Abstract
Purpose
Hypertension is one of the major risk factors for renal failure and cardiovascular diseases, and is caused by various abnormalities including the contractility of blood vessels. Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats, which mimic human type 2 diabetes, are frequently used to study obesity-induced insulin resistance (IR) and hypertension. Human omentin-1 is one of the recently identified adipocytokines. We previously demonstrated that human omentin-1 not only caused vasodilation in rat isolated blood vessels, but also prevented inflammatory responses, a possible mechanism relating IR, in human vascular endothelial cells. Taken together, we hypothesized that human omentin-1 may reduce obesity-induced IR and hypertension in OLETF rats.
Methods
OLETF rats were intraperitoneally administered with human omentin-1 for 7 days.
Results
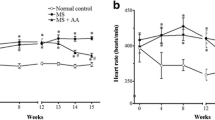
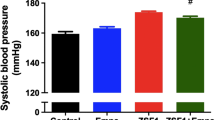
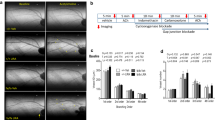
Human omentin-1 had no influence on overweight, hyperglycemia, urinary glucose extraction, hyperinsulinemia, and systemic IR in OLETF rats. Human omentin-1 decreased systolic blood pressure in OLETF rats. The measurement of isometric contraction revealed that human omentin-1 had no influence on the agonist-induced contractile and relaxant responses in isolated thoracic aorta from OLETF rats. However, the relaxant response mediated by human insulin was converted into the contractile response in thoracic aorta from OLETF rats, which was prevented by human omentin-1. The Western blotting revealed that human omentin-1 improved the decrease in endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation in isolated thoracic aorta from OLETF rats.
Conclusion
In summary, we for the first time revealed that human omentin-1 partly reduces vascular IR and thereby inhibits hypertension in OLETF rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Alsenousy AHA, El-Tahan RA, Ghazal NA, Piñol R, Millán A, Ali LMA, Kamel MA (2022) The anti-obesity potential of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles against high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats: Possible involvement of mitochondrial biogenesis in the adipose tissues. Pharmaceutics 14(10):2134. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102134
Dong Q, Xing W, Li K, Zhou X, Wang S, Zhang H (2021) Tetrahydroxystilbene glycoside improves endothelial dysfunction and hypertension in obese rats: The role of omentin-1. Biochem Pharmacol 186:114489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114489
Kataoka Y, Shibata R, Ohashi K, Kambara T, Enomoto T, Uemura Y, Ogura Y, Yuasa D, Matsuo K, Nagata T, Oba T, Yasukawa H, Numaguchi Y, Sone T, Murohara T, Ouchi N (2014) Omentin prevents myocardial ischemic injury through AMP-activated protein kinase- and akt- dependent mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol 63(24):2722–2733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.032
Kazama K, Tatsuya U, Okada M, Hara Y, Yamawaki H (2012) Omentin plays an anti-inflammatory role through inhibition of TNF-α-induced superoxide production in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol 686(1–3):116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.04.033
Kazama K, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2014) A novel adipocytokine, omentin, inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration through antioxidative mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306(12):H1714–H1719. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00048.2014
Kazama K, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2015) Adipocytokine, omentin inhibits doxorubicin-induced H9c2 cardiomyoblasts apoptosis through the inhibition of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457(4):602–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.032
Kjeldsen SE (2018) Hypertension and cardiovascular risk: General aspects. Pharmacol Res 129:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.003
Kosegawa I, Katayama S, Kikushi C, Kashiwabara H, Negishi K, Ishii J, Inukai K, Oka Y (1996) Metformin decreases blood pressure and obesity in OLETF rats via improvement of insulin resistance. Hypertens Res 19(1):37–41. https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.19.37
Leandro A, Queiroz M, Azul L, Seiça R, Sena CM (2021) Omentin: A novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med 162:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.10.021
Lee HB, Blaufox MD (1985) Blood volume in the rat. J Nucl Med 26(1):72–76. https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/jnumed/26/1/72.full.pdf
Lin X, Sun Y, Yang S, Yu M, Pan L, Yang J, Yang J, Shao Q, Liu J, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Zhijian W (2021) Omentin-1 modulates macrophage function via integrin receptors αvβ3 and αvβ5 and reverse plaque vulnerability in animal models of atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:757926. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.757926
Liu F, Fang S, Liu X, Ji Li, Wang X, Cui J, Chen T, Li Z, Yang F, Tian J, Li H, Yin L, Yu B (2020) Omentin-1 protects against high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction via the AMPK/PPARδ signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 174:113830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113830
Miller AW, Tulbert C, Puskar M, Busija DW (2002) Enhanced endothelin activity prevents vasodilation to insulin in insulin resistance. Hypertension 40(1):78–82. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.0000022806.87281.62
Nishimoto S, Fukuda D, Higashikuni Y, Tanaka K, Hirata Y, Murata C, Kim-Kaneyama JR, Sato F, Bando M, Yagi S, Soeki T, Hayashi T, Imoto I, Sakaue H, Shimabukuro M, Sata M (2016) Obesity-induced DNA released from adipocytes stimulates chronic adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Sci Adv 2(3):e1501332. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1501332
Okamura Y, Otani K, Sekiguchi A, Kogane T, Kakuda C, Sakamoto Y, Kodama T, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2017) Vasculoprotective effect of BMS-309403 is independent of its specific inhibition of fatty acid-binding protein 4. Pflüg Arch Eur J Physiol 469(9):1177–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-1976-0
