Abstract
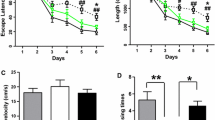
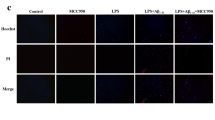
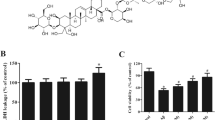
Pyroptosis-mediated neuron death plays a crucial role in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the effect of 1,7-diphenyl-4-hepten-3-one (C1), a natural diarylheptanoid, on AD is unclear. Herein, we investigated the therapeutic effect of C1 on APP/PS1 mice and β-amyloid (Aβ)-induced HT22 cells. Our findings showed that C1 attenuated cognitive impairment and mitigated pathological damage in APP/PS1 mice. Furthermore, we found that C1 prevented oxidative stress damage and decreased the levels of pyroptosis-related proteins. In vitro experiments showed that C1 can improve the proliferation of Aβ-induced HT22 cells and decrease the levels of pyroptosis-related proteins in them. When Nrf2 was silenced, the positive effects of C1 in inhibiting pyroptosis were inhibited. Particularly, the production of pyroptosis-associated proteins, including NLRP3, GSDMD, and caspase-1, and the secretion of pro-inflammatory molecules, including IL-1 and IL-18, were increased. Altogether, these findings indicate that C1 can mitigate AD-like pathology via the inhibition of pyroptosis by activating the Nrf2 pathway. We believe that this study can provide alternative strategies for the prevention and treatment of AD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data and materials are available in the paper.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Aβ:
-
β-Amyloid
- NLRP3:
-
NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3
- IL-18:
-
Interleukin-18
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- GSDMD:
-
Gasdermin-D
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- CCK-8:
-
Cell counting kit-8
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- MDA:
-
Malonaldehyde
- GSH:
-
L-Glutathione
- AOM:
-
Alpinia oxyphylla Mique
- CCK-F:
-
Cell fluorescence counting kit-F
- Edu:
-
5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine
- Mod:
-
Molde group
- C1L:
-
C1 low-dose group
- C1H:
-
C1 high-dose group
- MFI:
-
Median fluorescence intensity
- AOD:
-
Average optical density
References
Ahami Monfared AA, Byrnes MJ, White LA, Zhang Q (2022) Alzheimer’s disease: epidemiology and clinical progression. Neurol Ther 11:553–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40120-022-00338-8
Cai J, Yi M, Tan Y, Li X, Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W, Xiang B (2021) Natural product triptolide induces GSDME-mediated pyroptosis in head and neck cancer through suppressing mitochondrial hexokinase-ΙΙ. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40:190. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-01995-7
Cai H, Liang Q, Ge G (2016) Gypenoside attenuates β amyloid-induced inflammation in N9 microglial cells via SOCS1 signaling. Neural Plast 6362707. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6362707
Chen JC, Xiao HH, Zhang Q, Kong L, Wang TM, Tian Y, Zhao YM, Li H, Tian JM, Wang C, Yang JX (2022) Jujuboside A inhibits oxidative stress damage and enhances immunomodulatory capacity of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells through up-regulating IDO expression, Chin. J Nat Med 20:494–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5364(22)60176-6
Chen X, Sun G, Tian E, Zhang M, Davtyan H, Beach TG, Reiman EM, Blurton-Jones M, Holtzman DM, Shi Y (2021) Modeling sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in human brain organoids under serum exposure. Adv Sci (Weinh) 8:e2101462T. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202101462
Forman HJ, Zhang H (2021) Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 20:689–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
Guo C, Bi J, Li X, Lyu J, Liu X, Wu X, Liu J (2021) Immunomodulation effects of polyphenols from thinned peach treated by different drying methods on RAW264.7 cells through the NF-κB and Nrf2 pathways. Food Chem 340:127931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127931
Han C, Yang Y, Guan Q, Zhang X, Shen H, Sheng Y, Wang J, Zhou X, Li W, Guo L, Jiao Q (2020) New mechanism of nerve injury in Alzheimer’s disease: β-amyloid-induced neuronal pyroptosis. J Cell Mol Med 24:8078–8090. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15439
Hasel P, Liddelow SA (2021) Astrocytes. Curr Biol 31:326–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2021.01.056
Hasel P, Rose IVL, Sadick JS, Kim RD, Liddelow SA (2021) Neuroinflammatory astrocyte subtypes in the mouse brain. Nat Neurosci 24:1475–1487. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00905-6
He B, Nie Q, Wang F, Han Y, Yang B, Sun M, Fan X, Ye Z, Liu P, Wen J (2021) Role of pyroptosis in atherosclerosis and its therapeutic implications. J Cell Physiol 236:7159–7175. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30366
Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou R (2021) NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 18:2114–2127. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-021-00740-6
Huang W, Wen F, Gu P, Liu J, Xia Y, Li Y, Zhou J, Song S, Ruan S, Gu S, Chen X, Shu P (2022) The inhibitory effect and mechanism of Yi-qi-hua-yu-jie-du decoction on the drug resistance of gastric cancer stem cells based on ABC transporters. Chin Med 17:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-022-00647-y
Koo BS, Lee WC, Chang YC, Kim CH (2004) Protective effects of Alpinae oxyphyllae Fructus (Alpinia oxyphylla MIQ) water-extracts on neurons from ischemic damage and neuronal cell toxicity. Phytother Res 18:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.1382
