Abstract
Rationale
Regular use of the street drug, ecstasy, produces a number of cognitive and behavioral deficits. One possible mechanism for these deficits is functional changes in serotonin (5-HT) receptors as a consequence of prolonged 3,4 methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)-produced 5-HT release. Of particular interest are the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptor subtypes since they have been implicated in several of the behaviors that have been shown to be impacted in ecstasy users and in animals exposed to MDMA.
Objectives
This study aimed to determine the effect of extensive MDMA self-administration on behavioral responses to the 5-HT1A agonist, 8-hydroxy-2-(n-dipropylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), and the 5-HT1B/1A agonist, RU 24969.
Methods
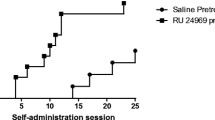
Male Sprague-Dawley rats self-administered a total of 350 mg/kg MDMA, or vehicle, over 20–58 daily self-administration sessions. Two days after the last self-administration session, the hyperactive response to 8-OH-DPAT (0.03–1.0 mg/kg) or the adipsic response to RU 24969 (0.3–3.0 mg/kg) were assessed.
Results
8-OH-DPAT dose dependently increased horizontal activity, but this response was not altered by MDMA self-administration. The dose-response curve for RU 24969-produced adipsia was also not altered by MDMA self-administration.
Conclusions
Cognitive and behavioral deficits produced by repeated exposure to MDMA self-administration are not likely due to alterations in 5-HT1A or 5-HT1B receptor mechanisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre N, Galbete J, Lasheras B, Del Río J (1995) Methylenedioxymethamphetamine induces opposite changes in central pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 281:101–105
Aguirre N, Frechilla D, García‐Osta A, Lasheras B, Del RIo J (1997) Differential regulation by methylenedioxymethamphetamine of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor density and mRNA expression in rat hippocampus, frontal cortex, and brainstem: the role of corticosteroids. J Neurochem 68:1099–1105
Aguirre N, Ballaz S, Lasheras B, Del Rio J (1998) MDMA (“ecstasy”) enhances 5-HT1A receptor density and 8-OH-DPAT-induced hypothermia: blockade by drugs preventing 5-hydroxytryptamine depletion. Eur J Pharmacol 346:181–188
Aronsen D, Webster J, Schenk S (2014) RU 24969-produced adipsia and hyperlocomotion: differential role of 5HT1A and 5HT1B receptor mechanisms. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:1–4
Assié M-B, Bardin L, Auclair AL, Carilla-Durand E, Depoortère R, Koek W, Kleven MS, Colpaert F, Vacher B, Newman-Tancredi A (2010) F15599, a highly selective post-synaptic 5-HT1A receptor agonist: in-vivo profile in behavioural models of antidepressant and serotonergic activity. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13:1285–1298
Baumann MH, Rothman RB (2009) Neural and cardiac toxicities associated with 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). Int Rev Neurobiol 88:257–296
Bhide NS, Lipton JW, Cunningham JI, Yamamoto BK, Gudelsky GA (2009) Repeated exposure to MDMA provides neuroprotection against subsequent MDMA-induced serotonin depletion in brain. Brain Res 1286:32–41
Bjorvatn B, Ursin R (1994) Effects of the selective 5-HT1B agonist, CGS 12066B, on sleep/waking stages and EEG power spectrum in rats. J Sleep Res 3:97–105
Bull EJ, Hutson PH, Fone KC (2004) Decreased social behaviour following 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is accompanied by changes in 5-HT2A receptor responsivity. Neuropharmacology 46:202–210
Callaway CW, Geyer MA (1992) Tolerance and cross-tolerance to the activating effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and a 5-hydroxytryptamine1B agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:318–326
Carli M, Samanin R (1992) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin impairs spatial learning in a water maze: role of postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Br J Pharmacol 105:720
