Abstract
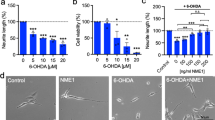
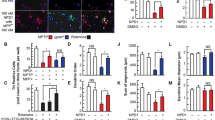
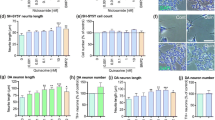
Doxycycline (DOX) is a widely used antibiotic that is able to cross the blood–brain barrier. Several studies have shown its neuroprotective effect against neurodegeneration and have associated it with antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. We have recently demonstrated that DOX mimics nerve growth factor (NGF) signaling in PC12 cells. However, the involvement of this mechanism in the neuroprotective effect of DOX is unknown. Axonal degeneration and synaptic loss are key events at the early stages of neurodegeneration, and precede the neuronal death in neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease (PD). Therefore, the regeneration of the axonal and synaptic network might be beneficial in PD. The effect of DOX in PC12 cells treated with the Parkinsonian neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+) was addressed. Doxycycline reduced the inhibition of neuritogenesis induced by MPP+, even in cells deprived of NGF. The mechanism involved the upregulation of GAP-43, synapsin I, β-III-tubulin, F-actin, and neurofilament-200, proteins that are associated with axonal and synaptic plasticity. Considering the role of axonal degeneration and synaptic loss at the initial stages of PD, the recent advances in early diagnosis of neurodegeneration, and the advantages of drug repurposing, doxycycline is a promising candidate to treat PD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Original source data and western blot membranes are presented in Supplementary Material (S1).
References
Agwuh KN, Macgowan A (2006) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:256–265
Alexander GE (2004) Biology of Parkinson’s disease: pathogenesis and pathophysiology of a multisystem neurodegenerative disorder. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 6:259–280
Amaral LD, Santos N, Sisti FM, del Bel E, Santos ACD (2021) The antibiotic doxycycline mimics the NGF signaling in PC12 cells: a relevant mechanism for neuroprotection. Chem Biol Interact 341:109454
Balducci C, Santamaria G, la Vitola P, Brandi E, Grandi F, Viscomi AR, Beeg M, Gobbi M, Salmona M, Ottonello S, Forloni G (2018) Doxycycline counteracts neuroinflammation restoring memory in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Neurobiol Aging 70:128–139
Bennison SA, Blazejewski SM, Smith TH, Toyo-Oka K (2020) Protein kinases: master regulators of neuritogenesis and therapeutic targets for axon regeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:1511–1530
Blanquie O, Bradke F (2018) Cytoskeleton dynamics in axon regeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 51:60–69
Bortolanza M, Nascimento GC, Socias SB, Ploper D, Chehin RN, Raisman-Vozari R, Del-Bel E (2018) Tetracycline repurposing in neurodegeneration: focus on Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 125:1403–1415
Burke RE, O’Malley K (2013) Axon degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 246:72–83
Caminiti SP, Presotto L, Baroncini D, Garibotto V, Moresco RM, Gianolli L, Volonte MA, Antonini A, Perani D (2017) Axonal damage and loss of connectivity in nigrostriatal and mesolimbic dopamine pathways in early Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage Clin 14:734–740
Cappelletti G, Surrey T, Maci R (2005) The parkinsonism producing neurotoxin MPP+ affects microtubule dynamics by acting as a destabilising factor. FEBS Lett 579:4781–4786
Castrén E, Antila H (2017) Neuronal plasticity and neurotrophic factors in drug responses. Mol Psychiatry 22:1085–1095
Cataldi S, Codini M, Hunot S, Legeron FP, Ferri I, Siccu P, Sidoni A, Ambesi-Impiombato FS, Beccari T, Curcio F, Albi E (2016) e-Cadherin in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinson disease. Mediators Inflamm 2016:3937057
Cho Y, Son HJ, Kim EM, Choi JH, Kim ST, Ji IJ, Choi DH, Joh TH, Kim YS, Hwang O (2009) Doxycycline is neuroprotective against nigral dopaminergic degeneration by a dual mechanism involving MMP-3. Neurotox Res 16:361–371
Costa R, Speretta E, Crowther DC, Cardoso I (2011) Testing the therapeutic potential of doxycycline in a Drosophila melanogaster model of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem 286:41647–41655
Cunha BA, Comer JB, Jonas M (1982) The tetracyclines. Med Clin North Am 66:293–302
del Rey NL, Quiroga-Varela A, Garbayo E, Carballo-Carbajal I, Fernandez-Santiago R, Monje MHG, Trigo-Damas I, Blanco-Prieto MJ, Blesa J (2018) Advances in Parkinson’s disease: 200 years later. Front Neuroanat 12:113
