Abstract
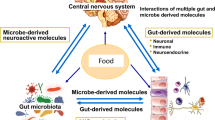
Schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder have long been associated with elevated levels of various small phenolic molecules (SPMs). In turn, the gut microbiota (GMB) has been implicated in the kinetics of many of these analytes. Unfortunately, research into the possible relevance of GMB-mediated SPMs to neuropsychiatry continues to be limited by heterogeneous study design, numerous sources of variance and technical challenges. Some SPMs have multiple structural isomers and most have conjugates. Without specialized approaches, SPMs can be incorrectly assigned or inaccurately quantified. In addition, SPM levels can be affected by dietary polyphenol or protein consumption and by various medications and diseases. Nonetheless, heterotypical excretion of various SPMs in association with schizophrenia or autism continues to be reported in independent samples. Recent studies in human cerebrospinal fluid demonstrate the presence of many SPMs A large number of these are bioactive in experimental models. Whether such mechanisms are relevant to the human brain in health or disease is not known. Systematic metabolomic and microbiome studies of well-characterized populations, an appreciation of multiple confounds, and implementation of standardized approaches across platforms and sites are needed to delineate the potential utility of the phenolic interactome in neuropsychiatry.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-HCA :
-
2-hydroxycinnamic acid
- 2-HPAA:
-
2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid
- 2,3-DHHCA:
-
2,3-dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
- 2,4-DHHCA:
-
2,4-dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
- 2,4-HPPA :
-
2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- 3-PPA:
-
3-phenylpropionic acid
- 3-HHA:
-
3-hydroxyhippuric acid
- 3-HBA:
-
3-hydroxybenzoic acid
- 3-HCA:
-
3-hydroxycinnamic acid
- 3-HHA :
-
3-hydroxyhippuric acid
- 3-HPAA :
-
3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid
- 3,2-HPPA:
-
3-(2-hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid
- 3,3-HPHPA:
-
3-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- 3,3-HPPA :
-
3-(3-hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid
- 3,4-DHCA:
-
3,4-dhydroxycinnamic acid
- 3,4-DHHCA:
-
3,4-dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
- 3,4-DOPAC:
-
3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
- 3,4-HMPHA:
-
3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl) hydracrylic acid
- 3,4-HPPA:
-
3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propionic acid
- 3,5-DHHCA:
-
3,5-dihydroxyhydrocinnamic acid
- 4-HHA:
-
4-hydroxyhippuric acid
- 4-HBA:
-
4-hydroxybenzoic acid
- 4-HCA:
-
4-hydroxycinnamic acid
- 4-HPAA:
-
4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid
- 4-HPLA:
-
4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid
- 4-HPPU:
-
4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid
- BA:
-
Benzoic acid
- FA:
-
Ferulic acid
- HA:
-
Hippuric acid
- HMA:
-
Hydroxymandelic acid
- HVA:
-
Homovanillic acid
- L-PHE:
-
l-Phenylalanine
- L-TYR:
-
l-Tyrosine
- PAA:
-
Phenylacetic acid
- PPG:
-
Phenylpropionylglycine
- VMA:
-
Vanillylmandelic acid
- ADOS:
-
Autism Diagnostic Observation Scale
- APD:
-
Antipsychotic drug
- BBB:
-
Blood brain barrier
- BPD:
-
Bipolar disorder
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DSM:
-
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual
- FEP:
-
First episode psychosis
- GMB:
-
Gut microbiota
- HR:
-
High risk
- ICD:
-
International Classification of Diseases
- LC:
-
Liquid chromatography
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- np:
-
Not provided
- NSIB:
-
Neurotypical siblings
- nsd:
-
Not significantly different
- PDD:
-
Pervasive developmental disorder
- PSE:
-
Present state examination
- quaL:
-
Qualitative
- quaN:
-
Quantitative
- RDC:
-
Research Diagnostic Criteria
- RIS:
-
Risperidone
- SGA:
-
Second-generation antipsychotic
- SPM:
-
Small phenolic molecule
- UC:
-
Unrelated control
- UHR:
-
Ultra high risk
References
FSANZ (2005) The 21st Australian Total Diet Study. A total diet study of sulphites, benzoates and sorbates. Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ), Canberra, AU.
Aarbakke J, Bakke OM (1972) Localization of microbial L-tyrosine degradation in the intestine of coprophagy-prevented rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 7:417–421
Acheson RM, Paul RM, Tomlinson RV (1958) Some constituents of the urine of normal and schizophrenic individuals. Can J Biochem Physiol 36:295–305
Almanza-Aguilera E, Urpi-Sarda M, Llorach R, Vazquez-Fresno R, Garcia-Aloy M, Carmona F, Sanchez A, Madrid-Gambin F, Estruch R, Corella D, Andres-Lacueva C (2017) Microbial metabolites are associated with a high adherence to a Mediterranean dietary pattern using a (1)H-NMR-based untargeted metabolomics approach. J Nutr Biochem 48:36–43
Altieri L, Neri C, Sacco R, Curatolo P, Benvenuto A, Muratori F, Santocchi E, Bravaccio C, Lenti C, Saccani M, Rigardetto R, Gandione M, Urbani A, Persico AM (2011) Urinary p-cresol is elevated in small children with severe autism spectrum disorder. Biomarkers 16:252–260
Aretz I, Meierhofer D (2016) Advantages and Pitfalls of mass spectrometry based metabolome profiling in systems biology. Int J Mol Sci 17
Armstrong MD, Shaw KN (1957) The occurrence of (-)-beta-m-hydroxyphenyl-hydracrylic acid in human urine. J Biol Chem 225:269–278
Armstrong MD, Shaw KN, Wall PE (1956) The phenolic acids of human urine; paper chromatography of phenolic acids. J Biol Chem 218:293–303
Asatoor AM (1968) The origin of urinary tyramine. Formation in tissue and by intestinal microorganisms. Clin Chim Acta 22:223–229
Asatoor AM, Chamberlain MJ, Emmerson BT, Johnson JR, Levi AJ, Milne MD (1967) Metabolic effects of oral neomycin. Clin Sci 33:111–124
