Abstract
Rationale
Aging is characterized by a decrease in N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) in the hippocampus, which might be one of the factors involved in the age-dependent cognitive decline. D-Cycloserine (DCS), a partial agonist of the NMDAR glycine recognition site, could improve memory deficits associated to neurodegenerative disorders and cognitive deficits observed in normal aging.
Objectives and Methods
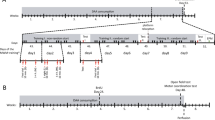
The aim of the present study was to explore whether DCS would reverse age-dependent memory deficits and decreases in NMDA receptor subunits (GluN1, GluN2A, and GluN2B) and the presynaptic protein synaptophysin in Wistar rats. We investigated the effects of pre-training infusions of DCS (10 μg/hemisphere) in the ventral hippocampus on two hippocampal-dependent learning tasks, the social transmission of food preference (STFP), and the Morris water maze (MWM).
Results
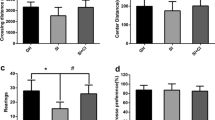
The results revealed that infusions of DCS administered before the acquisition sessions rescued deficits in the STFP retention and MWM reversal learning in old rats. DCS also significantly increased the hippocampal levels of synaptophysin in old rats, which correlated with STFP and MWM performance in all tests. Moreover, although the levels of the GluN1 subunit correlated with the MWM acquisition and reversal, DCS did not enhance the expression of such synaptic protein.
Conclusions
The present behavioral results support the role of DCS as a cognitive enhancer and suggest that enhancing the function of NMDARs and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus may be related to improvement in social memory and spatial learning reversal in aged animals.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MM, Shi L, Linville MC, Forbes ME, Long AB, Bennett C, Newton IG, Carter CS, Sonntag WE, Riddle DR, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2008) Caloric restriction and age affect synaptic proteins in hippocampal CA3 and spatial learning ability. Exp Neurol 211:141–149
Alvarez P, Lipton PA, Melrose R, Eichenbaum H (2001) Differential effects of damage within the hippocampal region on memory for a natural, nonspatial odor-odor association. Learn Mem 8(2):79–86
Anderson RM, Birnie AK, Koblesky NK, Romig-Martin SA, Radley JJ (2014) Adrenocortical status predicts the degree of age-related deficits in prefrontal structural plasticity and working memory. J Neurosci 34:8387–8397
Aura J, Riekkinen M, Riekkinen P (1998) Tetrahydroaminoacridine and D-cycloserine stimulate acquisition of water maze spatial navigation in aged rats. Eur J Pharmacol 342:15–20
Aura J, Riekkinen P (2000) Pre-training blocks the improving effect of tetrahydroaminoacridine and D-cycloserine on spatial navigation performance in aged rats. Eur J Pharmacol 390:313–318
Bannerman DM, Deacon RMJ, Offen S, Friswell J, Grubb M, Rawlins JNP (2002) Double dissociation of function within the hippocampus: spatial memory and hyponeophagia. Behav Neurosci 116(5):884
Bannerman DM, Rawlins JNP, McHugh SB, Deacon RMJ, Yee BK, Bast T et al (2004) Regional dissociations within the hippocampus-memory and anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:273–283
Baxter MG, Lanthorn TH, Frick KM, Golski S, Wan RQ, Olton DS (1994) D-Cycloserine, a novel cognitive enhancer, improves spatial memory in aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 15:207–213
Billard J, Rouaud E (2007) Deficit of NMDA receptor activation in CA1 hippocampal area of aged rats is rescued by D-cycloserine. Eur J Neurosci 25(8):2260–2268
Billard JM (2015) d-Serine in the aging hippocampus. J Pharm Biomed Anal 116:18–24
Bolognin S, Buffelli M, Puoliväli J, Iqbal K (2014) Rescue of cognitive-aging by administration of a neurogenic and/or neurotrophic compound. Neurobiol Aging 35:2134–2146
Brim BL, Haskell R, Awedikian R, Ellinwood NM, Jin L, Kumar A, Foster TC, Magnusson KR (2013) Memory in aged mice is rescued by enhanced expression of the GluN2B subunit of the NMDA receptor. Behav Brain Res 238:211–226
