Abstract
Rationale
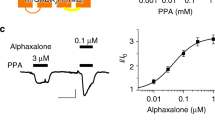
The neurosteroid 3α,5β-THP (3α-OH-5β-pregnan-20-one, pregnanolone) is a modulator of the GABAA receptor (GABAR), with α4β2δ GABARs the most sensitive. However, the effects of 3α,5β-THP at α4β2δ are polarity-dependent: 3α,5β-THP potentiates depolarizing current, as has been widely reported, but decreases hyperpolarizing current by accelerating desensitization.
Objectives
The present study further characterized 3α,5β-THP inhibition of hyperpolarizing current at this receptor and compared effects of other related steroids at α4β2δ GABARs.
Methods
α4β2δ GABARs were expressed in HEK-293 cells, and agonist-gated current recorded with whole cell voltage-clamp techniques using a theta tube to rapidly apply agonist before and after application of neurosteroids.
Results
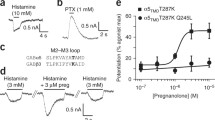
The GABA-modulatory steroids (30 nM) 3α,5α-THP (3α-OH-5α-pregnan-20-one, allopregnanolone) and THDOC (3α,21-dihydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one) inhibited hyperpolarizing GABA (10 μM)-gated current at α4β2δ GABARs similar to 3α,5β-THP, while the inactive 3β,5β-THP isomer had no effect. Greater inhibition was seen for current gated by the high efficacy agonist gaboxadol (THIP, 100 μM) than for GABA (0.1–1000 μM), consistent with an effect of 3α,5β-THP on desensitization. Inhibitory effects of the steroid were not seen under low [Cl−] conditions or in the presence of calphostin C (500 nM), an inhibitor of protein kinase C. Chimeras swapping the IL (intracellular loop) of α4 with α1, when expressed with β2 and δ, produced receptors (α[414]β2δ) which were not inhibited by 3α,5β-THP when GABA-gated current was hyperpolarizing, while α[141]β2δ exhibited steroid-induced polarity-dependent modulation.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that numerous neurosteroids exhibit polarity-dependent effects at α4β2δ GABARs, which are dependent upon protein kinase C and the IL of α4.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramian AM, Comenencia-Ortiz E, Vithlani M, Tretter EV, Sieghart W, Davies PA, Moss SJ (2010) Protein kinase C phosphorylation regulates membrane insertion of GABAA receptor subtypes that mediate tonic inhibition. J Biol Chem 285:41795–417805
Agis-Balboa RC, Pinna G, Zhubi A, Maloku E, Veldic M, Costa E, Guidotti A (2006) Characterization of brain neurons that express enzymes mediating neurosteroid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:14602–14607
Akk G, Covey DF, Evers AS, Mennerick S, Zorumski CF, Steinbach JH (2010) Kinetic and structural determinants for GABAA receptor potentiation by neuroactive steroids. Curr Neuro Pharmacol 8:18–25
Barbaccia ML, Roscetti G, Trabucchi M, Mostallino MC, Concas A, Purdy RH, Biggio G (1996) Time-dependent changes in rat brain neuroactive steroid concentrations and GABAA receptor function after acute stress. Neuroendocrinology 63:166–172
Belelli D, Casula A, Ling A, Lambert JJ (2002) The influence of subunit composition on the interaction of neurosteroids with GABAA receptors. Neuro Pharmcol 43:651–661
Bianchi MT, Macdonald RL (2003) Neurosteroids shift partial agonist activation of GABAA receptor channels from low- to high-efficacy gating patterns. J Neurosci 23:10934–10943
Bianchi MT, Haas KF, Macdonald RL (2002) Alpha1 and alpha6 subunits specify distinct desensitization, deactivation and neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors containing the delta subunit. Neuropharmacology 43:492–502
Bracamontes JR, Li P, Akk G, Steinbach JH (2012) A neurosteroid potentiation site can be moved among GABAA receptor subunits. J Physiol 590:5739–5747
Bright DP, Renzi M, Bartram J, McGee TP, MacKenzie G, Hosie AM, Farrant M, Brickley SG (2011) Profound desensitization by ambient GABA limits activation of δ-containing GABAA receptors during spillover. J Neurosci 31:753–763
Brown N, Kerby J, Bonnert TP, Whiting PJ, Wafford KA (2002) Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell line expressing human α4βδ GABAA receptors. Br J Pharmacol 136:965–974
Burgard EC, Tietz EI, Neelands TR, Macdonald RL (1996) Properties of recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor isoforms containing the α5 subunit subtype. Mol Pharmacol 50:119–127
Chang Y, Wang R, Barot S, Weiss DS (1990) Stoichiometry of a recombinant GABAA receptor. J Neurosci 16:534–541
Chen J, Mitcheson JS, Lin M, Sanguinetti MC (2000) Functional roles of charged residues in the putative voltage sensor of the HCN2 pacemaker channel. J Biol Chem 275:36465–36471