Dent EW, Gupton SL, Gertler FB (2011) The growth cone cytoskeleton in axon outgrowth and guidance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a001800
Dos Santos NA, Martins NM, Silva RDEB, Ferreira RS, Sisti FM, Dos Santos AC (2014) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) protects PC12 cells from MPP+ toxicity by inducing the expression of neuron-typical proteins. Neurotoxicology 45:131–8
Gonzalez-Lizarraga F, Socias SB, Avila CL, Torres-Bugeau CM, Barbosa LR, Binolfi A, Sepulveda-Diaz JE, Del-Bel E, Fernandez CO, Papy-Garcia D, Itri R, Raisman-Vozari R, Chehin RN (2017) Repurposing doxycycline for synucleinopathies: remodelling of alpha-synuclein oligomers towards non-toxic parallel beta-sheet structured species. Sci Rep 7:41755
Grau CM, Greene LA (2012) Use of PC12 cells and rat superior cervical ganglion sympathetic neurons as models for neuroprotective assays relevant to Parkinson’s disease. Methods Mol Biol 846:201–211
Greene LA, Tischler AS (1976) Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:2424–2428
HOLAHAN MR (2017) A shift from a pivotal to supporting role for the growth-associated protein (GAP-43) in the coordination of axonal structural and functional plasticity. Front Cell Neurosci 11:266
Kevenaar JT, Hoogenraad CC (2015) The axonal cytoskeleton: from organization to function. Front Mol Neurosci 8:44
Kiryushko D, Berezin V, Bock E (2004) Regulators of neurite outgrowth: role of cell adhesion molecules. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1014:140–154
Kounakis K, Tavernarakis N (2019) The cytoskeleton as a modulator of aging and neurodegeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol 1178:227–245
Kummer A, Teixeira AL (2009) Neuropsychiatry of Parkinson’s disease. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 67:930–939
L’Episcopo F, Serapide MF, Tirolo C, Testa N, Caniglia S, Morale MC, Pluchino S, Marchetti B (2011) A Wnt1 regulated Frizzled-1/beta-catenin signaling pathway as a candidate regulatory circuit controlling mesencephalic dopaminergic neuron-astrocyte crosstalk: therapeutical relevance for neuron survival and neuroprotection. Mol Neurodegener 6:49
LANGSTON JW (2017) The MPTP story. J Parkinsons Dis 7:S11–S19
Lazzarini M, Martin S, Mitkovski M, Vozari RR, Stuhmer W, Bel ED (2013) Doxycycline restrains glia and confers neuroprotection in a 6-OHDA Parkinson model. Glia 61:1084–1100
Li H, Li SH, Yu ZX, Shelbourne P, Li XJ (2001) Huntingtin aggregate-associated axonal degeneration is an early pathological event in Huntington’ disease mice. J Neurosci : Off J Soc Neurosci 21:8473–8481
Longo FM, Massa SM (2013) Small-molecule modulation of neurotrophin receptors: a strategy for the treatment of neurological disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:507–525
Longo FM, Yang T, Knowles JK, Xie Y, Moore LA, Massa SM (2007) Small molecule neurotrophin receptor ligands: novel strategies for targeting Alzheimer’s disease mechanisms. Curr Alzheimer Res 4:503–506
Mirza FJ, Zahid S (2018) The role of synapsins in neurological disorders. Neurosci Bull 34:349–358
Moon HE, Paek SH (2015) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 24:103–116
Morfini G, Pigino G, Opalach K, Serulle Y, Moreira JE, Sugimori M, Llinás RR, Brady ST (2007) 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium affects fast axonal transport by activation of caspase and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2442–2447
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C (2010) The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 67:181–198
O’Keeffe GW, Sullivan AM (2018) Evidence for dopaminergic axonal degeneration as an early pathological process in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 56:9–15
Papapetropoulos A, Szabo C (2018) Inventing new therapies without reinventing the wheel: the power of drug repurposing. Br J Pharmacol 175:165–167
Perrone-Bizzozero N, Bolognani F (2002) Role of HuD and other RNA-binding proteins in neural development and plasticity. J Neurosci Res 68:121–126
Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Neve RL, Irwin N, Lewis S, Fischer I, Benowitz LI (1991) Post-transcriptional regulation of GAP-43 rnRNA levels during neuronal differentiation and nerve regeneration. Mol Cell Neurosci 2:402–409
Perrone-Bizzozero NI, Cansino VV, Kohn DT (1993) Posttranscriptional regulation of GAP-43 gene expression in PC12 cells through protein kinase C-dependent stabilization of the mRNA. J Cell Biol 120:1263–1270