Brothers HM, Bardou I, Hopp SC, Kaercher RM, Corona AW, Fenn AM, Godbout JP, Wenk GL (2013) Riluzole partially rescues age-associated, but not LPS-induced, loss of glutamate transporters and spatial memory. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 8:1098–1105
Bunsey M, Eichenbaum H (1995) Selective damage to the hippocampal region blocks long-term retention of a natural and nonspatial stimulus-stimulus association. Hippocampus 5:546–556
Burger C, López MC, Feller JA, Baker HV, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ (2007) Changes in transcription within the CA1 field of the hippocampus are associated with age-related spatial learning impairments. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87:21–41
Carballo-Márquez A, Vale-Martínez A, Guillazo-Blanch G, Martí-Nicolovius M (2009) Muscarinic transmission in the basolateral amygdala is necessary for the acquisition of socially transmitted food preferences in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 91:98–101
Carter CS, Leeuwenburgh C, Daniels M, Foster TC (2009) Influence of calorie restriction on measures of age-related cognitive decline: role of increased physical activity. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64:850–859
Cercato MC, Vázquez CA, Kornisiuk E, Aguirre AI, Colettis N, Snitcofsky M, Baez MV (2017) GluN1 and GluN2A NMDA receptor subunits increase in the hippocampus during memory consolidation in the rat. Front Behav Neurosci 10:242
Clayton DA, Mesches MH, Alvarez E, Bickford PC, Browning MD (2002) A hippocampal NR2B deficit can mimic age-related changes in long-term potentiation and spatial learning in the Fischer 344 rat. J Neurosci 22:3628–3637
Countryman RA, Gold PE (2007) Rapid forgetting of social transmission of food preferences in aged rats: relationship to hippocampal CREB activation. Learn Mem 14:350–358
Counts SE, Perez SE, Mufson EJ (2008) Galanin in Alzheimer’s disease: neuroinhibitory or neuroprotective? Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1842–1853
Driscoll I, Sutherland RJ (2005) The aging hippocampus: navigating between rat and human experiments. Rev Neurosci 16:87–121
Espejo PJ, Ortiz V, Martijena ID, Molina VA (2016) Stress-induced resistance to the fear memory labilization/reconsolidation process. Involvement of the basolateral amygdala complex. Neuropharmacology 109:349–356
Fanselow MS, Dong HW (2010) Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 65:7–19
Ferbinteanu J, Ray C, McDonald RJ (2003) Both dorsal and ventral hippocampus contribute to spatial learning in Long–Evans rats. Neurosci Lett 345:131–135
Forsyth JK, Bachman P, Mathalon DH, Roach BJ, Asarnow RF (2015) Augmenting NMDA receptor signaling boosts experience-dependent neuroplasticity in the adult human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:15331–15336
Gallagher M, Burwell R, Burchinal M (1993) Severity of spatial learning impairment in aging: development of a learning index for performance in the Morris water maze. Behav Neurosci 107:618–626
Gallagher M, Stocker AM, Koh MT (2011) Mindspan: lessons from rat models of neurocognitive aging. ILAR J 52:32–40
García-Brito S, Morgado-Bernal I, Biosca-Simon N, Segura-Torres P (2017) Intracranial self-stimulation also facilitates learning in a visual discrimination task in the Morris water maze in rats. Behav Brain Res 317:360–366
Gerlai RT, McNamara A, Williams S, Phillips HS (2002) Hippocampal dysfunction and behavioral deficit in the water maze in mice: an unresolved issue? Brain Res Bull 57(1):3–9
Guo J, Bakshi V, Lin AL (2015) Early shifts of brain metabolism by caloric restriction preserve white matter integrity and long-term memory in aging mice. Front Aging Neurosci 7:213
Hajjar T, Goh YM, Rajion MA, Vidyadaran S, Li TA, Ebrahimi M (2013) Alterations in neuronal morphology and synaptophysin expression in the rat brain as a result of changes in dietary n-6: n-3 fatty acid ratios. Lipids Health Dis 12:113