Baba S, Furuta T, Horie M, Nakagawa H (1981) Studies on drug metabolism by use of isotopes XXVI: determination of urinary metabolites of rutin in humans. J Pharm Sci 70:780–782
Baba S, Furuta T, Fujioka M, Goromaru T (1983) Studies on drug metabolism by use of isotopes XXVII: urinary metabolites of rutin in rats and the role of intestinal microflora in the metabolism of rutin. J Pharm Sci 72:1155–1158
Bahr SM, Tyler BC, Wooldridge N, Butcher BD, Burns TL, Teesch LM, Oltman CL, Azcarate-Peril MA, Kirby JR, Calarge CA (2015) Use of the second-generation antipsychotic, risperidone, and secondary weight gain are associated with an altered gut microbiota in children. Transl Psychiatry 5:e652
Bai W, Wang C, Ren C (2014) Intakes of total and individual flavonoids by US adults. Int J Food Sci Nutr 65:9–20
Beckmann H, Reynolds GP, Sandler M, Waldmeier P, Lauber J, Riederer P, Gattaz WF (1982) Phenylethylamine and phenylacetic acid in CSF of schizophrenics and healthy controls. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 232:463–471
Bhala A, Bennett MJ, McGowan KL, Hale DE (1993) Limitations of 3-phenylpropionylglycine in early screening for medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. J Pediatr 122:100–103
Biedermann L, Zeitz J, Mwinyi J, Sutter-Minder E, Rehman A, Ott SJ, Steurer-Stey C, Frei A, Frei P, Scharl M, Loessner MJ, Vavricka SR, Fried M, Schreiber S, Schuppler M, Rogler G (2013) Smoking cessation induces profound changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota in humans. PLoS One 8:e59260
Bitner BF, Ray JD, Kener KB, Herring JA, Tueller JA, Johnson DK, Tellez Freitas CM, Fausnacht DW, Allen ME, Thomson AH, Weber KS, McMillan RP, Hulver MW, Brown DA, Tessem JS, Neilson AP (2018) Common gut microbial metabolites of dietary flavonoids exert potent protective activities in beta-cells and skeletal muscle cells. J Nutr Biochem 62:95–107
Blander JM, Longman RS, Iliev ID, Sonnenberg GF, Artis D (2017) Regulation of inflammation by microbiota interactions with the host. Nat Immunol 18:851–860
Bone E, Tamm A, Hill M (1976) The production of urinary phenols by gut bacteria and their possible role in the causation of large bowel cancer. Am J Clin Nutr 29:1448–1454
Bongiovanni R, Kirkbride B, Newbould E, Durkalski V, Jaskiw GE (2010) Relationships between large neutral amino acid levels in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, brain microdialysate and brain tissue in the rat. Brain Res 1334:45–57
Bongiovanni R, Leonard S, Jaskiw GE (2013) A simplified method to quantify dysregulated tyrosine transport in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 150:386–391
Bongiovanni R, Mchaourab AS, McClellan F, Elsworth J, Double M, Jaskiw GE (2016) Large neutral amino acids levels in primate cerebrospinal fluid do not confirm competitive transport under baseline conditions. Brain Res 1648:372–379
Bouatra S, Aziat F, Mandal R, Guo AC, Wilson MR, Knox C, Bjorndahl TC, Krishnamurthy R, Saleem F, Liu P, Dame ZT, Poelzer J, Huynh J, Yallou FS, Psychogios N, Dong E, Bogumil R, Roehring C, Wishart DS (2013) The human urine metabolome. PLoS One 8:e73076
Briggs MH (1962) A comparative study of urinary aromatic compounds from hospitalised mental patients and normal subjects. N Z Med J 61:317–320
Briggs MH, Harvey N (1962) Urinary metabolites of aromatic amino acids in schizophrenia. Life Sci 1:61–64
Cassidy A, Minihane AM (2017) The role of metabolism (and the microbiome) in defining the clinical efficacy of dietary flavonoids. Am J Clin Nutr 105:10–22
Chadwick RW, George SE, Claxton LD (1992) Role of the gastrointestinal mucosa and microflora in the bioactivation of dietary and environmental mutagens or carcinogens. Drug Metab Rev 24:425–492
Collins SM, Surette M, Bercik P (2012) The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:735–742
Coretti L, Paparo L, Riccio MP, Amato F, Cuomo M, Natale A, Borrelli L, Corrado G, Comegna M, Buommino E, Castaldo G, Bravaccio C, Chiariotti L, Berni Canani R, Lembo F (2018) Gut microbiota features in young children with autism spectrum disorders. Front Microbiol 9:3146
Crozier A, Jaganath IB, Clifford MN (2006) Phenols, polyphenols and tannins: an overview. In: Crozier A, Clifford MN, Ashihara H (eds) Plant secondary metabolites: occurrence, structure and role in the human diet. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, pp 1–24
Cummings JH, Hill MJ, Bone ES, Branch WJ, Jenkins DJ (1979) The effect of meat protein and dietary fiber on colonic function and metabolism. II. Bacterial metabolites in feces and urine. Am J Clin Nutr 32:2094–2101
Cunha BA (2001) Antibiotic side effects. Med Clin North Am 85:149–185
Curtius HC, Mettler M, Ettlinger L (1976a) Study of the intestinal tyrosine metabolism using stable isotopes and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr 126:569–580
Curtius HC, Redweik U, Steinmann B, Leimbacher W, Wegmann H (1976b) Use of deuterated tyrosine and phenylalanine in the study of catecholamine and aromatic amino acid metabolism. In: Klein ER, Klein PD (eds) Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Stable Isotopes, October 20-23, 1975, Oak Brook, Illinois. U.S. Energy Research and Development Administration, Washington, DC, pp 385–391
Dai ZL, Wu G, Zhu WY (2011) Amino acid metabolism in intestinal bacteria: links between gut ecology and host health. Front Biosci 16:1768–1786
Das NP (1974) Studies on flavonoid metabolism. Excretion of m-hydroxyphenylhydracrylic acid from (plus)-catechin in the monkey (Macaca iris sp.). Drug Metab Dispos 2:209–213
Dastur DK, Mann JD, Pollin W (1963) Hippuric acid excretion coffee, and schizophremia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 9:79–82
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN, Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y, Fischbach MA, Biddinger SB, Dutton RJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 505:559–563
