Abstract
Numerical methods and analysis for compressible miscible flow in porous media have been investigated extensively in the last several decades. Amongst those methods, the lowest-order mixed method is the most popular one in practical applications. The method is based on the linear Lagrange approximation for the concentration and the lowest order (zero-order) Raviart–Thomas mixed approximation for the Darcy velocity/pressure. However, the existing error analysis only provides the first-order accuracy in \(L^2\)-norm for all three physical components in spatial direction, which was proved under certain extra restrictions on both time step and spatial meshes. The analysis is not optimal for the concentration mainly due to the strong coupling of the system and the drawback of the traditional approach which leads to serious pollution to the numerical concentration in analysis. The main task of this paper is to present a new analysis and establish the optimal error estimate of the commonly-used linearized lowest-order mixed FEM. In particular, the second-order accuracy for the concentration in spatial direction is proved unconditionally. Moreover, we propose a simple recovery technique to obtain a new numerical Darcy velocity/pressure of second-order accuracy by re-solving an elliptic pressure equation. Also we extend our analysis to a second-order time discrete scheme to obtain optimal error estimates in both spatial and temporal directions. Numerical results are provided to confirm our theoretical analysis and show the efficiency of the method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbogast, T., Juntumen, N., Pool, J., Wheeler, M.: A discontinuous Galerkin methods for two phase flow in a porous medium enforcing \(H(div)\) velocity and continuous capillary pressure. Comput. Geosci. 17, 1055–1078 (2013)
Amirat, Y., Moussaoui, M.: Analysis of a one-dimensional model for compressible miscible displacement in porous media. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 26, 659–674 (1995)
Amirat, Y., Shelukhin, V.: Global weak solutions to equations of compressible miscible flows in porous media. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 38, 1825–1846 (2007)
Bear, J., Bachmat, Y.: Introduction to Modeling of Transport Phenomena in Porous Media. Springer, New York (1990)
Bahriawati, C., Carstensen, C.: Three Matlab implementations of the lowest-order Raviart–Thomas MFEM with a posteriori error control. Comput. Methods Appl. Math. 5, 333–361 (2005)
Boffi, D., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed Finite Element Methods and Applications. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Brenner, S., Scott, L.: The Mathematical Theory of Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (2002)
Cai, W., Wang, J., Wang, K.: Convergence analysis of Crank–Nicolson Galerkin–Galerkin FEMs for miscible displacement in porous media. J. Sci. Comput. 83, 1–26 (2020)
Cai, W., Li, B., Lin, Y., Sun, W.: Analysis of fully discrete FEM for miscible displacement in porous media with Bear–Scheidegger diffusion tensor. Numer. Math. 141, 1009–1042 (2019)
Cannon, J.R., Lin, Y.: Non-classical \(H^1\) projection and Galerkin methods for non-linear parabolic integro-differential equations. Calcolo 25, 187–201 (1988)
Cannon, J.R., Lin, Y.: A priori \(L^2\) error estimates for finite-element methods for nonlinear diffusion equations with memory. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27, 595–607 (1990)
Cheng, A.J.: The optimal error estimate of the finite element method in the \(L^\infty (J;H^1(\Omega ))\) norm for a problem of miscible compressible displacement in porous media. Numer. Math. J. Chin. Univ. 16, 134–144 (1994)
Cheng, H., Droniou, J., Le, K.N.: Convergence analysis of a family of ELLAM schemes for a fully coupled model of miscible displacement in porous media. Numer. Math. 141, 353–397 (2019)
Chou, S.H., Li, Q.: Mixed finite element methods for compressible miscible displacement in porous media. Math. Comput. 57, 507–527 (1991)
Douglas, J.J., Roberts, J.E.: Numerical methods for a model for compressible miscible displacement in porous media. Math. Comput. 41, 441–459 (1983)
Douglas, J.J., Roberts, J.E.: Global estimates for mixed methods for second order elliptic equations. Math. Comput. 44, 39–52 (1985)
Douglas, J.J., Ewing, R., Wheeler, M.F.: A time-discretization procedure for a mixed finite element approximation of miscible displacement in porous media. RAIRO Anal. Numer. 17, 249–265 (1983)
Ewing, R.E., Yuan, Y.R., Li, G.: Time stepping along characteristics for a mixed finite-element approximation for compressible flow of contamination from nuclear waste in porous media. SIAM. J. Numer. Anal. 26, 1513–1524 (1989)
Ewing, R.E. (ed.): The Mathematics of Reservoir Simulation. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics. SIAM, Philadelphia (1983)
Ewing, R.E., Wang, H.: A summary of numerical methods for time-dependent advection-dominated partial differential equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 128, 423–445 (2001)
Ewing, R.E., Russell, T.F., Wheeler, M.F.: Convergence analysis of an approximation of miscible displacement in porous media by mixed finite elements and a modified method of characteristics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 47, 73–92 (1984)
Feng, X.: Strong solutions to a nonlinear parabolic system modeling compressible miscible displacement in porous media. Nonlinear Anal. 23, 1515–1531 (1994)
Guo, H., Yang, Y.: Bound-preserving discontinuous Galerkin method for compressible miscible displacement in porous media. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 39, A1969–A1990 (2017)
Gao, H., Sun, W.: Optimal error analysis of Crank-Nicolson lowest-order Galerkin-mixed FEM for incompressible miscible flow in porous media. Numer. Methods PDEs 36, 1773–1789 (2020)
