsecond time scale. Front Behav Neurosci 10:184
Li P, Beck WD, Callahan PM, Terry AV, Bartlett MG (2012) Quantitation of cotinine and its metabolites in rat plasma and brain tissue by hydrophilic interaction chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-MS/MS). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 907:117–125
Lin YC, Zhao LL, Clarke PBS (2018) Effects of acute morphine withdrawal on ultrasonic vocalizations in adult rats: unchanged 50-kHz call rate and altered subtype profile. Psychopharmacology 235:1945–1953
Liu B, Chen C, Wu D, Su Q (2008) Enantiomeric analysis of anatabine, nornicotine and anabasine in commercial tobacco by multi-dimensional gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 865:13–17
Louis M, Clarke PBS (1998) Effect of ventral tegmental 6-hydroxydopamine lesions on the locomotor stimulant action of nicotine in rats. Neuropharmacology 37:1503–1513
Lu Y, Grady S, Marks MJ, Picciotto M, Changeux JP, Collins AC (1998) Pharmacological characterization of nicotinic receptor-stimulated GABA release from mouse brain synaptosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:648–657
Lu Y, Marks MJ, Collins AC (1999) Desensitization of nicotinic agonist-induced [3H]gamma-aminobutyric acid release from mouse brain synaptosomes is produced by subactivating concentrations of agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291:1127–1134
Marusich JA, Darna M, Wilson AG, Denehy ED, Ebben A, Deaciuc AG, Dwoskin LP, Bardo MT, Lefever TW, Wiley JL, Reissig CJ, Jackson KJ (2017) Tobacco’s minor alkaloids: effects on place conditioning and nucleus accumbens dopamine release in adult and adolescent rats. Eur J Pharmacol 814:196–206
Miksys S, Hoffmann E, Tyndale RF (2000) Regional and cellular induction of nicotine-metabolizing CYP2B1 in rat brain by chronic nicotine treatment. Biochem Pharmacol 59:1501–1511
Moyer TP, Charlson JR, Enger RJ, Dale LC, Ebbert JO, Schroeder DR, Hurt RD (2002) Simultaneous analysis of nicotine, nicotine metabolites, and tobacco alkaloids in serum or urine by tandem mass spectrometry, with clinically relevant metabolic profiles. Clin Chem 48:1460–1471
Oliver JL, Pashmi G, Barnett P, Mettens P, Biemans R, Monteyne P, Palmantier R, Gallagher T, Ramaya S, Wonnacott S (2007) Development of an anti-cotinine vaccine to potentiate nicotine-based smoking cessation strategies. Vaccine 25:7354–7362
Papke RL, Dwoskin LP, Crooks PA (2007) The pharmacological activity of nicotine and nornicotine on nAChRs subtypes: relevance to nicotine dependence and drug discovery. J Neurochem 101:160–167
Pereira M, Andreatini R, Schwarting RK, Brenes JC (2014) Amphetamine-induced appetitive 50-kHz calls in rats: a marker of affect in mania? Psychopharmacology 231:2567–2577
Picciotto MR, Addy NA, Mineur YS, Brunzell DH (2008) It is not “either/or”: activation and desensitization of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors both contribute to behaviors related to nicotine addiction and mood. Prog Neurobiol 84:329–343
Risner ME, Cone EJ, Benowitz NL, Jacob P (1988) Effects of the stereoisomers of nicotine and nornicotine on schedule-controlled responding and physiological parameters of dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:807–813
Rollema H, Hurst RS (2018) The contribution of agonist and antagonist activities of alpha4beta2* nAChR ligands to smoking cessation efficacy: a quantitative analysis of literature data. Psychopharmacology 235:2479–2505
Sepkovic DW, Haley NJ, Axelrad CM, LaVoie EJ (1984) Thyroid hormone concentrations in rats after chronic nicotine metabolite administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 177:412–416
Simola N, Brudzynski SM (2018) Rat 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations as a tool in studying neurochemical mechanisms that regulate positive emotional states. J Neurosci Methods 310:33–44
Simola N, Fenu S, Costa G, Pinna A, Plumitallo A, Morelli M (2012) Pharmacological characterization of 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in rats: comparison of the effects of different psychoactive drugs and relevance in drug-induced reward. Neuropharmacology 63:224–234
Simola N, Frau L, Plumitallo A, Morelli M (2014) Direct and long-lasting effects elicited by repeated drug administration on 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations are regulated differently: implications for the study of the affective properties of drugs of abuse. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:429–441
Simola N, Granon S (2018) Ultrasonic vocalizations as a tool in studying emotional states in rodent models of social behavior and brain disease. Neuropharmacology
Stairs DJ, Neugebauer NM, Wei X, Boustany C, Hojahmat M, Cassis LA, Crooks PA, Dwoskin LP, Bardo MT (2007) Effects of nornicotine enantiomers on intravenous S(−)-nicotine self-administration and cardiovascular function in rats. Psychopharmacology 190:145–155