Davis BA, Yu PH, Carlson K, O'Sullivan K, Boulton AA (1982) Plasma levels of phenylacetic acid, m- and p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, and platelet monoamine oxidase activity in schizophrenic and other patients. Psychiatry Res 6:97–105
Davis BA, Shrikhande S, Paralikar VP, Hirsch SR, Durden DA, Boulton AA (1991) Phenylacetic acid in CSF and serum in Indian schizophrenic patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 15:41–47
Dayman J, Jepson JB (1969) The metabolism of caffeic acid in humans: the dehydroxylating action of intestinal bacteria. Biochem J 113:11P
De Angelis M, Piccolo M, Vannini L, Siragusa S, De Giacomo A, Serrazzanetti DI, Cristofori F, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R (2013) Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS One 8:e76993
De Hert M, Hudyana H, Dockx L, Bernagie C, Sweers K, Tack J, Leucht S, Peuskens J (2011) Second-generation antipsychotics and constipation: a review of the literature. Eur Psychiatry 26:34–44
DeQuattro VL, Sjoerdsma A (1967) Origin of urinary tyramine and tryptamine. Clin Chim Acta 16:227–233
Dieme B, Mavel S, Blasco H, Tripi G, Bonnet-Brilhault F, Malvy J, Bocca C, Andres CR, Nadal-Desbarats L, Emond P (2015) Metabolomics study of urine in autism spectrum disorders using a multiplatform analytical methodology. J Proteome Res 14:5273–5282
DiLalla LF, McCrary M, Diaz E (2017) A review of endophenotypes in schizophrenia and autism: the next phase for understanding genetic etiologies. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 175:354–361
Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2018) Schizophrenia and the microbiome: time to focus on the impact of antipsychotic treatment on the gut microbiota. World J Biol Psychiatry 19:568–570
Dodd D, Spitzer MH, Van Treuren W, Merrill BD, Hryckowian AJ, Higginbottom SK, Le A, Cowan TM, Nolan GP, Fischbach MA, Sonnenburg JL (2017) A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nature 551:648–652
Dragsted LO, Gao Q, Pratico G, Manach C, Wishart DS, Scalbert A, Feskens EJM (2017) Dietary and health biomarkers-time for an update. Genes Nutr 12:24
Elsden SR, Hilton MG, Waller JM (1976) The end products of the metabolism of aromatic amino acids by Clostridia. Arch Microbiol 107:283–288
Epps HM (1944) Studies on bacterial amino-acid decarboxylases: 2. l(-)-tyrosine decarboxylase from Streptococcus faecalis. Biochem J 38:242–249
Erlund I, Meririnne E, Alfthan G, Aro A (2001) Plasma kinetics and urinary excretion of the flavanones naringenin and hesperetin in humans after ingestion of orange juice and grapefruit juice. J Nutr 131:235–241
Faull KF, King RJ, Barchas JD, Csernansky JG (1989) CSF phenylacetic acid and hostility in paranoid schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 30:111–118
Fernell E, Karagiannakis A, Edman G, Bjerkenstedt L, Wiesel FA, Venizelos N (2007) Aberrant amino acid transport in fibroblasts from children with autism. Neurosci Lett 418:82–86
Finegold SM, Dowd SE, Gontcharova V, Liu C, Henley KE, Wolcott RD, Youn E, Summanen PH, Granpeesheh D, Dixon D, Liu M, Molitoris DR, Green JA 3rd (2010) Pyrosequencing study of fecal microflora of autistic and control children. Anaerobe 16:444–453
Finegold SM, Summanen PH, Downes J, Corbett K, Komoriya T (2017) Detection of Clostridium perfringens toxin genes in the gut microbiota of autistic children. Anaerobe 45:133–137
Flowers SA, Evans SJ, Ward KM, McInnis MG, Ellingrod VL (2017) Interaction between atypical antipsychotics and the gut microbiome in a bipolar disease cohort. Pharmacotherapy 37:261–267
Flowers SA, Baxter NT, Ward KM, Kraal AZ, McInnis MG, Schmidt TM, Ellingrod VL (2019) Effects of atypical antipsychotic treatment and resistant starch supplementation on gut microbiome composition in a cohort of patients with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. Pharmacotherapy
Frolinger T, Smith C, Cobo CF, Sims S, Brathwaite J, de Boer S, Huang J, Pasinetti GM (2018) Dietary polyphenols promote resilience against sleep deprivation-induced cognitive impairment by activating protein translation. FASEB J 32:5390–5404
Gabriele S, Sacco R, Cerullo S, Neri C, Urbani A, Tripi G, Malvy J, Barthelemy C, Bonnet-Brihault F, Persico AM (2014) Urinary p-cresol is elevated in young French children with autism spectrum disorder: a replication study. Biomarkers 19:463–470
Gabriele S, Sacco R, Altieri L, Neri C, Urbani A, Bravaccio C, Riccio MP, Iovene MR, Bombace F, De Magistris L, Persico AM (2016) Slow intestinal transit contributes to elevate urinary p-cresol level in Italian autistic children. Autism Res 9:752–759
Gale EF (1953) Amino-acid decarboxylases. Br Med Bull 9:135–138
Gandal MJ, Haney JR, Parikshak NN, Leppa V, Ramaswami G, Hartl C, Schork AJ, Appadurai V, Buil A, Werge TM, Liu C, White KP, Horvath S, Geschwind DH (2018) Shared molecular neuropathology across major psychiatric disorders parallels polygenic overlap. Science 359:693–697
Gao Q, Pratico G, Scalbert A, Vergeres G, Kolehmainen M, Manach C, Brennan L, Afman LA, Wishart DS, Andres-Lacueva C, Garcia-Aloy M, Verhagen H, Feskens EJM, Dragsted LO (2017) A scheme for a flexible classification of dietary and health biomarkers. Genes Nutr 12:34
Gasperotti M, Passamonti S, Tramer F, Masuero D, Guella G, Mattivi F, Vrhovsek U (2015) Fate of microbial metabolites of dietary polyphenols in rats: is the brain their target destination? ACS Chem Neurosci 6:1341–1352
Gattaz WF, Gasser T, Beckmann H (1985) Multidimensional analysis of the concentrations of 17 substances in the CSF of schizophrenics and controls. Biol Psychiatry 20:360–366
Gerhauser C (2018) Impact of dietary gut microbial metabolites on the epigenome. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 373.
