Abstract
Rationale
Environmental stimulus control over drug relapse requires the retrieval of context-response-cocaine associations, maintained in long-term memory through active reconsolidation processes. Identifying the neural substrates of these phenomena is important from a drug addiction treatment perspective.
Objectives
The present study evaluated whether the agranular insular cortex (AI) plays a role in drug context-induced cocaine-seeking behavior and cocaine memory reconsolidation.
Methods
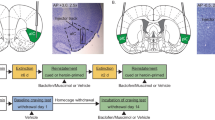
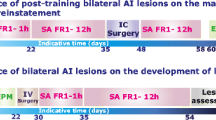
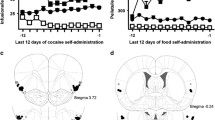
Rats were trained to lever press for cocaine infusions in a distinctive context, followed by extinction training in a different context. Rats in experiment 1 received bilateral microinfusions of vehicle or a GABA agonist cocktail (baclofen and muscimol (BM)) into the AI or the overlying somatosensory cortex (SSJ, anatomical control region) immediately before a test of drug-seeking behavior (i.e., non-reinforced lever presses) in the previously cocaine-paired context. The effects of these manipulations on locomotor activity were also assessed in a novel context. Rats in experiment 2 received vehicle or BM into the AI after a 15-min reexposure to the cocaine-paired context, intended to reactivate context-response-cocaine memories and initiate their reconsolidation. The effects of these manipulations on drug context-induced cocaine-seeking behavior were assessed 72 h later.
Results
BM-induced pharmacological inactivation of the AI, but not the SSJ, attenuated drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior without altering locomotor activity. Conversely, AI inactivation after memory reactivation failed to impair subsequent drug-seeking behavior and thus cocaine memory reconsolidation.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that the AI is a critical element of the neural circuitry that mediates contextual control over cocaine-seeking behavior.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addicott MA, Sweitzer MM, Froeliger B, Rose JE, McClernon FJ (2015) Increased functional connectivity in an insula-based network is associated with improved smoking cessation outcomes. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:2648–2656
Arguello AA, Hodges MA, Wells AM et al (2014) Involvement of amygdalar protein kinase A, but not calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, in the reconsolidation of cocaine-related contextual memories in rats. Psychopharmacology 231:55–65
Barak S, Liu F, Ben Hamida S et al (2013) Disruption of alcohol-related memories by mTORC1 inhibition prevents relapse. Nat Neurosci 16:1111–1117
Belin-Rauscent A, Daniel ML, Puaud M, Jupp B, Sawiak S, Howett D, McKenzie C, Caprioli D, Besson M, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ, Dalley JW, Belin D (2016) From impulses to maladaptive actions: the insula is a neurobiological gate for the development of compulsive behavior. Mol Psychiatry 21(4):491–499
Childress AR, Mozley PD, McElgin W et al (1999) Limbic activation during cue-induced cocaine craving. Am J Psychiatry 156:11–18
Clark L, Bechara A, Damasio H et al (2008) Differential effects of insular and ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions on risky decision-making. Brain 131:1311–1322
Contreras M, Ceric F, Torrealba F (2007) Inactivation of the interoceptive insula disrupts drug craving and malaise induced by lithium. Science 318:655–658
Contreras M, Billeke P, Vicencio S et al (2012) A role for the insular cortex in long-term memory for context-evoked drug craving in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:2101–2108
Cosme CV, Gutman AL, LaLumiere RT (2015) The dorsal agranular insular cortex regulates the cued reinstatement of cocaine-seeking, but not food-seeking, behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:2425–2433
Di Pietro NC, Black YD, Kantak KM (2006) Context-dependent prefrontal cortex regulation of cocaine self-administration and reinstatement behaviors in rats. Eur J Neurosci 24:3285–3298
Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, Childress AR, O’Brien CP (1992) Conditioned responses to cocaine-related stimuli in cocaine abuse patients. Psychopharmacology 107:523–529
Foltin RW, Haney M (2000) Conditioned effects of environmental stimuli paired with smoked cocaine in humans. Psychopharmacology 149:24–33
Franklin TR, Acton PD, Maldjian JA et al (2002) Decreased gray matter concentration in the insular, orbitofrontal, cingulate, and temporal cortices of cocaine patients. Biol Psychiatry 51:134–142
Fuchs RA, See RE (2002) Basolateral amygdala inactivation abolishes conditioned stimulus- and heroin-induced reinstatement of extinguished heroin-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 160:425–433