Kalia LV, Kalia SK, Salter MW (2008) NMDA receptors in clinical neurology: excitatory times ahead. Lancet Neurol 7:742–755
Kennard J, Woodruff-Pak DS (2011) Age sensitivity of behavioral tests and brain substrates of normal aging in mice. Front Aging Neurosci 3:9
Kishi A, Ohno M, Watanabe S (1998) Concurrent activation of hippocampal glycine and polyamine sites of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor synergistically reverses working memory deficits in rats. Neurosci Lett 257:131–134
Kjelstrup KB, Solstad T, Brun VH, Hafting T, Leutgeb S, Witter MP, Moser EI, Moser MB (2008) Finite scale of spatial representation in the hippocampus. Science 321:140–143
Klencklen G, Després O, Dufour A (2012) What do we know about aging and spatial cognition? Reviews and perspectives. Ageing Res Rev 11(1):123–135
Kovács T (2004) Mechanisms of olfactory dysfunction in aging and neurodegenerative disorders. Ageing Res Rev 3:215–232
Kraemer S, Apfelbach R (2004) Olfactory sensitivity, learning and cognition in young adult and aged male Wistar rats. Physiol Behav 81:435–442
Kumar A (2015) NMDA receptor function during senescence: implication on cognitive performance. Front Neurosci 9:473
Le Jeune H, Cécyre D, Rowe W, Meaney MJ, Quirion R (1996) Ionotropic glutamate receptor subtypes in the aged memory-impaired and unimpaired Long-Evans rat. Neuroscience 74:349–363
Lin CH, Huang YJ, Lin CJ, Lane HY, Tsai GE (2014) NMDA neurotransmission dysfunction in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 20:5169–5179
Liu P, Smith PF, Darlington CL (2008) Glutamate receptor subunits expression in memory-associated brain structures: regional variations and effects of aging. Synapse 62:834–841
Loureiro M, Lecourtier L, Engeln M, Lopez J, Cosquer B, Geiger K, Kelche C, Cassel JC, Pereira de Vasconcelos A (2012) The ventral hippocampus is necessary for expressing a spatial memory. Brain Struct Funct 217:93–106
Magnusson KR, Kresge D, Supon J (2006) Differential effects of aging on NMDA receptors in the intermediate versus the dorsal hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 27:324–333
Martin SJ, Grimwood PD, Morris RGM (2000) Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:649–711
McHugh SB, Niewoehner B, Rawlins JNP, Bannerman DM (2008) Dorsal hippocampal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors underlie spatial working memory performance during non-matching to place testing on the T-maze. Behav Brain Res 186(1):41–47
Ménard C, Quirion R, Bouchard S, Ferland G, Gaudreau P (2014) Glutamatergic signaling and low prodynorphin expression are associated with intact memory and reduced anxiety in rat models of healthy aging. Front Aging Neurosci 6:81
Ménard C, Quirion R, Vigneault E, Bouchard S, Ferland G, El Mestikawy S et al (2015) Glutamate presynaptic vesicular transporter and postsynaptic receptor levels correlate with spatial memory status in aging rat models. Neurobiol Aging 36:1471–1482
Mickley GA, Remus JL, Ramos L, Wilson GN, Biesan OR, Ketchesin KD (2012) Acute, but not chronic, exposure to d-cycloserine facilitates extinction and modulates spontaneous recovery of a conditioned taste aversion. Physiol Behav 105:417–427
Monahan JB, Handelmann GE, Hood WF, Cordi AA (1989) D-Cycloserine, a positive modulator of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, enhances performance of learning tasks in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:649–653
Monti B, Virgili M, Contestabile A (2004) Alterations of markers related to synaptic function in aging rat brain, in normal conditions or under conditions of long-term dietary manipulation. Neurochem Int 44:579–584
Morris RG, Garrud P, Rawlins JN, O’Keefe J (1982) Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297:681–683
Moser MB, Moser EI (1998) Functional differentiation in the hippocampus. Hippocampus 8:608–619
Newton IG, Forbes ME, Linville MC, Pang H, Tucker EW, Riddle DR, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2008) Effects of aging and caloric restriction on dentate gyrus synapses and glutamate receptor subunits. Neurobiol Aging 29:1308–1318