Gondalia SV, Palombo EA, Knowles SR, Cox SB, Meyer D, Austin DW (2012) Molecular characterisation of gastrointestinal microbiota of children with autism (with and without gastrointestinal dysfunction) and their neurotypical siblings. Autism Res 5:419–427
Gonzalez-Barrio R, Edwards CA, Crozier A (2011) Colonic catabolism of ellagitannins, ellagic acid, and raspberry anthocyanins: in vivo and in vitro studies. Drug Metab Dispos 39:1680–1688
Gora B, Gofron Z, Grosiak M, Aptekorz M, Kazek B, Kocelak P, Radosz-Komoniewska H, Chudek J, Martirosian G (2018) Toxin profile of fecal Clostridium perfringens strains isolated from children with autism spectrum disorders. Anaerobe 51:73–77
Grimaldi R, Cela D, Swann JR, Vulevic J, Gibson GR, Tzortzis G, Costabile A (2017) In vitro fermentation of B-GOS: impact on faecal bacterial populations and metabolic activity in autistic and non-autistic children. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93
Group BDW (2001) Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69:89–95
Gulyassy PF, Bottini AT, Jarrard EA, Stanfel LA (1983) Isolation of inhibitors of ligand: albumin-binding from uremic body fluids and normal urine. Kidney Int Suppl 16:S238–S242
Hafiz S, Oakley CL (1976) Clostridium difficile: isolation and characteristics. J Med Microbiol 9:129–136
Hagenfeldt L, Venizelos N, Bjerkenstedt L, Wiesel FA (1987) Decreased tyrosine transport in fibroblasts from schizophrenic patients. Life Sci 41:2749–2757
Hassanzadeh P, Arbabi E, Atyabi F, Dinarvand R (2017) Ferulic acid exhibits antiepileptogenic effect and prevents oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in the kindling model of epilepsy. Life Sci 179:9–14
He Y, Kosciolek T, Tang J, Zhou Y, Li Z, Ma X, Zhu Q, Yuan N, Yuan L, Li C, Jin K, Knight R, Tsuang MT, Chen X (2018) Gut microbiome and magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of subjects at ultra-high risk for psychosis may support the membrane hypothesis. Eur Psychiatry 53:37–45
Hervert-Hernandez D, Goni I (2011) Dietary polyphenols and human gut microbiota: a review. Food Rev Int 27:154–169
Hicks JM, Young DS, Wootton ID (1964) The effect of uraeic blood constituents on certain cerebral enzymes. Clin Chim Acta 9:228–235
Ho L, Zhao D, Ono K, Ruan K, Mogno I, Tsuji M, Carry E, Brathwaite J, Sims S, Frolinger T, Westfall S, Mazzola P, Wu Q, Hao K, Lloyd TE, Simon JE, Faith J, Pasinetti GM (2019) Heterogeneity in gut microbiota drive polyphenol metabolism that influences alpha-synuclein misfolding and toxicity. J Nutr Biochem 64:170–181
Holingue C, Newill C, Lee LC, Pasricha PJ, Daniele Fallin M (2018) Gastrointestinal symptoms in autism spectrum disorder: a review of the literature on ascertainment and prevalence. Autism Res 11:24–36
Hughes HK, Ashwood P (2018) Anti-Candida albicans IgG antibodies in children with autism spectrum disorders. Front Psychiatry 9:627
Hyland NP, Cryan JF (2016) Microbe-host interactions: Influence of the gut microbiota on the enteric nervous system. Dev Biol 417:182–187
Iovene MR, Bombace F, Maresca R, Sapone A, Iardino P, Picardi A, Marotta R, Schiraldi C, Siniscalco D, Serra N, de Magistris L, Bravaccio C (2017) Intestinal dysbiosis and yeast isolation in stool of subjects with autism spectrum disorders. Mycopathologia 182:349–363
Jaganath IB, Mullen W, Edwards CA, Crozier A (2006) The relative contribution of the small and large intestine to the absorption and metabolism of rutin in man. Free Radic Res 40:1035–1046
Kageyama Y, Kasahara T, Morishita H, Mataga N, Deguchi Y, Tani M, Kuroda K, Hattori K, Yoshida S, Inoue K, Kato T (2017) Search for plasma biomarkers in drug-free patients with bipolar disorder and schizophrenia using metabolome analysis. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 71:115–123
Kahn RS, Sommer IE, Murray RM, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR, Cannon TD, O'Donovan M, Correll CU, Kane JM, van Os J, Insel TR (2015) Schizophrenia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15067
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y, Morishima K (2017) KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D353–D361
Kang DW, Park JG, Ilhan ZE, Wallstrom G, Labaer J, Adams JB, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2013) Reduced incidence of Prevotella and other fermenters in intestinal microflora of autistic children. PLoS One 8:e68322
Kang DW, Ilhan ZE, Isern NG, Hoyt DW, Howsmon DP, Shaffer M, Lozupone CA, Hahn J, Adams JB, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2018) Differences in fecal microbial metabolites and microbiota of children with autism spectrum disorders. Anaerobe 49:121–131
Kantarcioglu AS, Kiraz N, Aydin A (2016) Microbiota-gut-brain axis: yeast species isolated from stool samples of children with suspected or diagnosed autism spectrum disorders and in vitro susceptibility against nystatin and fluconazole. Mycopathologia 181:1–7
Karoum F, Potkin S, Chuang LW, Murphy DL, Liebowitz MR, Wyatt RJ (1984) Phenylacetic acid excretion in schizophrenia and depression: the origins of PAA in man. Biol Psychiatry 19:165–178
Kawabata M, Kobayashi K, Shohmori T (1986) Determination of phenylacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Acta Med Okayama 40:271–276
Kesli R, Gokcen C, Bulug U, Terzi Y (2014) Investigation of the relation between anaerobic bacteria genus clostridium and late-onset autism etiology in children. J Immunoassay Immunochem 35:101–109
Kim S, Thiessen PA, Bolton EE, Chen J, Fu G, Gindulyte A, Han L, He J, He S, Shoemaker BA, Wang J, Yu B, Zhang J, Bryant SH (2016) PubChem substance and compound databases. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1202–D1213
Kuhnau J (1976) The flavonoids. A class of semi-essential food components: their role in human nutrition. World Rev Nutr Diet 24:117–191
Kunin CM, Chalmers TC, Leevy CM, Sebastyen SC, Lieber CS, Finland M (1960) Absorption of orally administered neomycin and kanamycin with special reference to patients with severe hepatic and renal disease. N Engl J Med 262:380–385
Lally J, MacCabe JH (2015) Antipsychotic medication in schizophrenia: a review. Br Med Bull 114:169–179
Le Bastard Q, Al-Ghalith GA, Gregoire M, Chapelet G, Javaudin F, Dailly E, Batard E, Knights D, Montassier E (2018) Systematic review: human gut dysbiosis induced by non-antibiotic prescription medications. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 47:332–345
Lee HC, Jenner AM, Low CS, Lee YK (2006) Effect of tea phenolics and their aromatic fecal bacterial metabolites on intestinal microbiota. Res Microbiol 157:876–884
Lewis SJ, Heaton KW (1997) Stool form scale as a useful guide to intestinal transit time. Scand J Gastroenterol 32:920–924
Li J, Jia H, Cai X, Zhong H, Feng Q, Sunagawa S, Arumugam M, Kultima JR, Prifti E, Nielsen T, Juncker AS, Manichanh C, Chen B, Zhang W, Levenez F, Wang J, Xu X, Xiao L, Liang S, Zhang D, Zhang Z, Chen W, Zhao H, Al-Aama JY, Edris S, Yang H, Wang J, Hansen T, Nielsen HB, Brunak S, Kristiansen K, Guarner F, Pedersen O, Dore J, Ehrlich SD, Meta HITC, Bork P, Wang J, Meta HITC (2014) An integrated catalog of reference genes in the human gut microbiome. Nat Biotechnol 32:834–841
Lis AW, McLaughlin I, Mpclaughlin RK, Lis EW, Stubbs EG (1976) Profiles of ultraviolet-absorbing components of urine from autistic children, as obtained by high-resolution ion-exchange chromatography. Clin Chem 22:1528–1532
Liu H, Garrett TJ, Tayyari F, Gu L (2015) Profiling the metabolome changes caused by cranberry procyanidins in plasma of female rats using (1) H NMR and UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS global metabolomics approaches. Mol Nutr Food Res 59:2107–2118
Loftfield E, Vogtmann E, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Nelson H, Knight R, Chia N, Sinha R (2016) Comparison of collection methods for fecal samples for discovery metabolomics in epidemiologic studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 25:1483–1490
Lord C, Rutter M, Goode S, Heemsbergen J, Jordan H, Mawhood L, Schopler E (1989) Autism diagnostic observation schedule: a standardized observation of communicative and social behavior. J Autism Dev Disord 19:185–212
Luca SV, Macovei I, Bujor A, Miron A, Skalicka-Wozniak K, Aprotosoaie AC, Trifan A (2019) Bioactivity of dietary polyphenols: the role of metabolites. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1–34.