Fuchs RA, Fuchs RA, Evans KA, Parker MP, See RE (2004) Differential involvement of orbitofrontal cortex subregions in conditioned cue-induced and cocaine-primed reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. J Neurosci 24(29):6600–6610
Fuchs RA, Evans KA, Ledford CC et al (2005) The role of the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, basolateral amygdala, and dorsal hippocampus in contextual reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 30(2):296–309
Fuchs RA, Eaddy JL, Su Z-I, Bell GH (2007) Interactions of the basolateral amygdala with the dorsal hippocampus and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex regulate drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking in rats. Eur J Neurosci 26:487–498
Fuchs RA, Bell GH, Ramirez DR et al (2009) Basolateral amygdala involvement in memory reconsolidation processes that facilitate drug context-induced cocaine seeking. Eur J Neurosci 30:889–900
García-DeLaTorre P, Rodriguez-Ortiz CJ, Arreguin-Martinez JL, Cruz-Castañeda P, Bermúdez-Rattoni F (2009) Simultaneous but not independent anisomycin infusions in insular cortex and amygdala hinder stabilization of taste memory when updated. Learn Mem 16(9):514–519
García-DeLaTorre P, Rodríguez-Ortiz CJ, Balderas I, Bermúdez-Rattoni F (2010) Differential participation of temporal structures in the consolidation and reconsolidation of taste aversion extinction. Eur J Neurosci 32(6):1018–1023
Grant S, London ED, Newlin DB et al (1996) Activation of memory circuits during cue-elicited cocaine craving. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:12040–12045
Grimm JW, See RE (2000) Dissociation of primary and secondary reward-relevant limbic nuclei in an animal model of relapse. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:473–479
Ishii H, Ohara S, Tobler PN et al (2012) Inactivating anterior insular cortex reduces risk taking. J Neurosci 32:16031–16039
Khani A, Rainer G (2016) Neural and neurochemical basis of reinforcement-guided decision making. J Neurophysiol 116:724–741
Kobilo T, Hazvi S, Dudai Y (2007) Role of cortical cannabinoid CB1 receptor in conditioned taste aversion memory. Eur J Neurosci 25(11):3417–3421
Kühn S, Gallinat J (2011) Common biology of craving across legal and illegal drugs - a quantitative meta-analysis of cue-reactivity brain response. Eur J Neurosci 33:1318–1326
Lasseter HC, Ramirez DR, Xie X, Fuchs RA (2009) Involvement of the lateral orbitofrontal cortex in drug context-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Eur J Neurosci 30:1370–1381
Lasseter HC, Xie X, Ramirez DR, Fuchs RA (2010) Prefrontal cortical regulation of drug seeking in animal models of drug relapse. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 3:101–117
Lee JLC, Di Ciano P, Thomas KL, Everitt BJ (2005) Disrupting reconsolidation of drug memories reduces cocaine-seeking behavior. Neuron 47:795–801
Lee JLC, Milton AL, Everitt BJ (2006) Cue-induced cocaine seeking and relapse are reduced by disruption of drug memory reconsolidation. J Neurosci 26:5881–5887
Liu P, Zhang J, Li M, Sui N (2016) Distinctive roles of 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine in anterior agranular insular and basolateral amygdala in reconsolidation of aversive memory associated with morphine in rats. Front Behav Neurosci. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00050
Lovero KL, Simmons AN, Aron JL, Paulus MP (2009) Anterior insular cortex anticipates impending stimulus significant. NeuroImage 45:976–983
McClernon FJ, Conklin CA, Kozink RV, Adcock RA, Sweitzer MM, Addicott MA, Chou YH, Chen NK, Hallyburton MB, DeVito AM (2016) Hippocampal and insular response to smoking-related environments: neuroimaging evidence for drug-context effects in nicotine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 41(3):877–885
Menon V, Uddin LQ (2010) Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Struct Funct 214:665–667
Milekic MH, Brown SD, Castellini C, Alberini CM (2006) Persistent disruption of an established morphine conditioned place preference. J Neurosci 26:3010–3020
Miller CA, Marshall JF (2005) Molecular substrates for retrieval and reconsolidation of cocaine-associated contextual memory. Neuron 47:873–884
Moreno-López L, Catena A, Fernández-Serrano MJ et al (2012) Trait impulsivity and prefrontal gray matter reductions in cocaine dependent individuals. Drug Alcohol Depend 125:208–214
Nader K, Schafe GE, Le Doux JE (2000) Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval. Nature 406:722–726
Naqvi NH, Gaznick N, Tranel D, Bechara A (2014) The insula: a critical neural substrate for craving and drug seeking under conflict and risk. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1316:53–70
National Research Council (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals: eight edition. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. doi:10.17266/12910
