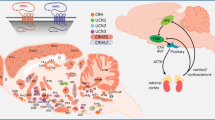
Abstract
Rationale
Previous studies indicate that psychosocial stressors could accelerate amyloid-β (Aβ) levels and accelerate plaque deposition in mouse models of Alzheimer disease (AD). Stressors enhanced the release of corticotrophin-releasing factor (CRF), and exogenous CRF administration mimicked the effects of stress on Aβ levels in mouse models of AD. However, whether CRF receptor 1 (CRF1) antagonists could influence the stress-induced acceleration of an AD-like process in mouse models has not been well studied.
Objective
We sought to examine whether CRF1 antagonists inhibit the effects of isolation stress on tissue Aβ levels, Aβ plaque deposition, and behaviors related to anxiety and memory in Tg2576 mice, and to investigate the molecular mechanism underlying such effects.
Methods
Cohorts of Tg2576 mouse pups were isolated or group-housed at 21 days of age, and then the subgroups of these cohorts received daily intraperitoneal injections of the CRF1 antagonists, antalarmin or R121919 (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg), or vehicle for 1 week. Other cohorts of Tg2576 mouse pups were isolated or group-housed at 21 days of age, and then at 4 months of age, subgroups of these mice were administered antalarmin (20 mg/kg) or vehicle in their drinking water for 6 months. Finally, cultured primary hippocampal neurons from regular Tg2576 pups (P0) were incubated with CRF (0.1, 1, and 10 nM), antalarmin (100 nM) or H-89 (1 μM) for 48 h. Brain tissues or cultured neurons were collected for histological and biochemical analyses, and behavioral measures were collected in the cohorts of mice that were chronically stressed.
Results
Administration of antalarmin at 20 mg/kg dose for 1 week significantly reduced Aβ1-42 levels in isolation stressed mice. Administration of antalarmin for 6 months significantly decreased plasma corticosterone levels, tissue Aβ1-42 levels, and Aβ plaque deposition in the brain and blocked the effects of isolation stress on behaviors related to anxiety and memory. Finally, incubation of neurons with 100 nM antalarmin inhibited the ability of 10 nM CRF to increase Aβ1-42 levels and protein kinase A IIβ expression. The effect of CRF1 on Aβ1-42 levels was also diminished by treatment with H-89, a c-AMP/PKA inhibitor.
Conclusions
These results suggest that CRF1 antagonists can slow an AD-like process in Tg2576 mice and that the c-AMP/PKA signaling pathway may be involved in this effect.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkadhi KA (2012) Chronic psychosocial stress exposes Alzheimer's disease phenotype in a novel at-risk model. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 4:214–229
Behan DP, Heinrichs SC, Troncoso JC, Liu XJ, Kawas CH, Ling N, De Souza EB (1995) Displacement of corticotropin releasing factor from its binding protein as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Nature 378:284–287
Binneman B, Feltner D, Kolluri S, Shi Y, Qiu R, Stiger T (2008) A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled trial of CP-316,311 (a selective CRH1 antagonist) in the treatment of major depression. Am J Psychiatry 165:617–620
Birnbaum SG, Yuan PX, Wang M, Vijayraghavan S, Bloom AK, Davis DJ, Gobeske KT, Sweatt JD, Manji HK, Arnsten AF (2004) Protein kinase C overactivity impairs prefrontal cortical regulation of working memory. Science 306:882–884
Carroll JC, Iba M, Bangasser DA, Valentino RJ, James MJ, Brunden KR, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2011) Chronic stress exacerbates tau pathology, neurodegeneration, and cognitive performance through a corticotropin-releasing factor receptor-dependent mechanism in a transgenic mouse model of tauopathy. J Neurosci 31:14436–14449
Choi DS, Wang D, Yu GQ, Zhu G, Kharazia VN, Paredes JP, Chang WS, Deitchman JK, Mucke L, Messing RO (2006) PKCepsilon increases endothelin converting enzyme activity and reduces amyloid plaque pathology in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8215–8220
Csernansky JG, Dong H, Fagan AM, Wang L, Xiong C, Holtzman DM, Morris JC (2006) Plasma cortisol and progression of dementia in subjects with Alzheimer-type dementia. Am J Psychiatry 163:2164–2169
Cuadrado-Tejedor M, Ricobaraza A, Frechilla D, Franco R, Perez-Mediavilla A, Garcia-Osta A (2012) Chronic mild stress accelerates the onset and progression of the Alzheimer's disease phenotype in Tg2576 mice. J Alzheimers Dis 28:567–578
da Cruz e Silva OA, Rebelo S, Vieira SI, Gandy S, da Cruz e Silva EF, Greengard P (2009) Enhanced generation of Alzheimer's amyloid-beta following chronic exposure to phorbol ester correlates with differential effects on alpha and epsilon isozymes of protein kinase C. J Neurochem 108:319–330
de Barry J, Liegeois CM, Janoshazi A (2010) Protein kinase C as a peripheral biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. Exp Gerontol 45:64–69
de Souza EB (1988) CRH defects in Alzheimer's and other neurologic diseases. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 23:59–71