Ma B, Liang J, Dai M, Wang J, Luo J, Zhang Z, Jing J (2019) Altered gut microbiota in Chinese children with autism spectrum disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:40
Macfarlane GT, Cummings JH (1991) The colonic flora, fermentation and large bowel digestive function. In: Phillips SF, Pemberton JH, Shorter RG (eds) The large intestine: physiology, pathophysiology and disease. Raven Press, New York, pp 51–92
Maier L, Pruteanu M, Kuhn M, Zeller G, Telzerow A, Anderson EE, Brochado AR, Fernandez KC, Dose H, Mori H, Patil KR, Bork P, Typas A (2018) Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 555:623–628
Mann JD, Labrosse EH (1959) Urinary excretion of phenolic acids by normal and schizophrenic male patients. AMA Arch Gen Psychiatry 1:547–551
Marshall DD, Powers R (2017) Beyond the paradigm: combining mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance for metabolomics. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 100:1–16
Mavel S, Nadal-Desbarats L, Blasco H, Bonnet-Brilhault F, Barthelemy C, Montigny F, Sarda P, Laumonnier F, Vourc'h P, Andres CR, Emond P (2013) 1H-13C NMR-based urine metabolic profiling in autism spectrum disorders. Talanta 114:95–102
Mazzoli R, Pessione E (2016) The neuro-endocrinological role of microbial glutamate and GABA signaling. Front Microbiol 7:1934
McGeer PL, McGeer EG, Boulding JE (1956) Relation of aromatic amino acids to excretory pattern of schizophrenics. Science 123:1078–1080
Mead GC (1971) The amino acid-fermenting clostridia. J Gen Microbiol 67:47–56
Ming X, Stein TP, Barnes V, Rhodes N, Guo L (2012) Metabolic perturbance in autism spectrum disorders: a metabolomics study. J Proteome Res 11:5856–5862
Monagas M, Khan N, Andres-Lacueva C, Urpi-Sarda M, Vazquez-Agell M, Lamuela-Raventos RM, Estruch R (2009) Dihydroxylated phenolic acids derived from microbial metabolism reduce lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cytokine secretion by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Br J Nutr 102:201–206
Mrochek JE, Dinsmore SR, Ohrt DW (1973) Monitoring phenylalanine-tyrosine metabolism by high-resolution liquid chromatography of urine. Clin Chem 19:927–936
Murota K, Nakamura Y, Uehara M (2018) Flavonoid metabolism: the interaction of metabolites and gut microbiota. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82:600–610
Muskens JB, Velders FP, Staal WG (2017) Medical comorbidities in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders: a systematic review. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 26:1093–1103
Nakagawa Y, Shetlar MR, Wender SH (1965) Urinary products from quercetin in neomycin-treated rats. Biochim Biophys Acta 97:233–241
Nguyen TT, Kosciolek T, Maldonado Y, Daly RE, Martin AS, McDonald D, Knight R, Jeste DV (2019) Differences in gut microbiome composition between persons with chronic schizophrenia and healthy comparison subjects. Schizophr Res 204:23–29
Noto A, Fanos V, Barberini L, Grapov D, Fattuoni C, Zaffanello M, Casanova A, Fenu G, De Giacomo A, De Angelis M, Moretti C, Papoff P, Ditonno R, Francavilla R (2014) The urinary metabolomics profile of an Italian autistic children population and their unaffected siblings. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 27(Suppl 2):46–52
Nunez-Montiel OL, Thompson FS, Dowell VR Jr (1983) Norleucine-tyrosine broth for rapid identification of Clostridium difficile by gas-liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol 17:382–385
Obrenovich MEM (2018) Leaky gut, leaky brain? Microorganisms 6
Obrenovich M, Mana TSC, Rai H, Shola D, Sass C, McCloskey B, Levison BS (2017) Recent findings within the microbiota–gut–brain–endocrine metabolic interactome. Pathol Lab Med Int 9:21–30
Obrenovich ME, Donskey CJ, Schiefer IT, Bongiovanni R, Li L, Jaskiw GE (2018) Quantification of phenolic acid metabolites in humans by LC-MS: a structural and targeted metabolomics approach. Bioanalysis 10:1591–1608
Ohnishi R, Ito H, Iguchi A, Shinomiya K, Kamei C, Hatano T, Yoshida T (2006) Effects of chlorogenic acid and its metabolites on spontaneous locomotor activity in mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:2560–2563
Olde Loohuis LM, Mangul S, Ori APS, Jospin G, Koslicki D, Yang HT, Wu T, Boks MP, Lomen-Hoerth C, Wiedau-Pazos M, Cantor RM, de Vos WM, Kahn RS, Eskin E, Ophoff RA (2018) Transcriptome analysis in whole blood reveals increased microbial diversity in schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry 8:96
Olthof MR, Hollman PC, Buijsman MN, van Amelsvoort JM, Katan MB (2003) Chlorogenic acid, quercetin-3-rutinoside and black tea phenols are extensively metabolized in humans. J Nutr 133:1806–1814
Ottaviani JI, Borges G, Momma TY, Spencer JP, Keen CL, Crozier A, Schroeter H (2016) The metabolome of [2-(14)C](-)-epicatechin in humans: implications for the assessment of efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action of polyphenolic bioactives. Sci Rep 6:29034
Pallister T, Jennings A, Mohney RP, Yarand D, Mangino M, Cassidy A, MacGregor A, Spector TD, Menni C (2016) Characterizing blood metabolomics profiles associated with self-reported food intakes in female twins. PLoS One 11:e0158568
Patel KP, Luo FJ, Plummer NS, Hostetter TH, Meyer TW (2012) The production of p-cresol sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in vegetarians versus omnivores. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:982–988
Pereira-Caro G, Borges G, van der Hooft J, Clifford MN, Del Rio D, Lean ME, Roberts SA, Kellerhals MB, Crozier A (2014) Orange juice (poly)phenols are highly bioavailable in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 100:1378–1384
Perry TL, Hansen S, Diamond S, Melancon SB, Lesk D (1971) Acetic and benzoic acids in the urine of patients with chronic schizophrenia. Clin Chim Acta 31:181–186
Plaza-Diaz J, Gomez-Fernandez A, Chueca N, Torre-Aguilar MJ, Gil A, Perez-Navero JL, Flores-Rojas K, Martin-Borreguero P, Solis-Urra P, Ruiz-Ojeda FJ, Garcia F, Gil-Campos M (2019) Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) with and without mental regression is associated with changes in the fecal microbiota. Nutrients 11