Carli M, Samanin R (2000) The 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT reduces rats’ accuracy of attentional performance and enhances impulsive responding in a five-choice serial reaction time task: role of presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Psychopharmacology 149:259–268
Carli M, Tranchina S, Samanin R (1992) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist, impairs performance in a passive avoidance task. Eur J Pharmacol 211:227–234
Castro ME, Diaz A, del Olmo E, Pazos A (2003) Chronic fluoxetine induces opposite changes in G protein coupling at pre and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 44:93–101
Cole JC, Sumnall HR (2003) The pre-clinical behavioural pharmacology of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:199–217
Compan V, Segu L, Buhot M, Daszuta A (1998) Selective increases in serotonin 5-HT1B/1D and 5-HT2A/2C binding sites in adult rat basal ganglia following lesions of serotonergic neurons. Brain Res 793:103–111
Cottler LB, Womack SB, Compton WM, Ben-Abdallah A (2001) Ecstasy abuse and dependence among adolescents and young adults: applicability and reliability of DSM-IV criteria. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 16:599–606
Crino PB, Vogt BA, Volicer L, Wiley RG (1990) Cellular localization of serotonin 1A, 1B and uptake sites in cingulate cortex of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:651–656
Cunningham KA, Anastasio NC (2014) Serotonin at the nexus of impulsivity and cue reactivity in cocaine addiction. Neuropharmacology 76:460–478
Dawson LA, Hughes ZA, Starr KR, Storey JD, Bettelini L, Bacchi F, Arban R, Poffe A, Melotto S, Hagan JJ (2006) Characterisation of the selective 5-HT1B receptor antagonist SB-616234-A (1-[6-(cis-3, 5-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl)-2, 3-dihydro-5-methoxyindol-1-yl]-1-[2′-methyl-4′-(5-methyl-1, 2, 4-oxadiazol-3-yl) biphenyl-4-yl] methanone hydrochloride): in vivo neurochemical and behavioural evidence of anxiolytic/antidepressant activity. Neuropharmacology 50:975–983
De La Garza R II, Fabrizio K, Gupta A (2007) Relevance of rodent models of intravenous MDMA self-administration to human MDMA consumption patterns. Psychopharmacology 189:425–434
De Souza R, Goodwin G, Green A, Heal D (1986) Effect of chronic treatment with 5-HT1 agonist (8-OH-DPAT and RU 24969) and antagonist (isapirone) drugs on the behavioural responses of mice to 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 agonists. Br J Pharmacol 89:377
Degenhardt L, Barker B, Topp L (2004) Patterns of ecstasy use in Australia: findings from a national household survey. Addiction 99:187–195
Dhonnchadha BÁN, Cunningham KA (2008) Serotonergic mechanisms in addiction-related memories. Behav Brain Res 195:39–53
Do J, Schenk S (2011) Self-administered MDMA produces dose‐ and time‐dependent serotonin deficits in the rat brain. Addict Biol 18(3):441–447
Duncan MJ, Hester JM, Hopper JA, Franklin KM (2010) The effects of aging and chronic fluoxetine treatment on circadian rhythms and suprachiasmatic nucleus expression of neuropeptide genes and 5-HT1B receptors. Eur J Neurosci 31:1646–1654
Dworkin SI, Mirkis S, Smith JE (1995) Response-dependent versus response-independent presentation of cocaine: differences in the lethal effects of the drug. Psychopharmacology 117:262–266
Frances H, Monier C (1991) Tolerance to the behavioural effect of serotonergic (5-HT1B) agonists in the isolation induced social behavioural deficit test. Neuropharmacology 30:623–627
Frankfurt M, Mendelson SD, McKittrick CR, McEwen BS (1993) Alterations of serotonin receptor binding in the hypothalamus following acute denervation. Brain Res 601:349–352
Granoff MI, Ashby CRJ (2001) Effect of the repeated administration of (±)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on the behavioral response of rats to the 5-HT1A receptor agonist (±)-8-hydroxy-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin. Neuropsychobiology 43:42–48