Nicholson DA, Yoshida R, Berry RW, Gallagher M, Geinisman Y (2004) Reduction in size of perforated postsynaptic densities in hippocampal axospinous synapses and age-related spatial learning impairments. J Neurosci 24:7648–7653
Nieves-Martinez E, Haynes K, Childers SR, Sonntag WE, Nicolle MM (2012) Muscarinic receptor/G-protein coupling is reduced in the dorsomedial striatum of cognitively impaired aged rats. Behav Brain Res 227:258–264
Norberg MM, Krystal JH, Tolin DF (2008) A meta-analysis of D-cycloserine and the facilitation of fear extinction and exposure therapy. Biol Psychiatry 63:1118–1126
Novier A, Van Skike CE, Diaz-Granados JL, Mittleman G, Matthews DB (2013) Acute alcohol produces ataxia and cognitive impairments in aged animals: a comparison between young adult and aged rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1–8
Ohno M, Watanabe S (1996) D-Cycloserine, a glycine site agonist, reverses working memory failure by hippocampal muscarinic receptor blockade in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 318:267–271
Ohno M, Kobayashi M, Kishi A, Watanabe S (1997) Working memory failure by combined blockade of muscarinic and β‐adrenergic transmission in the rat hippocampus. Neuroreport 8(7):1571–1575
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. San Diego Acad. Press
Portero-Tresserra M, Cristóbal-Narváez P, Martí-Nicolovius M, Guillazo-Blanch G, Vale-Martínez A (2013b) D-Cycloserine in prelimbic cortex reverses scopolamine-induced deficits in olfactory memory in rats. PLoS One 8:e70584
Portero-Tresserra M, Del Olmo N, Martí-Nicolovius M, Guillazo-Blanch G, Vale-Martínez A (2014) D-Cycloserine prevents relational memory deficits and suppression of long-term potentiation induced by scopolamine in the hippocampus. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24:1798–1807
Portero-Tresserra M, Martí-Nicolovius M, Guillazo-Blanch G, Boadas-Vaello P, Vale-Martínez A (2013a) D-Cycloserine in the basolateral amygdala prevents extinction and enhances reconsolidation of odor-reward associative learning in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 100:1–11
Quartermain D, Mower J, Rafferty MF, Herting RL, Lanthorn TH (1994) Acute but not chronic activation of the NMDA-coupled glycine receptor with D-cycloserine facilitates learning and retention. Eur J Pharmacol 257:7–12
Ren J, Li X, Zhang X, Li M, Wang Y, Ma Y (2013) The effects of intra-hippocampal microinfusion of D-cycloserine on fear extinction, and the expression of NMDA receptor subunit NR2B and neurogenesis in the hippocampus in rats. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 44:257–264
Riekkinen M, Kemppainen S, Riekkinen P (1997) Effects of stimulation of alpha 1-adrenergic and NMDA/glycine-B receptors on learning defects in aged rats. Psychopharmacology 131(1):49–56
Riekkinen P, Ikonen S, Riekkinen M (1998) D-Cycloserine, a partial NMDA receptor-associated glycine-B site agonist, enhances reversal learning, but a cholinesterase inhibitor and nicotine has no effect. Neuroreport 9:3647–3651
Robitsek RJ, Fortin NJ, Koh MT, Gallagher M, Eichenbaum H (2008) Cognitive aging: a common decline of episodic recollection and spatial memory in rats. J Neurosci 28:8945–8954
Rosenzweig ES, Barnes CA (2003) Impact of aging on hippocampal function: plasticity, network dynamics, and cognition
Ruediger S, Spirig D, Donato F, Caroni P (2012) Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning. Nat Neurosci 15:1563–1571
Schwartz BL, Hashtroudi S, Herting RL, Schwartz P, Deutsch SI (1996) d-Cycloserine enhances implicit memory in Alzheimer patients. Neurology 46:420–424
Shi L, Adams MM, Linville MC, Newton IG, Forbes ME, Long AB, Riddle DR, Brunso-Bechtold JK (2007) Caloric restriction eliminates the aging-related decline in NMDA and AMPA receptor subunits in the rat hippocampus and induces homeostasis. Exp Neurol 206:70–79