De Souza EB (1995) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors: physiology, pharmacology, biochemistry and role in central nervous system and immune disorders. Psychoneuroendocrinology 20:789–819
Dong H, Goico B, Martin M, Csernansky CA, Bertchume A, Csernansky JG (2004) Modulation of hippocampal cell proliferation, memory, and amyloid plaque deposition in APPsw (Tg2576) mutant mice by isolation stress. Neuroscience 127:601–609
Dong H, Yuede CM, Yoo HS, Martin MV, Deal C, Mace AG, Csernansky JG (2008) Corticosterone and related receptor expression are associated with increased beta-amyloid plaques in isolated Tg2576 mice. Neuroscience 155:154–163
Funk CK, Zorrilla EP, Lee MJ, Rice KC, Koob GF (2007) Corticotropin-releasing factor 1 antagonists selectively reduce ethanol self-administration in ethanol-dependent rats. Biol Psychiatry 61:78–86
Gallagher JP, Orozco-Cabal LF, Liu J, Shinnick-Gallagher P (2008) Synaptic physiology of central CRH system. Eur J Pharmacol 583:215–225
Hains AB, Arnsten AF (2008) Molecular mechanisms of stress-induced prefrontal cortical impairment: implications for mental illness. Learn Mem 15:551–564
Handley SL, Mithani S (1984) Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists in a maze-exploration model of 'fear'-motivated behaviour. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 327:1–5
Harrington CR (2012) The molecular pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 22:11–22, vii
Hauger RL, Risbrough V, Brauns O, Dautzenberg FM (2006) Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptor signaling in the central nervous system: new molecular targets. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 5:453–479
Herrmann N, Chau SA, Kircanski I, Lanctot KL (2011) Current and emerging drug treatment options for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review. Drugs 71:2031–2065
Hoogendijk WJ, Meynen G, Endert E, Hofman MA, Swaab DF (2006) Increased cerebrospinal fluid cortisol level in Alzheimer’s disease is not related to depression. Neurobiol Aging 27:780, e781-780 e782
Hsiao K, Chapman P, Nilsen S, Eckman C, Harigaya Y, Younkin S, Yang F, Cole G (1996) Correlative memory deficits, Abeta elevation, and amyloid plaques in transgenic mice. Science 274:99–102
Huang HJ, Liang KC, Chang YY, Ke HC, Lin JY, Hsieh-Li HM (2010) The interaction between acute oligomer Abeta(1-40) and stress severely impaired spatial learning and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:8–18
Jedema HP, Grace AA (2004) Corticotropin-releasing hormone directly activates noradrenergic neurons of the locus ceruleus recorded in vitro. J Neurosci 24:9703–9713
Kang JE, Cirrito JR, Dong H, Csernansky JG, Holtzman DM (2007) Acute stress increases interstitial fluid amyloid-beta via corticotropin-releasing factor and neuronal activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:10673–10678
Kim T, Hinton DJ, Choi DS (2011) Protein kinase C-regulated abeta production and clearance. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:857368
Lee W, Boo JH, Jung MW, Park SD, Kim YH, Kim SU, Mook-Jung I (2004) Amyloid beta peptide directly inhibits PKC activation. Mol Cell Neurosci 26:222–231
Lee KW, Kim JB, Seo JS, Kim TK, Im JY, Baek IS, Kim KS, Lee JK, Han PL (2009) Behavioral stress accelerates plaque pathogenesis in the brain of Tg2576 mice via generation of metabolic oxidative stress. J Neurochem 108:165–175
Li Y, Ndubuka C, Rubin CS (1996) A kinase anchor protein 75 targets regulatory (RII) subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase II to the cortical actin cytoskeleton in non-neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 271:16862–16869
Martin B, Lopez de Maturana R, Brenneman R, Walent T, Mattson MP, Maudsley S (2005) Class II G protein-coupled receptors and their ligands in neuronal function and protection. Neuromol Med 7:3–36
Migliore L, Coppede F (2009) Genetics, environmental factors and the emerging role of epigenetics in neurodegenerative diseases. Mutat Res 667:82–97
Miller DB, O'Callaghan JP (2008) Do early-life insults contribute to the late-life development of Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases? Metabolism 57(Suppl 2):S44–S49
Mitani Y, Yarimizu J, Saita K, Uchino H, Akashiba H, Shitaka Y, Ni K, Matsuoka N (2012) Differential effects between gamma-secretase inhibitors and modulators on cognitive function in amyloid precursor protein-transgenic and nontransgenic mice. J Neurosci 32:2037–2050
Nelson TJ, Cui C, Luo Y, Alkon DL (2009) Reduction of beta-amyloid levels by novel protein kinase C(epsilon) activators. J Biol Chem 284:34514–34521
Nielsen DM (2006) Corticotropin-releasing factor type-1 receptor antagonists: the next class of antidepressants? Life Sci 78:909–919
O'Brien JT, Ames D, Schweitzer I, Colman P, Desmond P, Tress B (1996) Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging correlates of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis function in depression and Alzheimer's disease. Br J Psychiatry 168:679–687
Orozco-Cabal L, Pollandt S, Liu J, Shinnick-Gallagher P, Gallagher JP (2006) Regulation of synaptic transmission by CRF receptors. Rev Neurosci 17:279–307