Poduslo JF, Curran GL (1996) Permeability at the blood-brain and blood-nerve barriers of the neurotrophic factors: NGF, CNTF, NT-3, BDNF. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 36:280–286
Powers R, Lei S, Anandhan A, Marshall DD, Worley B, Cerny RL et al. (2017) Metabolic investigations of the molecular mechanisms associated with parkinson's disease. Metabolites 7(2)
Reglodi D, Renaud J, Tamas A, Tizabi Y, Socias SB, Del-Bel E, Raisman-Vozari R (2017) Novel tactics for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease: role of antibiotics, polyphenols and neuropeptides. Prog Neurobiol 155:120–148
REICHARDT LF (2006) Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361:1545–1564
Santa-Cecília FV, Leite CA, Del-Bel E, Raisman-Vozari R (2019) The neuroprotective effect of doxycycline on neurodegenerative diseases. Neurotox Res 35:981–986
Schimmelpfeng J, Weibezahn KF, Dertinger H (2004) Quantification of NGF-dependent neuronal differentiation of PC-12 cells by means of neurofilament-L mRNA expression and neuronal outgrowth. J Neurosci Methods 139:299–306
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to imageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9(7):671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Serulle Y, Morfini G, Pigino G, Moreira JE, Sugimori M, Brady ST, Llinas RR (2007) 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium induces synaptic dysfunction through a pathway involving caspase and PKCdelta enzymatic activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2437–2441
Smalheiser NR, Dissanayake S, Kapil A (1996) Rapid regulation of neurite outgrowth and retraction by phospholipase A2-derived arachidonic acid and its metabolites. Brain Res 721:39–48
Son JH, Shim JH, Kim KH, Ha JY, Han JY (2012) Neuronal autophagy and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Mol Med 44:89–98
Storch A, Ludolph AC, Schwarz J (2004) Dopamine transporter: involvement in selective dopaminergic neurotoxicity and degeneration. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 111:1267–1286
Tagliaferro P, Burke RE (2016) Retrograde axonal degeneration in Parkinson disease. J Parkinsons Dis 6:1–15
Tao T, Feng JZ, Xu GH, Fu J, Li XG, Qin XY (2017) Minocycline promotes neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation through regulation of MLCP/MLC signaling pathways. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37:417–426
Wang H, Wu M, Zhan C, Ma E, Yang M, Yang X, Li Y (2012) Neurofilament proteins in axonal regeneration and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res 7:620–626
Weissmiller AM, Wu C (2012) Current advances in using neurotrophic factors to treat neurodegenerative disorders. Transl Neurodegener 1:14
Wiatrak B, Kubis-Kubiak A, Piwowar A, Barg E (2020) PC12 Cell line: cell types, coating of culture vessels, differentiation and other culture conditions. Cells 14;9(4):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040958
Xu J, Lacoske MH, Theodorakis EA (2014) Neurotrophic natural products: chemistry and biology. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:956–987
Yao JS, Shen F, Young WL, Yang GY (2007) Comparison of doxycycline and minocycline in the inhibition of VEGF-induced smooth muscle cell migration. Neurochem Int 50:524–530
Yu R, Zheng L, Cui Y, Zhang H, Ye H (2016) Doxycycline exerted neuroprotective activity by enhancing the activation of neuropeptide GPCR PAC1. Neuropharmacol 103:1–15
Zhang GB, Feng YH, Wang PQ, Song JH, Wang P, Wang SA (2015) A study on the protective role of doxycycline upon dopaminergic neuron of LPS-PD rat model rat. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:3468–3474
Funding
This study was financially supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, code 001), and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq grant number 305823/2019–1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ACS, NS, and EDB conceived and designed research. LA and FS conducted experiments. LA and NS analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
do Amaral, L., dos Santos, N.A.G., Sisti, F.M. et al. Doxycycline inhibits dopaminergic neurodegeneration through upregulation of axonal and synaptic proteins. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 1787–1796 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02435-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02435-3