Choi DS, Wei W, Deitchman JK, Kharazia VN, Lesscher HM, McMahon T, Wang D, Qi ZH, Sieghart W, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Mody I, Messing RO (2008) Protein kinase C δ regulates ethanol intoxication and enhancement of GABA-stimulated tonic current. J Neurosci 28:11890–11899
Compagnone NA, Mellon SH (2000) Neurosteroids: biosynthesis and function of these novel neuromodulators. Front Neuroendo 21:1–56
Concas A, Mostallino MC, Porcu P, Follesa P, Barbaccia ML, Trabucchi M, Purdy RH, Grisenti P, Biggio G (1998) Role of brain allopregnanolone in the plasticity of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor in rat brain during pregnancy and after delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:13284–13289
Corpechot C, Collins B, Carey M, Tsouros A, Robel P, Fry J (1997) Brain neurosteroids during the mouse oestrous cycle. Brain Res 766:276–280
Droogleever Fortuyn HA, van Broekhoven F, Span PN, Backstrom T, Zitman FG, Verkes RJ (2004) Effects of Ph. D. examination stress on allopregnanolone and cortisol plasma levels and peripheral benzodiazepine receptors density. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29:1341–1344
Girdler SS, Straneva PA, Light KC, Pedersen CA, Morrow AL (2001) Allopregnanolone levels and reactivity to mental stress in premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Biol Psychiatry 49:788–797
Girdler SS, Lindgren M, Porcu P, Rubinow DR, Johnson JL, Morrow AL (2012) A history of depression in women is associated with an altered GABAergic neuroactive steroid profile. Psychoneuroendo 37:543–553
Glykys J, Peng Z, Chandra D, Homanics GE, Houser CR, Mody I (2007) A new naturally occurring GABAA receptor subunit partnership with high sensitivity to ethanol. Nat Neurosci 10:40–48
Havlikova H, Hill M, Kancheva L, Vrbikova J, Pouzar V, Cerny I, Kancheva R, Starka L (2006) Serum profiles of free and conjugated neuroactive pregnanolone isomers in nonpregnant women of fertile age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3092–3099
Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, da Silva HM, Smart TG (2006) Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature 444:486–489
Houston CM, Bright DP, Sivilotti LG, Beato M, Smart TG (2009) Intracellular chloride ions regulate the time course of GABA-mediated inhibitory synaptic transmission. J Neurosci 29:10416–10423
Jia F, Yue M, Cjandra D, Keramides A, Goldstein PA, Homanics GE, Harrison NL (2008) Taurine is a potent activator of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the thalamus. J Neurosci 28:106–115
Kumar S, Sieghart W, Morrow AL (2002) Association of protein kinase C with GABAA receptors containing α1 and α4 subunits in the cerebral cortex: selective effects of chronic ethanol consumption. J Neuro Chem 82:110–117
Kuver A, Shen H, Smith SS (2012) Regulation of the surface expression of α4β2δ GABAA receptors by high efficacy states. Brain Res 1463:1–20
Luisi S, Petraglia F, Benedetto C, Nappi RE, Bernardi F, Fadalti M, Reis FM, Luisi M, Genazzani AR (2000) Serum allopregnanolone levels in pregnant women: changes during pregnancy, at delivery, and in hypertensive patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:2429–2433
Majewska MD, Harrison NL, Schwartz RD, Barker JL, Paul SM (1986) Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science 232:1004–1007
Meera P, Wallner M, Otis T (2011) Molecular basis for the high THIP/gaboxadol sensitivity of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors. J Neurophysiol 106:2057–2011
Mukai H, Higashi T, Nagura Y, Shimada K (2008) Studies on neurosteroids XXV. Influence of 5 α-reductase inhibitor, finasteride, on rat brain neurosteroid levels and metabolism. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1646–1650
Olsen RW, Sieghart W (2009) GABAA receptors: subtypes provide diversity of function and pharmacology. Neuropharmcology 56:141–148
Olsen RW, Snowman A (1982) Chloride-dependent enhancment by barbiturates of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding. J Neurosci 2:1812–1823
Palumbo MA, Salvestroni C, Gallo R, Guo AL, Gennazini AD, Artini PG, Petraglia F, Gennazani AR (1995) Allopregnanolone concentration in hippocampus of prepubertal rats and female rats throughout estrous cycle. J Endocrinol Invest 18:853–856
Porcu P, O'Buckley TK, Alward SE, Marx CE, Shampine LJ, Girdler SS, Morow AL (2009) Simultaneous quantification of GABAergic 3a,5a/3a,5b neuroactive steroids in human and rat serum. Steroids 74:463–473