Postorino V, Sanges V, Giovagnoli G, Fatta LM, De Peppo L, Armando M, Vicari S, Mazzone L (2015) Clinical differences in children with autism spectrum disorder with and without food selectivity. Appetite 92:126–132
Potkin SG, Wyatt RJ, Karoum F (1980) Phenylethylamine (PEA) and phenylacetic acid (PAA) in the urine of chronic schizophrenic patients and controls. Psychopharmacol Bull 16:52–54
Prata J, Santos SG, Almeida MI, Coelho R, Barbosa MA (2017) Bridging autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia through inflammation and biomarkers - pre-clinical and clinical investigations. J Neuroinflammation 14:179
Pulikkan J, Maji A, Dhakan DB, Saxena R, Mohan B, Anto MM, Agarwal N, Grace T, Sharma VK (2018) Gut microbial dysbiosis in Indian children with autism spectrum disorders. Microb Ecol 76:1102–1114
Quastel JHW (1938) Faulty detoxification in schizophrenia. Lancet 232:301–305
Rampini S, Vollmin JA, Bosshard HR, Muller M, Curtius HC (1974) Aromatic acids in urine of healthy infants, persistent hyperphenylalaninemia, and phenylketonuria, before and after phenylalanine load. Pediatr Res 8:704–709
Rashid MU, Zaura E, Buijs MJ, Keijser BJ, Crielaard W, Nord CE, Weintraub A (2015) Determining the long-term effect of antibiotic administration on the human normal intestinal microbiota using culture and pyrosequencing methods. Clin Infect Dis 60(Suppl 2):S77–S84
Roick C, Fritz-Wieacker A, Matschinger H, Heider D, Schindler J, Riedel-Heller S, Angermeyer MC (2007) Health habits of patients with schizophrenia. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 42:268–276
Rothschild D, Weissbrod O, Barkan E, Kurilshikov A, Korem T, Zeevi D, Costea PI, Godneva A, Kalka IN, Bar N, Shilo S, Lador D, Vila AV, Zmora N, Pevsner-Fischer M, Israeli D, Kosower N, Malka G, Wolf BC, Avnit-Sagi T, Lotan-Pompan M, Weinberger A, Halpern Z, Carmi S, Fu J, Wijmenga C, Zhernakova A, Elinav E, Segal E (2018) Environment dominates over host genetics in shaping human gut microbiota. Nature 555:210–215
Russell WR, Duncan SH, Scobbie L, Duncan G, Cantlay L, Calder AG, Anderson SE, Flint HJ (2013) Major phenylpropanoid-derived metabolites in the human gut can arise from microbial fermentation of protein. Mol Nutr Food Res 57:523–535
Sandler M, Ruthven CR, Goodwin BL, King GS, Pettit BR, Reynolds GP, Tyrer SP, Weller MP, Hirsch SR (1978) Raised cerebrospinal fluid phenylacetic acid concentration: preliminary support for the phenylethylamine hypothesis of schizophrenia? Commun Psychopharmacol 2:199–202
Sandler RH, Finegold SM, Bolte ER, Buchanan CP, Maxwell AP, Vaisanen ML, Nelson MN, Wexler HM (2000) Short-term benefit from oral vancomycin treatment of regressive-onset autism. J Child Neurol 15:429–435
Sasaki T (1914) Uber die biochemische Umwandlung primarer Ei wei β-spaltprodukte durch Bakterien. I. Das Verhalten von Tyrosin gegen Bact. coli commune. Eine einfache biochemische Darstellungsmethode von p-Oxyphenylathylamin. Biochem Zeitschr 59:429–435
Savin Z, Kivity S, Yonath H, Yehuda S (2018) Smoking and the intestinal microbiome. Arch Microbiol 200:677–684
Scalbert A, Williamson G (2000) Dietary intake and bioavailability of polyphenols. J Nutr 130:2073S–2085S
Schantz M, Erk T, Richling E (2010) Metabolism of green tea catechins by the human small intestine. Biotechnol J 5:1050–1059
Scheline RR (1973) Metabolism of foreign compounds by gastrointestinal microorganisms. Pharmacol Rev 25:451–523
Schmidt JA, Rinaldi S, Ferrari P, Carayol M, Achaintre D, Scalbert A, Cross AJ, Gunter MJ, Fensom GK, Appleby PN, Key TJ, Travis RC (2015) Metabolic profiles of male meat eaters, fish eaters, vegetarians, and vegans from the EPIC-Oxford cohort. Am J Clin Nutr 102:1518–1526
Schmitt A, Rujescu D, Gawlik M, Hasan A, Hashimoto K, Iceta S, Jarema M, Kambeitz J, Kasper S, Keeser D, Kornhuber J, Koutsouleris N, Lanzenberger R, Malchow B, Saoud M, Spies M, Stober G, Thibaut F, Riederer P, Falkai P (2016) Consensus paper of the WFSBP Task force on biological markers: Criteria for biomarkers and endophenotypes of schizophrenia part II: cognition, neuroimaging and genetics. World J Biol Psychiatry 17:406–428
Schmitt A, Martins-de-Souza D, Akbarian S, Cassoli JS, Ehrenreich H, Fischer A, Fonteh A, Gattaz WF, Gawlik M, Gerlach M, Grunblatt E, Halene T, Hasan A, Hashimoto K, Kim YK, Kirchner SK, Kornhuber J, Kraus TFJ, Malchow B, Nascimento JM, Rossner M, Schwarz M, Steiner J, Talib L, Thibaut F, Riederer P, Falkai P (2017) Consensus paper of the WFSBP Task Force on biological markers: criteria for biomarkers and endophenotypes of schizophrenia, part III: molecular mechanisms. World J Biol Psychiatry 18:330–356
Schwarz E, Maukonen J, Hyytiainen T, Kieseppa T, Oresic M, Sabunciyan S, Mantere O, Saarela M, Yolken R, Suvisaari J (2018) Analysis of microbiota in first episode psychosis identifies preliminary associations with symptom severity and treatment response. Schizophr Res 192:398–403
Selmer T, Andrei PI (2001) p-Hydroxyphenylacetate decarboxylase from Clostridium difficile. A novel glycyl radical enzyme catalysing the formation of p-cresol. Eur J Biochem 268:1363–1372
Severance EG, Yolken RH (2019) From infection to the microbiome: an evolving role of microbes in schizophrenia. Curr Top Behav Neurosci
Severance EG, Gressitt KL, Stallings CR, Katsafanas E, Schweinfurth LA, Savage CL, Adamos MB, Sweeney KM, Origoni AE, Khushalani S, Leweke FM, Dickerson FB, Yolken RH (2016) Candida albicans exposures, sex specificity and cognitive deficits in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. NPJ schizophrenia 2:16018
Shangari N, Chan TS, O'Brien PJ (2005) Sulfation and glucuronidation of phenols: implications in coenyzme Q metabolism. Methods Enzymol 400:342–359
Sharma RP, Faull K, Javaid JI, Davis JM (1995) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of phenylacetic acid in mental illness: behavioral associations and response to neuroleptic treatment. Acta Psychiatr Scand 91:293–298