Pomara N, Singh RR, Deptula D, LeWitt PA, Bissette G, Stanley M, Nemeroff CB (1989) CSF corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in Alzheimer's disease: its relationship to severity of dementia and monoamine metabolites. Biol Psychiatry 26:500–504
Rehman HU (2002) Role of CRH in the pathogenesis of dementia of Alzheimer's type and other dementias. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3:1637–1642
Rissman RA, Lee KF, Vale W, Sawchenko PE (2007) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptors differentially regulate stress-induced tau phosphorylation. J Neurosci 27:6552–6562
Rissman RA, Staup MA, Lee AR, Justice NJ, Rice KC, Vale W, Sawchenko PE (2012) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor-dependent effects of repeated stress on tau phosphorylation, solubility, and aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:6277–6282
Robert SJ, Zugaza JL, Fischmeister R, Gardier AM, Lezoualc'h F (2001) The human serotonin 5-HT4 receptor regulates secretion of non-amyloidogenic precursor protein. J Biol Chem 276:44881–44888
Sabino V, Cottone P, Koob GF, Steardo L, Lee MJ, Rice KC, Zorrilla EP (2006) Dissociation between opioid and CRF1 antagonist sensitive drinking in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 189:175–186
Swanwick GR, Kirby M, Bruce I, Buggy F, Coen RF, Coakley D, Lawlor BA (1998) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: lack of association between longitudinal and cross-sectional findings. Am J Psychiatry 155:286–289
Takashima A (2006) GSK-3 is essential in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 9:309–317
Tayeb HO, Yang HD, Price BH, Tarazi FI (2012) Pharmacotherapies for Alzheimer's disease: beyond cholinesterase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther 134:8–25
Thathiah A, De Strooper B (2011) The role of G protein-coupled receptors in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:73–87
Thathiah A, Horre K, Snellinx A, Vandewyer E, Huang Y, Ciesielska M, De Kloe G, Munck S, De Strooper B (2013) beta-Arrestin 2 regulates Abeta generation and gamma-secretase activity in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med 19:43–49
Umegaki H, Ikari H, Nakahata H, Endo H, Suzuki Y, Ogawa O, Nakamura A, Yamamoto T, Iguchi A (2000) Plasma cortisol levels in elderly female subjects with Alzheimer's disease: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Brain Res 881:241–243
Ungless MA, Singh V, Crowder TL, Yaka R, Ron D, Bonci A (2003) Corticotropin-releasing factor requires CRF binding protein to potentiate NMDA receptors via CRF receptor 2 in dopamine neurons. Neuron 39:401–407
Whitehouse PJ, Vale WW, Zweig RM, Singer HS, Mayeux R, Kuhar MJ, Price DL, De Souza EB (1987) Reductions in corticotropin releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in cerebral cortex in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 37:905–909
Wilson RS, Barnes LL, Bennett DA, Li Y, Bienias JL, Mendes de Leon CF, Evans DA (2005) Proneness to psychological distress and risk of Alzheimer disease in a biracial community. Neurology 64:380–382
Wilson RS, Arnold SE, Schneider JA, Kelly JF, Tang Y, Bennett DA (2006) Chronic psychological distress and risk of Alzheimer's disease in old age. Neuroepidemiology 27:143–153
Wood SK, Woods JH (2007) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor-1: a therapeutic target for cardiac autonomic disturbances. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11:1401–1413
Xu H, Sweeney D, Greengard P, Gandy S (1996) Metabolism of Alzheimer beta-amyloid precursor protein: regulation by protein kinase A in intact cells and in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:4081–4084
Zamora BM, Jiang M, Wang Y, Chai M, Lawson PT, Lawson GW (2009) Decreased blastocyst production in mice exposed to increased rack noise. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 48:486–491
Zorrilla EP, Koob GF (2004) The therapeutic potential of CRF1 antagonists for anxiety. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 13:799–828
Zorrilla EP, Koob GF (2010) Progress in corticotropin-releasing factor-1 antagonist development. Drug Discov Today 15:371–383
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation (grant 20111208, JGC). A portion of this research was supported by the Intramural Research Programs of the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, NIH, US Department of Health and Human Services (KCR). Drs. Csernansky and Dong have received research grants from the NIMH, NIA, and Dr. John G. Csernansky has served as a Data Safety and Monitoring Board (DSMB) member for Eli Lilly and Sanofi-Aventis and has received funding for his research from Genentech. The rest of the authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, H., Wang, S., Zeng, Z. et al. Effects of corticotrophin-releasing factor receptor 1 antagonists on amyloid-β and behavior in Tg2576 mice. Psychopharmacology 231, 4711–4722 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3629-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3629-8