Hu, H., Chen, Y., Huang, Y.: A characteristic finite element two-grid algorithm for a compressible miscible displacement problem. Adv. Comput. Math. 46, 15 (2020)
Lee, S., Wheeler, M.F.: Adaptive enriched Galerkin methods for miscible displacement problems with entropy residual stabilization. J. Comput. Phys. 331, 19–37 (2017)
Li, B., Sun, W.: Unconditional convergence and optimal error estimates of a Galerkin-mixed FEM for incompressible miscible flow in porous media. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 51, 1959–1977 (2013)
Li, B., Sun, W.: Regularity of the diffusion-dispersion tensor and error analysis of Galerkin FEMs for a porous medium flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 53, 1418–1437 (2015)
Li, B., Wang, J., Sun, W.: The stability and convergence of fully discrete Galerkin–Galerkin FEMs for porous medium flows. Commun. Comput. Phys. 15, 1141–1158 (2014)
Li, D., Wang, J.: Unconditionally optimal error analysis of Crank-Nicolson Galerkin FEMs for a strongly nonlinear parabolic system. J. Sci. Comput. 72, 892–915 (2017)
Memon, S., Nataraj, N., Pani, A.K.: An a posteriori error analysis of mixed finite element Galerkin approximations to second order linear parabolic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50, 1367–1393 (2012)
Mohamed, A.N.A., Pani, A.K.: Mixed finite element methods for compressible miscible displacement problems in reservoir studies, Functional analysis with current applications in science, technology and industry (Aligarh, 1996), 332–352, Pitman Res. Notes Math. Ser., 377, Longman, Harlow (1998)
Nirenberg, L.: An extended interpolation inequality. Ann. Scuola Norm. Sup. Pisa 3(20), 733–737 (1966)
Park, E.-J.: Mixed finite element methods for generalized Forchheimer flow in porous media. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 21, 213–228 (2005)
Raviart, P.A., Thomas, J.M.: A Mixed Finite Element Method for 2-nd Order Elliptic Problems, Mathematical Aspects of Finite Element Methods, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 606, pp. 292–315. Springer, New York (1977)
Scheidegger, A.E.: The Physics of Flow Through Porous Media. The MacMillan Company, New York (1957)
Scovazzi, G., Wheeler, M.F., Mikelić, A., Lee, S.: Analytical and variational numerical methods for unstable miscible displacement flows in porous media. J. Comput. Phys. 335, 444–496 (2017)
Sun, W., Wu, C.: New analysis of Galerkin-mixed FEMs for incompressible miscible flow in porous media. Math. Comput. 90, 81–102 (2021)
Sun, W., Wu, C.: Efficient fully discrete Galerkin-mixed FEMs for incompressible miscible flow in porous media. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 17, 350–367 (2020)
Thomée, V.: Galerkin Finite Element Methods For Parabolic Problems. Springer, New York (1997)
Wang, H.: An optimal-order error estimate for a family of ELLAM-MFEM approximations to porous medium flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 46, 2133–2152 (2008)
Wang, H., Liang, D., Ewing, R.E., Lyons, S.L., Qin, G.: An ELLAM-MFEM solution technique for compressible fluid flows in porous media with point sources and sinks. J. Comput. Phys. 159, 344–376 (2000)
Wang, H., Liang, D., Ewing, R.E., Lyons, S.L., Qin, G.: An ELLAM approximation for highly compressible multicomponent flows in porous media. Comput. Geosci. 6, 227–251 (2002)
Wang, H., Zhao, W., Ewing, R.E.: A numerical modeling of multicomponent compressible flows in porous media with multiple wells by an Eulerian–Lagrangian method. Comput. Vis. Sci. 8, 69–81 (2005)
Wang, H., Zhao, W., Ewing, R.E., Al-Lawatia, M., Espedal, M.S., Telyakovskiy, A.S.: A Eulerian–Lagrangian solution technique for single-phase compositional flow in three-dimensional porous media. Comput. Math. Appl. 52, 607–624 (2006)
Wang, H., Zheng, X.: An optimal-order error estimate of the lowest-order ELLAM-MFEM approximation to miscible displacement in three space dimensions. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 375, 112819 (2020)
Wang, J., Si, Z., Sun, W.: A new error analysis of characteristics-mixed FEMs for miscible displacement in porous media. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52, 3300–3020 (2014)
Wheeler, M.F.: A priori \(L^2\) error estimates for Galerkin approximations to parabolic partial differential equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 10, 723–759 (1973)
Xu, Z., Yang, Y.: High-order bound-preserving discontinuous Galerkin methods for compressible miscible displacements in porous media on triangular meshes. J. Comput. Phys. 378, 110–128 (2019)
Yan, Y.: Postprocessing the finite element method for semilinear parabolic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 44, 1681–1702 (2006)
Zlámal, M.: Curved elements in the finite element method I. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 10, 229–240 (1973)
Acknowledgements
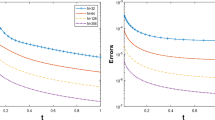
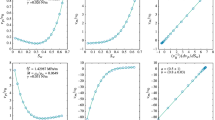
The author would like to thank the anonymous referees for their valuable suggestions and comments and also, Professor R. An (Wenzhou University) and Dr. J. Wang (BCSRC, Beijing) for providing a FreeFEM code and Fig. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The research is partially supported by a Grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Number 12071040 and internal funds (R5202009, R72021111) from United International College (BNU-HKBU)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W. New analysis and recovery technique of mixed FEMs for compressible miscible displacement in porous media. Numer. Math. 150, 179–215 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-021-01249-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-021-01249-w