Singh R, Manchanda S, Kaur T, Kumar S, Lakhanpal D, Lakhman SS, Kaur G (2015) Middle age onset short-term intermittent fasting dietary restriction prevents brain function impairments in male Wistar rats. Biogerontology 16:775–788
Smith TD, Adams MM, Gallagher M, Morrison JH, Rapp PR (2000) Circuit-specific alterations in hippocampal synaptophysin immunoreactivity predict spatial learning impairment in aged rats. J Neurosci 20:6587–6593
Snyder JS, Radik R, Wojtowicz JM, Cameron HA (2009) Anatomical gradients of adult neurogenesis and activity: young neurons in the ventral dentate gyrus are activated by water maze training. Hippocampus 19:360–370
Speakman JR, Mitchell SE (2011) Caloric restriction. Mol Asp Med 32:159–221
Stephens ML, Quintero JE, Pomerleau F, Huettl P, Gerhardt GA (2011) Age-related changes in glutamate release in the CA3 and dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 32:811–820
Thompson LT, Disterhoft JF (1997) Age- and dose-dependent facilitation of associative eyeblink conditioning by D-cycloserine in rabbits. Behav Neurosci 111:1303–1312
Villarejo-Rodríguez I, Vale-Martínez A, Guillazo-Blanch G, Martí-Nicolovius M (2010) d-Cycloserine in prelimbic cortex enhances relearning of an odor-reward associative task. Behav Brain Res 213(1):113–116
Villarejo-Rodríguez I, Boadas-Vaello P, Portero-Tresserra M, Vale-Martínez A, Martí-Nicolovius M, Guillazo-Blanch G (2013) Learning deficits in an odor reward-task induced by parafascicular thalamic lesions are ameliorated by pretraining d-cycloserine in the prelimbic cortex. Behav Brain Res 238:289–292
Von Lubitz DK, Paul IA, Bartus RT, Jacobson KA (1993) Effects of chronic administration of adenosine A1 receptor agonist and antagonist on spatial learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 249:271–280
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2014) Assessing spatial learning and memory in rodents. ILAR J 55:310–332
Waddell J, Mallimo E, Shors T (2010) D-Cycloserine reverses the detrimental effects of stress on learning in females and enhances retention in males. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:31–36
Weimer RM, Jorgensen EM (2003) Controversies in synaptic vesicle exocytosis. J Cell Sci 116:3661–3666
Yamamoto S, Morinobu S, Fuchikami M, Kurata A, Kozuru T, Yamawaki S (2008) Effects of single prolonged stress and D-cycloserine on contextual fear extinction and hippocampal NMDA receptor expression in a rat model of PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2108–2116
Yankner BA, Lu T, Loerch P (2008) The aging brain. Annu Rev Pathol 3:41–66
Walker WC, Murdoch JM (1957) Cycloserine in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. A report on toxicity. Tubercle, Lond 38:297
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (PSI2014-52660-R). The authors thank Dr. Jose Aguilera for his advice in conducting and interpreting the western blots data and Mr. Gerald-Patrick Fannon for his support with the English-language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MPT, MMN, GGB, and AVM designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. MPT, MMN, MTG, and AC conducted the experiments. MPT and MMN analyzed the data. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures were carried out in compliance with the European Community Council Directive for care and use of laboratory animals (86/609/ECC) and with the Generalitat de Catalunya’s authorization (DOGC 2450 7/ 8/1997, DARP protocol number 3046).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have contributed to the work and agree with the findings. This work has not been published before nor is it being considered for publication in another journal. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Portero-Tresserra, M., Martí-Nicolovius, M., Tarrés-Gatius, M. et al. Intra-hippocampal d-cycloserine rescues decreased social memory, spatial learning reversal, and synaptophysin levels in aged rats. Psychopharmacology 235, 1463–1477 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4858-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4858-z