Okamura Y, Niijima R, Kameshima S, Kodama T, Otani K, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2023) Human omentin-1 administration ameliorates hypertensive complications without affecting hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Mol Sci 24(4):3835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043835
Otani K, Yokoya M, Kodama T, Hori K, Matsumoto K, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2018) Plasma exosomes regulate systemic blood pressure in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(2):776–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.075
Otani K, Funada H, Teranishi R, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2022) Cardiovascular characteristics of Zucker fatty diabetes mellitus rats, an animal model for obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 23(8):4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084228
Quintela AM, Jiménez R, Piqueras L, Gómez-Guzmán M, Haro J, Zarzuelo MJ, Cogolludo A, Sanz MJ, Toral M, Romero M, Pérez-Vizcaíno F, Duarte J (2014) PPARβ activation restores the high glucose-induced impairment of insulin signalling in endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 171(12):3089–3102. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12646
Schäffler A, Neumeier M, Herfarth H, Fürst A, Schölmerich J, Büchler C (2005) Genomic structure of human omentin, a new adipocytokine expressed in omental adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Gene Struct Expr 1732(1–3):96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaexp.2005.11.005
Sugiyama A, Hirano Y, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2018) Endostatin stimulates proliferation and migration of myofibroblasts isolated from myocardial infarction model rats. Int J Mol Sci 19(3):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030741
Sugiyama A, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2020) Canstatin suppresses isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy through inhibition of calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T-cells pathway in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 871:172849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172849
Takada A, Takayuki M, Kuno A, Kouzu H, Sunagawa D, Itoh T, Tanno M, Yano T, Sato T, Ishikawa S, Miura T (2012) Role of ER stress in ventricular contractile dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 7(6):e39893. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039893
Takatori S, Fujiwara H, Zamami Y, Hashiwaka-Hobara N, Kawasaki H (2014) Decreased perivascular CGRP-containing nerves in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats with insulin resistance and hypertension. Hypertens Res 37(5):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2013.151
Tao M, Yan W, Chen C, Tang M, Zhao X, Feng Q, Fei X, Fu Y (2023) Omentin-1 ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease via Nrf2 activation and redox regulation. Life Sci 328(1):121847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121847
Touyz RM, Alves-Lopes R, Rios FJ, Camargo LL, Anagnostopoulou A, Arner A, Montezano AC (2018) Vascular smooth muscle contraction in hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 114(4):529–539. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvy023
Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y, Yamawaki H (2012) Death-associated protein kinase 3 mediates vascular inflammation and development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 60(4):1031–1039. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.112.200337
Watanabe K, Watanabe R, Konii H, Shirai R, Sato K, Matsuyama T, Ishibashi-Ueda H, Koba S, Kobayashi Y, Hirano T, Watanabe T (2016) Counteractive effects of omentin-1 against atherogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 110(1):118–128. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvw016
Yamamoto A, Otani K, Okada M, Yamawaki H (2021) Chemokine-like receptor 1 in brain of spontaneously hypertensive rats mediates systemic hypertension. Int J Mol Sci 22(21):1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111812
Yamawaki H (2011) Vascular effects of novel adipocytokines: Focus on vascular contractility and inflammatory responses. Biol Pharm Bull 34(3):307–310. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.34.307
Yamawaki H, Tsubaki N, Mukohda M, Okada M, Hara Y (2010) Omentin, a novel adipokine, induces vasodilation in rat isolated blood vessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393(4):668–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.053
Yamawaki H, Kuramoto J, Kameshima S, Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y (2011) Omentin, a novel adipocytokine inhibits TNF-induced vascular inflammation in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 408(2):339–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.039
Acknowledgements
We appreciate Kitasato University Veterinary Teaching Hospital for lending the Echo system.
Funding
This study was supported by a Kitasato University Research Grant (to HY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: YO, TK, KO, MO, and HY.
Investigation: YO, KA, RN, KO, and MO.
Resources: KO, MO, and HY.
Data curation: YO, KA, RN, and HY.
Writing-original draft preparation: YO.
Writing review and editing: HY.
Visualization: YO and HY.
Supervision: TK, KO, MO, and HY.
Project administration: KO, MO, and HY.
Funding acquisition: HY.
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
An animal study was approved by the ethical committee of School of Veterinary Medicine, the Kitasato University (approval no. 21–066), and was performed in conformity with an institutional guideline of the Kitasato University.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Okamura, Y., Adachi, K., Niijima, R. et al. Human omentin-1 reduces vascular insulin resistance and hypertension in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 3379–3387 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02795-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02795-w