Hansen D, Maycock B, Lower T (2001) “Weddings, parties, anything…”, a qualitative analysis of ecstasy use in Perth, Western Australia. Int J Drug Policy 12:181–199
Hensler JG (2003) Regulation of 5-HT1A receptor function in brain following agonist or antidepressant administration. Life Sci 72:1665–1682
Hirst WD, Andree TH, Aschmies S, Childers WE, Comery TA, Dawson LA, Day M, Feingold IB, Grauer SM, Harrison BL (2008) Correlating efficacy in rodent cognition models with in vivo 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor occupancy by a novel antagonist, (R)-N-(2-methyl-(4-indolyl-1-piperazinyl) ethyl)-N-(2-pyridinyl)-cyclohexane carboxamide (WAY-101405). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325:134–145
Hoplight B, Vincow E, Neumaier J (2007) Cocaine increases 5-HT1B mRNA in rat nucleus accumbens shell neurons. Neuropharmacology 52:444–449
Howell LL, Cunningham KA (2015) Serotonin 5-HT2 receptor interactions with dopamine function: implications for therapeutics in cocaine use disorder. Pharmacological Rev 67:176–197
Kalkman HO (1995) RU 24969-induced locomotion in rats is mediated by 5-HT1A receptors. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 352:583–584
Kindlundh-Högberg AM, Svenningsson P, Schiöth HB (2006) Quantitative mapping shows that serotonin rather than dopamine receptor mRNA expressions are affected after repeated intermittent administration of MDMA in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 51:838–847
Lanteri C, Doucet E, Vallejo SH, Godeheu G, Bobadilla A, Salomon L, Lanfumey L, Tassin J (2014) Repeated exposure to MDMA triggers long-term plasticity of noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons. Mol Psychiatry 19:823–833
Le Poul E, Boni C, Nm H, Laporte A-M, Laaris N, Chauveau J, Hamon M, Lanfumey L (2000) Differential adaptation of brain 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors and 5-HT transporter in rats treated chronically with fluoxetine. Neuropharmacology 39:110–122
Lucki I, Singh A, Kreiss DS (1994) Antidepressant-like behavioral effects of serotonin receptor agonists. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 18:85–95
Manrique C, Segu L, Hery M, Faudon M, François-Bellan M (1993) Increase of central 5-HT1B binding sites following 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine axotomy in the adult rat. Brain Res 623:345–348
Manrique C, Francois-Bellan A, Segu L, Becquet D, Hery M, Faudon M, Hery F (1994) Impairment of serotoninergic transmission is followed by adaptive changes in 5HT1B binding sites in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res 663:93–100
Manrique C, Bosler O, Becquet D, Héry F, Faudon M, François-Bellan A (1998) Post-lesion up-regulation of 5-HT1B binding sites in the suprachiasmatic nucleus may be reversed after spontaneous or graft-induced serotonin reinnervation. Brain Res 788:332–336
McCann UD, Mertl M, Eligulashvili V, Ricaurte GA (1999) Cognitive performance in (±) 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “ecstasy”) users: a controlled study. Psychopharmacology 143:417–425
McCreary AC, Bankson MG, Cunningham KA (1999) Pharmacological studies of the acute and chronic effects of (+)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on locomotor activity: role of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A and 5-hydroxytryptamine1B/1D receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:965–973
McGregor IS, Clemens KJ, Van der Plasse G, Li KM, Hunt GE, Chen F, Lawrence AJ (2003) Increased anxiety 3 months after brief exposure to MDMA (“ecstasy”) in rats: association with altered 5-HT transporter and receptor density. Neuropsychopharmacology 28(8):1472–1484
McNamara MG, Kelly JP, Leonard BE (1995) Some behavioural and neurochemical aspects of subacute (±) 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 52:479–484
Mechan AO, O’Shea E, Elliott MJ, Colado M, Green RA (2001) A neurotoxic dose of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA; ecstasy) to rats results in a long term defect in thermoregulation. Psychopharmacology 155:413–418