Porcu P, O'Buckley TK, Alward SE, Song SC, Grant KA, de Wit H, Leslie Morrow A (2010) Differential effects of ethanol on serum GABAergic 3α,5α/3α,5β neuroactive steroids in mice, rats, cynomolgus monkeys and humans. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34:432–442
Purdy RH, Morrow AL, Moore PH Jr, Paul SM (1991) Stress-induced elevations of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor-active steroids in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:4553–4557
Ramsey IS, Moran MM, Chong JA, Clapham DE (2006) A voltage-gated proton-selective channel lacking the pore domain. Nature 440:1213–1216
Sarkar J, Wakefield S, MacKenzie G, Moss SJ, Maguire J (2011) Neurosteroidogenesis is required for the physiological response to stress: role of neurosteroid-sensitive GABAA receptors. J Neurosci 31:18198–18210
Savage A, Zeng L, Houslay MD (1995) A role for protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation in eliciting glucagon desensitization in rat hepatocytes. Biochem J 307(Pt 1):281–285
Shen H, Gong QH, Aoki C, Yuan M, Ruderman Y, Dattilo M, Williams K, Smith SS (2007) Reversal of neurosteroid effects at α4βδ GABAA receptors triggers anxiety at puberty. Nat Neurosci 10:469–477
Shen H, Sabaliauskas N, Sherpa A, Fenton AA, Stelzer A, Aoki C, Smith SS (2010) A critical role for α4βδ GABAA receptors in shaping learning deficits at puberty in mice. Science 327:1515–1518
Shen H, Mohammad A, Ramroop J, Smith SS (2013) A stress steroid triggers anxiety via increased expression of α4βδ GABAA receptors in methamphetamine dependence. Neurosci 254:452–475
Smith SS (2013) α4βδ GABAA receptors and tonic inhibitory current during adolescence: effects on mood and synaptic plasticity. Front Neural Circuits 7:135
Smith SS, Gong QH (2005) Neurosteroid administration and withdrawal alter GABAA receptor kinetics in CA1 hippocampus of female rats. J Physiol 564:421–436
Smith SS, Gong QH, Hsu FC, Markowitz RS, Ffrench-Mullen JMH, Li X (1998) GABAA receptor α4 subunit suppression prevents withdrawal properties of an endogenous steroid. Nature 392:926–929
Song I, Savtchenko L, Semyanov A (2011) Tonic excitation or inhibition is set by GABAA conductance in hippocampal interneurons. Nat Commun 2:376
Staley KJ, Mody I (1992) Shunting of excitatory input to dentate gyrus granule cells by a depolarizing GABAA receptor-mediated postsynaptic conductance. J Neurophysiol 68:197–212
Stell BM, Mody I (2002) Receptors with different affinities mediate phasic and tonic GABAA conductances in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 22:RC223
Stell BM, Brickley SG, Tang CY, Farrant M, Mody I (2003) Neuroactive steroids reduce neuronal excitability by selectively enhancing tonic inhibition mediated by δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:14439–14444
Trifiletti RR, Snowman AM, Snyder SH (1984) Solubilization and anionic regulation of cerebral sedative/convulsant receptors labeled with [35S] tert-butylbicyclophosphorothionate (TBPS). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:692–699
Turner JH, Raymond JR (2005) Interaction of calmodulin with the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor. A putative regulator of G protein coupling and receptor phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 280:30741–30750
Wei W, Zhang N, Peng Z, Houser CR, Mody I (2003) Perisynaptic localization of δ subunit-containing GABAA receptors and their activation by GABA spillover in the mouse dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 23:10650–10661
Wisden W, Laurie DJ, Monyer H, Seeburg P (1992) The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. I. Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon. J Neurosci 12:1040–1062
Wohlfarth KM, Bianchi MT, Macdonald RL (2002) Enhanced neurosteroid potentiation of ternary GABAA receptors containing the delta subunit. J Neurosci 22:1541–1549
Zheleznova N, Sedelnikova A, Weiss DS (2008) α1β2δ, a silent GABAA receptor: recruitment by tracazolate and neurosteroids. Br J Pharmacol 153:1062–1071
Zhu WJ, Vicini S (1997) Neurosteroid prolongs GABAA channel deactivation by altering kinetics of desensitized states. J Neurosci 17:4022–4031
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health: DA09618, AA12958 and MH100561 to S.S.S. We also thank D. H. Smith, M. Yuan, M. Dattilo and A. Kuver for helpful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Q.H., Smith, S.S. Characterization of neurosteroid effects on hyperpolarizing current at α4β2δ GABAA receptors. Psychopharmacology 231, 3525–3535 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3538-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3538-x