Paulus MP, Tapert SF, Schuckit MA (2005) Neural activation patterns of methamphetamine-dependent subjects during decision making predict relapse. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:761–768
Paxinos G, Watson C (2014) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, seventh edition. Academic Press, San Diego, United States
Pelloux Y, Murray JE, Everitt BJ (2013) Differential roles of the prefrontal cortical subregions and basolateral amygdala in compulsive cocaine seeking and relapse after voluntary abstinence in rats. Eur J Neurosci 38(7):3018–3026
Pushparaj A, Hamani C, Yu W, Shin DS, Kang B, Nobrega JN, Le Foll B (2013) Electrical stimulation of the insular region attenuates nicotine-taking and nicotine-seeking behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(4):690–698
Pushparaj A, Kim AS, Musiol M et al (2015a) Involvement of the rostral agranular insular cortex in nicotine self-administration in rats. Behav Brain Res 290:77–83
Pushparaj A, Kim AS, Musiol M et al (2015b) Differential involvement of the agranular vs granular insular cortex in the acquisition and performance of choice behavior in a rodent gambling task. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:2832–2842
Ramirez DR, Bell GH, Lasseter HC et al (2009) Dorsal hippocampal regulation of memory reconsolidation processes that facilitate drug context-induced cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Eur J Neurosci 30:901–912
Rohsenow DJ, Niaura RS, Childress AR et al (1990) Cue reactivity in addictive behaviors: theoretical and treatment implications. Int J Addict 25:957–993
Schoenbaum G, Roesch MR, Stalnaker TA, Takahashi YK (2009) A new perspective on the role of the orbitofrontal cortex in adaptive behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(12):885–892
Seif T, Chang S-J, Simms JA et al (2013) Cortical activation of accumbens hyperpolarization-active NMDARs mediates aversion-resistant alcohol intake. Nat Neurosci 16:1094–1100
Sorg BA (2012) Reconsolidation of drug memories. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:1400–1417
Sorg BA, Todd RP, Slaker M, Churchill L (2015) Anisomycin in the medial prefrontal cortex reduces reconsolidation of cocaine-associated memories in the rat self-administration model. Neuropharmacology 92:25–33
St. Onge JR, Floresco SB (2010) Prefrontal cortical contribution to risk-based decision making. Cereb Cortex 20:1816–1828
Stehberg J, Levy D, Zangen A (2009) Impairment of aversive memory reconsolidaiton by localized intracranial electrical stimulation. Eur J Neurosci 29:964–969
Taylor JR, Olausson P, Quinn JJ, Torregrossa MM (2009) Targeting extinction and reconsolidation mechanisms to combat the impact of drug cues on addiction. Neuropharmacology 56(Suppl 1):186–195
Théberge FRM, Milton AL, Belin D et al (2010) The basolateral amygdala and nucleus accumbens core mediate dissociable aspects of drug memory reconsolidation. Learn Mem 17:444–453
Tronson NC, Taylor JR (2007) Molecular mechanisms of memory reconsolidation. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:262–275
Wang Y, Zhang TY, Xin J, Li T, Yu H, Li N, Chen ZY (2012) Differential involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in reconsolidation and consolidation of conditioned taste aversion memory. PLoS One 7(11):e49942
Wells AM, Lasseter HC, Xie X et al (2011) Interaction between the basolateral amygdala and dorsal hippocampus is critical for cocaine-memory reconsolidation and subsequent drug context-induced cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Learn Mem 18:693–702
Wells AM, Arguello AA, Xie X et al (2013) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase in the basolateral amygdala, but not the nucleus accumbens core, is critical for context-response-cocaine-memory reconsolidation in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:753–762
Zubedat S, Akirav I (2017) The involvement of cannabinoids and mTOR in the reconsolidation of an emotional memory in the hippocampal-amygdala-insular circuit. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2017.01.011
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIDA grants R01 DA017673 and DA025646.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All protocols for the housing and treatment of animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and followed the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Rats (Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources on Life Sciences 2011).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arguello, A.A., Wang, R., Lyons, C.M. et al. Role of the agranular insular cortex in contextual control over cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 234, 2431–2441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4632-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4632-7