Meneses A (2001) Could the 5-HT1B receptor inverse agonism affect learning consolidation? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:193–201
Meneses A (2007) Stimulation of 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT2A/2C, 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptors or 5-HT uptake inhibition: short- and long-term memory. Behav Brain Res 184:81–90
Meyer JS, Piper BJ, Vancollie VE (2008) Development and characterization of a novel animal model of intermittent MDMA (“ecstasy”) exposure during adolescence. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139:151–163
Miguéns M, Crespo JA, Del Olmo N, Higuera-Matas A, Montoya GL, García-Lecumberri C, Ambrosio E (2008) Differential cocaine-induced modulation of glutamate and dopamine transporters after contingent and non-contingent administration. Neuropharmacology 55:771–779
Monti JM, Jantos H (1992) Dose-dependent effects of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT on sleep and wakefulness in the rat. J Sleep Res 1:169–175
Monti JM, Pineyro G, Orellana C, Boussard M, Jantos H, Labraga P, Olivera S, Alvarino F (1990) 5-HT receptor agonists 1-(2, 5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and 8-OH-DPAT increase wakefulness in the rat. Biog Amines 7:145–151
Monti JM, Monti D, Jantos H, Ponzoni A (1995) Effects of selective activation of the 5-HT1B receptor with CP-94,253 on sleep and wakefulness in the rat. Neuropharmacology 34:1647–1651
O’Dell LE, Manzardo AM, Polis I, Stouffer DG, Parsons LH (2006) Biphasic alterations in serotonin-1B (5-HT1B) receptor function during abstinence from extended cocaine self-administration. J Neurochem 99:1363–1376
Offord SJ, Ordway GA, Frazer A (1988) Application of [125I] iodocyanopindolol to measure 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptors in the brain of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:144–153
Ohmura Y, Kumamoto H, Tsutsui-Kimura I, Minami M, Izumi T, Yoshida T, Yoshioka M (2013) Tandospirone suppresses impulsive action by possible blockade of the 5-HT1A receptor. J Pharmacol Sci 122:84–92
Parrott AC (2005) Chronic tolerance to recreational MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) or ecstasy. J Psychopharmacol 19:71–83
Parrott AC (2013) MDMA, serotonergic neurotoxicity, and the diverse functional deficits of recreational “ecstasy” users. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1466–1484
Piper BJ, Vu HL, Safain MG, Oliver AJ, Meyer JS (2006) Repeated adolescent 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) exposure in rats attenuates the effects of a subsequent challenge with MDMA or a 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:838–849
Piper BJ, Ali SF, Daniels LG, Meyer JS (2010) Repeated intermittent methylenedioxymethamphetamine exposure protects against the behavioral and neurotoxic, but not hyperthermic, effects of an MDMA binge in adult rats. Synapse 64:421–431
Pitsikas N, Sakellaridis N (2005) The 5-HT2c receptor antagonist RO 60–0491 counteracts rats’ retention deficits in a recognition memory task. Brain Res 1054:200–202
Pranzatelli MR, Razi P (1994) Drug-induced regulation of [125I] iodocyanopindolol-labeled 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor binding sites in the central nervous system. Neuropsychopharmacology 10:259–264
Przegaliński E, Czepiel K, Nowak E, Dlaboga D, Filip M (2003) Withdrawal from chronic cocaine up-regulates 5-HT1B receptors in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 351:169–172
Reneman L, Endert E, de Bruin K, Lavalaye J, Feenstra MG, de Wolff FA, Booij J (2002) The acute and chronic effects of MDMA (“ecstasy”) on cortical 5-HT2A receptors in rat and human brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 26(3):387–396
Reveron ME, Maier EY, Duvauchelle CL (2010) Behavioral, thermal and neurochemical effects of acute and chronic 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“ecstasy”) self-administration. Behav Brain Res 207:500–507