Stolerman IP, Chandler CJ, Garcha HS, Newton JM (1997) Selective antagonism of behavioural effects of nicotine by dihydro-b-erythroidine in rats. Psychopharmacology 129:390–397
Stolerman IP, Garcha HS, Mirza NR (1995) Dissociations between the locomotor stimulant and depressant effects of nicotinic agonists in rats. Psychopharmacology 117:430–437
Swalve N, Mulholland MM, Li M (2019) Alterations of acoustic features of 50 kHz vocalizations by nicotine and phencyclidine in rats. Behav Pharmacol 30:446–451
Swalve N, Mulholland MM, Schulz TD, Li M (2016) Effects of the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia and nicotine on total and categorized ultrasonic vocalizations in rats. Behav Pharmacol 27:321–330
Takada K, Swedberg MD, Goldberg SR, Katz JL (1989) Discriminative stimulus effects of intravenous l-nicotine and nicotine analogs or metabolites in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology 99:208–212
Teng LH, Crooks PA, Buxton ST, Dwoskin LP (1997) Nicotinic-receptor mediation of S(−)nornicotine-evoked [3H]overflow from rat striatal slices preloaded with [3H]dopamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:778–787
Terry AV, Buccafusco JJ, Schade RF, Vandenhuerk L, Callahan PM, Beck WD, Hutchings EJ, Chapman JM, Li P, Bartlett MG (2012) The nicotine metabolite, cotinine, attenuates glutamate (NMDA) antagonist-related effects on the performance of the five choice serial reaction time task (5C-SRTT) in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 83:941–951
Terry AV, Callahan PM, Bertrand D (2015) R-(+) and S-(−) isomers of cotinine augment cholinergic responses in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 352:405–418
Turner DM (1975) Influence of route of administration on metabolism of [14C]nicotine in four species. Xenobiotica 5:553–561
Vainio PJ, Tornquist K, Tuominen RK (2000) Cotinine and nicotine inhibit each other’s calcium responses in bovine chromaffin cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 163:183–187
Vieira-Brock PL, Andrenyak DM, Nielsen SM, Fleckenstein AE, Wilkins DG (2013) Age-related differences in the disposition of nicotine and metabolites in rat brain and plasma. Nicotine Tob Res 15:1839–1848
Vieira-Brock PL, Miller EI, Nielsen SM, Fleckenstein AE, Wilkins DG (2011) Simultaneous quantification of nicotine and metabolites in rat brain by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:3465–3474
Wiley JL, Marusich JA, Thomas BF, Jackson KJ (2015) Determination of behaviorally effective tobacco constituent doses in rats. Nicotine Tob Res 17:368–371
Willadsen M, Best LM, Wohr M, Clarke PBS (2018) Effects of anxiogenic drugs on the emission of 22- and 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in adult rats. Psychopharmacology 235:2435–2445
Wohr M, Schwarting RK (2013) Affective communication in rodents: ultrasonic vocalizations as a tool for research on emotion and motivation. Cell Tissue Res 354:81–97
Wright JM, Deng L, Clarke PB (2012a) Failure of rewarding and locomotor stimulant doses of morphine to promote adult rat 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations. Psychopharmacology 224:477–487
Wright JM, Dobosiewicz MR, Clarke PB (2012b) Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors differentially modulate the emission of spontaneous and amphetamine induced 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in adult rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:808–821
Wright JM, Gourdon J, Clarke PBS (2010) Identification of multiple call categories within the rich repertoire of adult rat 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations: effects of amphetamine and social context. Psychopharmacology 211:1–13
Wu J, Lukas RJ (2011) Naturally-expressed nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. Biochem Pharmacol 82:800–807
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Lucas Marques and Adithi Sundarakrishnan for providing comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) discovery grant (155055, to P.B.S.C). Y.W. was supported by a McGill University Faculty of Medicine BSc/MSc fast-track award. P.B.S.C. is a member of the Center for Studies in Behavioral Neurobiology at Concordia University, Montreal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments comply with the current laws of Canada. All research procedures were reviewed and approved by the McGill Animal Care Committee in accordance with the guidelines of the Canadian Council on Animal Care.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wan, B., Huang, J. et al. Effects of nicotine, nornicotine and cotinine, alone or in combination, on locomotor activity and ultrasonic vocalization emission in adult rats. Psychopharmacology 237, 2809–2822 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05574-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05574-0