Shaw W (2010) Increased urinary excretion of a 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic acid (HPHPA), an abnormal phenylalanine metabolite of Clostridia spp. in the gastrointestinal tract, in urine samples from patients with autism and schizophrenia. Nutr Neurosci 13:135–143
Shaw W (2016) Clostridia bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract as a major cause of depression and other neuropsychiatric disorders. In: Greenblatt J, Brogan K (eds) Integrative Psychiatry for Depression: Redefining Models for Assessment, Treatment, and Prevention of Mood Disorders. Taylor and Francis, New York, pp 31–48
Shaw W (2017) Elevated urinary glyphosate and clostridia metabolites with altered dopamine metabolism in triplets with autistic spectrum disorder or suspected seizure disorder: a case study. Integr Med (Encinitas) 16:50–57
Shaw KN, Trevarthen J (1958) Exogenous sources of urinary phenol and indole acids. Nature 182:797–798
Shaw KNF, Gutenstein M, Jepson JB (1961) Intestinal flora and diet in relation to m-hydroxyphenyl acids of human urine. In: Sissakian NM (ed) Fifth International Congress of Biochemistry. Pergamon Press, Moscow, p 427
Shaw W, Kassen E, Chaves E (2000) Assessment of antifungal drug therapy in autism by measurement of suspected microbial metabolites in urine with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin Pract Altern Med 1:15–26
Shen Y, Xu J, Li Z, Huang Y, Yuan Y, Wang J, Zhang M, Hu S, Liang Y (2018) Analysis of gut microbiota diversity and auxiliary diagnosis as a biomarker in patients with schizophrenia: a cross-sectional study. Schizophr Res
Sherwin E, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2018) Recent developments in understanding the role of the gut microbiota in brain health and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1420:5–25
Singh RK, Chang HW, Yan D, Lee KM, Ucmak D, Wong K, Abrouk M, Farahnik B, Nakamura M, Zhu TH, Bhutani T, Liao W (2017) Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J Transl Med 15:73
Stalmach A, Edwards CA, Wightman JD, Crozier A (2013) Colonic catabolism of dietary phenolic and polyphenolic compounds from concord grape juice. Food Funct 4:52–62
Strati F, Cavalieri D, Albanese D, De Felice C, Donati C, Hayek J, Jousson O, Leoncini S, Renzi D, Calabro A, De Filippo C (2017) New evidences on the altered gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders. Microbiome 5:24
Tanaka T (1964) The decomposition of L-tyrosine and its derivatives by Proteus vulgaris. Bull Pharm Res Inst 50:1–7
Tanaka T (1968) The decomposition of 1-tyrosine and its derivatives by proteus vulgaris. (4) The decomposition pathway of p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, p-hydroxyphenylacrylic acid and p-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid. Bull Pharm Res Inst 74:1–10
Theriot CM, Young VB (2015) Interactions between the gastrointestinal microbiome and Clostridium difficile. Annu Rev Microbiol 69:445–461
Thibaut F, Boutros NN, Jarema M, Oranje B, Hasan A, Daskalakis ZJ, Wichniak A, Schmitt A, Riederer P, Falkai P (2015) Consensus paper of the WFSBP Task Force on biological markers: criteria for biomarkers and endophenotypes of schizophrenia part I: neurophysiology. World J Biol Psychiatry 16:280–290
Tomova A, Husarova V, Lakatosova S, Bakos J, Vlkova B, Babinska K, Ostatnikova D (2015) Gastrointestinal microbiota in children with autism in Slovakia. Physiol Behav 138:179–187
Trošt K, Ulaszewska MM, Stanstrup J, Albanese D, De Filippo C, Tuohy KM, Natella F, Scaccini C, Mattivi F (2018) Host: microbiome co-metabolic processing of dietary polyphenols – an acute, single blinded, cross-over study with different doses of apple polyphenols in healthy subjects. Food Res Int 112:108–128
Ulaszewska MM, Weinert CH, Trimigno A, Portmann R, Andres Lacueva C, Badertscher R, Brennan L, Brunius C, Bub A, Capozzi F, Cialiè Rosso M, Cordero CE, Daniel H, Durand S, Egert B, Ferrario PG, Feskens EJM, Franceschi P, Garcia-Aloy M, Giacomoni F, Giesbertz P, González-Domínguez R, Hanhineva K, Hemeryck LY, Kopka J, Kulling SE, Llorach R, Manach C, Mattivi F, Migné C, Münger LH, Ott B, Picone G, Pimentel G, Pujos-Guillot E, Riccadonna S, Rist MJ, Rombouts C, Rubert J, Skurk T, Sri Harsha PSC, Van Meulebroek L, Vanhaecke L, Vázquez-Fresno R, Wishart D, Vergères G (2019) nutrimetabolomics: an integrative action for metabolomic analyses in human nutritional studies. Mol Nutr Food Res 63:1800384
Vissiennon C, Nieber K, Kelber O, Butterweck V (2012) Route of administration determines the anxiolytic activity of the flavonols kaempferol, quercetin and myricetin--are they prodrugs? J Nutr Biochem 23:733–740
Vollmin JA, Bosshard HR, Muller M, Rampini S, Curtius HC (1971) Determination of urinary aromatic acids by gas chromatography. Results from healthy infants and from patients with phenylketonuria. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem 9:402–404
Vonstudnitz W, Engelman K, Sjoerdsma A (1964) Urinary excretion of phenolic acids in human subjects on a glucose diet. Clin Chim Acta 9:224–227
Wang L, Christophersen CT, Sorich MJ, Gerber JP, Angley MT, Conlon MA (2013) Increased abundance of Sutterella spp. and Ruminococcus torques in feces of children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol Autism 4:42
Wang D, Ho L, Faith J, Ono K, Janle EM, Lachcik PJ, Cooper BR, Jannasch AH, D'Arcy BR, Williams BA, Ferruzzi MG, Levine S, Zhao W, Dubner L, Pasinetti GM (2015) Role of intestinal microbiota in the generation of polyphenol-derived phenolic acid mediated attenuation of Alzheimer's disease beta-amyloid oligomerization. Mol Nutr Food Res 59:1025–1040
Wang J, Hodes GE, Zhang H, Zhang S, Zhao W, Golden SA, Bi W, Menard C, Kana V, Leboeuf M, Xie M, Bregman D, Pfau ML, Flanigan ME, Esteban-Fernandez A, Yemul S, Sharma A, Ho L, Dixon R, Merad M, Han MH, Russo SJ, Pasinetti GM (2018) Epigenetic modulation of inflammation and synaptic plasticity promotes resilience against stress in mice. Nat Commun 9:477