Scanzello CR, Hatzidimitriou G, Martello AL, Katz JL, Ricaurte G (1993) Serotonergic recovery after (+/−) 3,4-(methylenedioxy) methamphetamine injury: observations in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:1484–1491
Scheffel U, Lever J, Stathis M, Ricaurte G (1992) Repeated administration of MDMA causes transient down-regulation of serotonin 5-HT2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 31:881–893
Schenk S, Hely L, Lake B, Daniela E, Gittings D, Mash DC (2007) MDMA self‐administration in rats: acquisition, progressive ratio responding and serotonin transporter binding. Eur J Neurol 26:3229–3236
Schenk S, Gittings D, Colussi-Mas J (2011) Dopaminergic mechanisms of reinstatement of MDMA‐seeking behaviour in rats. Br J Pharmacol 162:1770–1780
Schenk S, Colussi-Mas J, Do J, Bird J (2012) Profile of MDMA self-administration from a large cohort of rats: MDMA develops a profile of dependence with extended testing. J Drug Alcohol Res 1:1–6
Schenk S, Abraham B, Aronsen D, Colussi-Mas J, Do J (2013) Effects of repeated exposure to MDMA on 5HT1a autoreceptor function: behavioral and neurochemical responses to 8-OHDPAT. Psychopharmacology 227:355–361
Sexton T, McEvoy C, Neumaier J (1999) (+) 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“ecstasy”) transiently increases striatal 5-HT1B binding sites without altering 5-HT1B mRNA in rat brain. Mol Psychiatry 4:572–579
Sharpley A, Elliott J, Attenburrow M-J, Cowen P (1994) Slow wave sleep in humans: role of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. Neuropharmacology 33:467–471
Siuciak JA, Chapin DS, McCarthy SA, Guanowsky V, Brown J, Chiang P, Marala R, Patterson T, Seymour PA, Swick A (2007) CP-809,101, a selective 5-HT2c agonist, shows activity in animal models of antipsychotic activity. Neuropharmacology 52:279–290
Tatarczynska E, Klodzinska A, Stachowicz K, Chojnacka-Wojcik E (2004) Effects of a selective 5-HT1B receptor agonist and antagonists in animal models of anxiety and depression. Behav Pharmacol 15:523–534
Taurah L, Chandler C, Sanders G (2014) Depression, impulsiveness, sleep, and memory in past and present polydrug users of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy). Psychopharmacology 231:737–751
Thompson MR, Callaghan PD, Hunt GE, McGregor IS (2008) Reduced sensitivity to MDMA-induced facilitation of social behaviour in MDMA pre-exposed rats. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1013–1021
Topp L, Hall W, Hando J (1997) Is there a dependence syndrome for ecstasy? NDARC, Sydney, pp 1–36
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (2015) World drug report
Verheyden SL, Henry JA, Curran HV (2003) Acute, sub-acute and long-term subjective consequences of “ecstasy” (MDMA) consumption in 430 regular users. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 18:507–517
Wagner D, Becker B, Koester P, Gouzoulis‐Mayfrank E, Daumann J (2013) A prospective study of learning, memory, and executive function in new MDMA users. Addiction 108:136–145
Weissmann D, Mach E, Oberlander C, Demassey Y, Pujol J-F (1986) Evidence for hyperdensity of 5HT1B binding sites in the substantia nigra of the rat after 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine intraventricular injection. Neurochem Int 9:191–200
Welner S, De Montigny C, Desroches J, Desjardins P, Suranyi‐Cadotte B (1989) Autoradiographic quantification of serotonin1A receptors in rat brain following antidepressant drug treatment. Synapse 4:347–352
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical support of Michael Roberts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Victoria University of Wellington.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aronsen, D., Schenk, S. MDMA self-administration fails to alter the behavioral response to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Psychopharmacology 233, 1323–1330 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4226-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4226-9