Koutsodendris N, Nelson MR, Rao A, Huang Y (2022) Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease: findings, hypotheses, and potential mechanisms. Annu Rev Pathol 17:73–99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-030421-112756
Lee HG, Wheeler MA, Quintana FJ (2022) Function and therapeutic value of astrocytes in neurological diseases. Nat Rev Nat Rev Drug Discov 21:339–358. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-022-00390-x
Li J, Du Q, Li N, Du S, Sun Z (2021) Alpiniae oxyphyllae Fructus and Alzheimer’s disease: an update and current perspective on this traditional Chinese medicine. Biomed Pharmacother 135:111167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111167
Lyu Z, Li Q, Yu Z, Chan Y, Fu L, Li Y, Zhang C (2021) Yi-Zhi-Fang-Dai Formula exerts neuroprotective effects against pyroptosis and blood-brain barrier-glymphatic dysfunctions to prevent amyloid-beta acute accumulation after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Front Pharmacol 12:791059. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.791059
Martin M, Vermeiren S, Bostaille N, … Vanhollebeke B (2022) Engineered Wnt ligands enable blood-brain barrier repair in neurological disorders. Science 375:6582 https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abm4459
Plascencia-Villa G, Perry G (2021) Preventive and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s disease: focus on oxidative stress, redox metals, and ferroptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 34:591–610. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2020.8134
Simon MS, Schiweck C, Arteaga-Henríquez G, … Drexhage HA (2021) Monocyte mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammaging, and inflammatory pyroptosis in major depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 111:110391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110391
Smith AM, Davey K, Tsartsalis S, Khozoie C, Fancy N, Tang SS, Liaptsi E, Weinert M, McGarry A, Muirhead RCJ, Gentleman S, Owen DR, Matthews PM (2022) Diverse human astrocyte and microglial transcriptional responses to Alzheimer’s pathology. Acta Neuropathol 143:75–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-021-02372-6
Tang G, Dong X, Huang X, Huang XJ, Liu H, Wang Y, Ye WC, Shi L (2015) A natural diarylheptanoid promotes neuronal differentiation via activating ERK and PI3K-Akt dependent pathways. Neuroscience 303:389–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.07.019
Wang Y, Shi P, Chen Q, Huang Z, Zou D, Zhang J, Gao X, Lin Z (2019) Mitochondrial ROS promote macrophage pyroptosis by inducing GSDMD oxidation. J Mol Cell Biol 11:1069–1082. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjz020
Wang C, Chen JC, Xiao HH, Kong L, Zhao YM, Tian Y, Li H, Tian JM, Cui L, Wen CM, Shi YJ, Yang JX, Shang DJ (2022) Jujuboside A promotes proliferation and neuronal differentiation of APPswe-overexpressing neural stem cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Neurosci Lett 772:136473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136473
Wu P, Chen J, Chen J, Tao J, Wu S, Xu G, Wang Z, Wei D, Yin W (2020) Trimethylamine N-oxide promotes apoE-/- mice atherosclerosis by inducing vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis via the SDHB/ROS pathway. J Cell Physiol 235:6582–6591. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29518
Xiao Y, Zhang T, Ma X, Yang QC, Yang LL, Yang SC, Liang M, Xu Z, Sun ZJ (2021) Microenvironment-responsive prodrug-induced pyroptosis boosts cancer immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh) 8:e2101840. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202101840
Zhang T, Hu Q, Shi L, Qin L, Zhang Q, Mi M (2016) Equol attenuates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress via activation of Nrf2 in endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 11:e0167020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167020
Zhang Q, Zheng Y, Hu X, Hu X, Lv W, Lv D, Chen J, Wu M, Song Q, Shentu J (2018) Ethnopharmacological uses, phytochemistry, biological activities, and therapeutic applications of Alpinia oxyphylla Miquel: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 224:149–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.05.002
Zhou Y, Zhou H, Hua L, Hou C, Jia Q, Chen J, Zhang S, Wang Y, He S, Jia E (2021) Verification of ferroptosis and pyroptosis and identification of PTGS2 as the hub gene in human coronary artery atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med 171:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.05.009
Funding
The authors appreciate the support from the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (grant no. 20170540201) and the Key Research and Development Plan of Anhui Province in 2022 (grant no. 2022e07020065).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu-Sheng Shi: conceptualization, methodology, software, and writing—original draft. Yan Zhang: writing—original draft, data curation, and investigation. Xiao Luo: validation and resources. Hong-Kai Yang: validation and resources. Yong-Sheng He: methodology, writing—review and editing, and funding acquisition. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The animals were acclimated for 1 week before experimentation. This study was conducted following the guidelines of the Ethics Committee of Dalian Minzu University (Dalian, China) (Approval AEWC-20210303-1).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, YS., Zhang, Y., Luo, X. et al. 1,7-diphenyl-4-hepten-3-one mitigates Alzheimer’s-like pathology by inhibiting pyroptosis via activating the Nrf2 pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 3065–3075 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02765-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02765-2