Wang M, Wan J, Rong H, He F, Wang H, Zhou J, Cai C, Wang Y, Xu R, Yin Z, Zhou W (2019) Alterations in gut glutamate metabolism associated with changes in gut microbiota composition in children with autism spectrum disorder. mSystems 4
Westphal JF, Vetter D, Brogard JM (1994) Hepatic side-effects of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother 33:387–401
Williams BL, Hornig M, Buie T, Bauman ML, Cho Paik M, Wick I, Bennett A, Jabado O, Hirschberg DL, Lipkin WI (2011) Impaired carbohydrate digestion and transport and mucosal dysbiosis in the intestines of children with autism and gastrointestinal disturbances. PLoS One 6:e24585
Williams BL, Hornig M, Parekh T, Lipkin WI (2012) Application of novel PCR-based methods for detection, quantitation, and phylogenetic characterization of Sutterella species in intestinal biopsy samples from children with autism and gastrointestinal disturbances. mBio 3
Williamson G, Clifford MN (2017) Role of the small intestine, colon and microbiota in determining the metabolic fate of polyphenols. Biochem Pharmacol 139:24–39
Willmann PK, Bidzinski A, Jakimow B, Puzynski S (1977) [Psychomimetic compounds in the urine of schizophrenics. I. Study of catechol derivatives: so-called Pink Spot and 3.4-dimethoxyphenylethylamine (DMPEA)]. Psychiatr Pol 11:143–149
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Marcu A, Guo AC, Liang K, Vazquez-Fresno R, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Karu N, Sayeeda Z, Lo E, Assempour N, Berjanskii M, Singhal S, Arndt D, Liang Y, Badran H, Grant J, Serra-Cayuela A, Liu Y, Mandal R, Neveu V, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M, Manach C, Scalbert A (2018) HMDB 4.0: the human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D608–D617
Xiong X, Liu D, Wang Y, Zeng T, Peng Y (2016) Urinary 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropionic acid, 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid, and 3-hydroxyhippuric acid are elevated in children with autism spectrum disorders. BioMed research international 2016:9485412
Yap IK, Angley M, Veselkov KA, Holmes E, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK (2010) Urinary metabolic phenotyping differentiates children with autism from their unaffected siblings and age-matched controls. J Proteome Res 9:2996–3004
Yolken RH, Severance EG, Sabunciyan S, Gressitt KL, Chen O, Stallings C, Origoni A, Katsafanas E, Schweinfurth LA, Savage CL, Banis M, Khushalani S, Dickerson FB (2015) Metagenomic sequencing indicates that the oropharyngeal phageome of individuals with schizophrenia differs from that of controls. Schizophr Bull 41:1153–1161
Yoshimoto S, Kaku H, Shimogawa S, Watanabe A, Nakagawara M, Takahashi R (1987) Urinary trace amine excretion and platelet monoamine oxidase activity in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 21:229–236
Young MK Jr, Berry HK, Beerstecher E Jr, Berry JS (1951) Metabolic patterns of schizophrenic and control groups. Biochemical Institute Studies IV: Individual metabolic patterns and human disease: an exploratory study utilizing predominantly paper chromatographic methods. The University of Texas Publication). University of Texas, Austin, pp 189–197
Yuan X, Zhang P, Wang Y, Liu Y, Li X, Kumar BU, Hei G, Lv L, Huang XF, Fan X, Song X (2018) Changes in metabolism and microbiota after 24-week risperidone treatment in drug naive, normal weight patients with first episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 201:299–306
Zeni AL, Zomkowski AD, Maraschin M, Rodrigues AL, Tasca CI (2012) Ferulic acid exerts antidepressant-like effect in the tail suspension test in mice: evidence for the involvement of the serotonergic system. Eur J Pharmacol 679:68–74
Zeni ALB, Camargo A, Dalmagro AP (2017) Ferulic acid reverses depression-like behavior and oxidative stress induced by chronic corticosterone treatment in mice. Steroids 125:131–136
Zhai Q, Cen S, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W (2019) Disturbance of trace element and gut microbiota profiles as indicators of autism spectrum disorder: A pilot study of Chinese children. Environ Res 171:501–509
Zheng W, Chodobski A (2005) The blood-cerebrospinal barrier. Taylor and Francis, New York
Zheng P, Zeng B, Liu M, Chen J, Pan J, Han Y, Liu Y, Cheng K, Zhou C, Wang H, Zhou X, Gui S, Perry SW, Wong ML, Licinio J, Wei H, Xie P (2019) The gut microbiome from patients with schizophrenia modulates the glutamate-glutamine-GABA cycle and schizophrenia-relevant behaviors in mice. Sci Adv 5:eaau8317
Zhernakova A, Kurilshikov A, Bonder MJ, Tigchelaar EF, Schirmer M, Vatanen T, Mujagic Z, Vila AV, Falony G, Vieira-Silva S, Wang J, Imhann F, Brandsma E, Jankipersadsing SA, Joossens M, Cenit MC, Deelen P, Swertz MA, Weersma RK, Feskens EJ, Netea MG, Gevers D, Jonkers D, Franke L, Aulchenko YS, Huttenhower C, Raes J, Hofker MH, Xavier RJ, Wijmenga C, Fu J (2016) Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity. Science 352:565–569
Ziedonis D, Hitsman B, Beckham JC, Zvolensky M, Adler LE, Audrain-McGovern J, Breslau N, Brown RA, George TP, Williams J, Calhoun PS, Riley WT (2008) Tobacco use and cessation in psychiatric disorders: National Institute of Mental Health report. Nicotine Tob Res 10:1691–1715
Acknowledgements
This works was supported by the Louis Stokes Cleveland DVAMC Research Service and by a grant from the VISN 10 Research Initiative Program (to CJD and GEJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to a Special Issue on Microbiome in Psychiatry & Psychopharmacology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaskiw, G.E., Obrenovich, M.E. & Donskey, C.J. The phenolic interactome and gut microbiota: opportunities and challenges in developing applications for schizophrenia and autism. Psychopharmacology 236, 1471–1489 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05267-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05267-3