Abstract
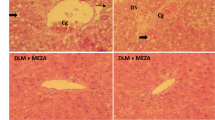
Pteris cretica L. var. nervosa is one of the most well-known Chinese medicines. Although it is widely used to treat jaundice hepatitis, the main ingredient for its treatment was not thoroughly explored until recently. Essentially, the purpose of this study is to find the monomer compound in Pteris cretica L. var. nervosa, which is most likely to be effective in treating liver injury. Through the model of LPS/D-gal-induced liver injury in mice, the best therapeutic site of the total extract was explored, the chemical components of the parts with the best therapeutic effect were separated, a total of 10 flavonoids were isolated, and the RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS were used as the experimental model to explore the preliminary anti-inflammatory activity of NO production in vitro. Finally, the anti-inflammatory activity and the highest content in this plant Luteolin-7-O-rutinoside (LUT) were selected, as the object of study in vivo. It was found that LUT could not only reduce alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels, but also significantly reduce the release of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and inhibit PI3K/AKT/AMPK/NF-κB pathway. In addition, LUT can increase levels of SOD and GSH to reduce oxidative stress. It has an obvious therapeutic effect on acute liver injury induced by LPS/D-gal in mice. Therefore, infer LUT is a functional substance in Pteris cretica L. var. nervosa.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chung M-Y, Jung SK, Lee H-J, Shon DH, Kim H-K (2015) Ethanol extract of Sarcodon asparatus mitigates inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-challenged mice and murine macrophages. Journal of Medicinal Food 18:1198–1206. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2014.3422
Ismail FA, El-Garawani F, Islam AE (2021) Acute hepatitis A virus infection in Tobruk, Eastern Libya: increasing trends after 2017. Food Environ Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-021-09499-5
Katopodi A, Detsi A (2021) Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers of natural products as promising systems for their bioactivity enhancement: The case of essential oils and flavonoids. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127529
Lee JH, Han Y (2011) Antiarthritic effect of lonicerin on Candida albicans arthritis in mice. Arch Pharm Res 34:853–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0520-6
Li C, Si J, Tan F, Park K, Zhao X (2021a) Lactobacillus plantarum KSFY06 prevents inflammatory response and oxidative stress in acute liver injury induced by D-Gal/LPS in mice. Drug design, development and therapy 15:37–50. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S286104
Li Z, Li J, Li Z, Zhang H, Yang S, Ouyang H, He M, Feng Y (2021b) Protective activity of cubebin from Syringa oblata against CCl4-induced hepatic damage in mice. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 31:322–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-021-00171-4
Liao H, Du S, Jiang T, Zheng M, Xiang Z, Yang J (2021) UMSCs attenuate LPS/D-GalN-induced acute liver failure in mice by down-regulating the MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology 000: 000-000. https://doi.org/10.14218/jcth.2020.00157
Liu G-Z, Xu X-W, Tao S-H, Gao M-J, Hou Z-H (2021a) HBx facilitates ferroptosis in acute liver failure via EZH2 mediated SLC7A11 suppression. Journal of Biomedical Science 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-021-00762-2
Liu J, Xu P, Liu D, Wang R, Cui S, Zhang Q, Li Y, Yang W, Zhang D (2021b) TCM regulates PI3K/Akt signal pathway to intervene atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM 2021: 4854755. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4854755
Liu Q, Tian H, Kang Y, Tian Y, Li L, Kang X, Yang H, Wang Y, Tian J, Zhang F, Tong M, Cai H, Fan W (2021c) Probiotics alleviate autoimmune hepatitis in mice through modulation of gut microbiota and intestinal permeability. J Nutrition Biochem 98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2021.108863
Long F, Wang N, Zhang R, Qiu H, Lv J, Wang X, Wang M, Mao D (2017) Effects of transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on hepatic injury and metabolism in rats with acute liver failure. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 10:4881–4888
Luo Y, Yang Y, Shen Y, Li L, Huang J, Tang L, Zhang L (2020) Luzindole attenuates LPS/d-galactosamine-induced acute hepatitis in mice. Innate Immunity 26:319–327. https://doi.org/10.1177/1753425919890912
Lv Q, Xing Y, Liu J, Dong D, Liu Y, Qiao H, Zhang Y, Hu L (2021) Lonicerin targets EZH2 to alleviate ulcerative colitis by autophagy-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome inactivation. Acta pharmaceutica Sinica B 11:2880–2899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.03.011
Mohseni A, Casolaro V, Bermúdez-Humarán L, Keyvani H, Taghinezhad-S S (2021) Modulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway by probiotics as a fruitful target for orchestrating the immune response. Gut microbes 13:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2021.1886844
Noh I, Ahmad I, Suraiya S, Musa N, Nurul A, Ruzilawati A (2021) Cytokine (IL-10, IL-6, TNF-α and TGF-β1) gene polymorphisms in chronic hepatitis C virus infection among Malay male drug abusers. Biomedicines 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091115
Osundare FA, Klink P, Akanbi OA, Wang B, Harms D, Ojurongbe O, Ajayi MA, Babaranti EO, Bock CT, Opaleye OO (2021) Hepatitis E virus infection in high-risk populations in Osun State, Nigeria. One health (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 13:100256–100256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2021.100256
Peng X, Yang Y, Tang L, Wan J, Dai J, Li L, Huang J, Shen Y, Lin L, Gong X, Zhang L (2020) Therapeutic benefits of apocynin in mice with lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury via suppression of the late stage pro-apoptotic AMPK/JNK pathway. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 125:110020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110020
Pu Y, Yang Z, Mo X (2021) Protective effect of luteolin on D-galactosamine (D-Gal)/lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced hepatic injury by in mice. Biomed Research International 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2252705
Shi A, Li T, Zheng Y, Song Y, Wang H, Wang N, Dong L, Shi H (2021) Chlorogenic acid improves NAFLD by regulating gut microbiota and GLP-1. Front Pharmacol 12:693048. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.693048
van der Heide D, Weiskirchen R, Bansal R (2019) Therapeutic targeting of hepatic macrophages for the treatment of liver diseases. Front Immunol 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02852
Wang H, Cui S, Wu D, Yang X, Wang H, Wang Z (2021) Effects of kinetin on arsenic speciation and antioxidative enzymes in fronds of the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris cretica var. nervosa and non-hyperaccumulator Pteris ensiformis. Environ Exp Bot 191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104622
Wang M, Zhang J, Gong N (2022) Role of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in liver ischemia reperfusion injury: a narrative review. Ann Palliat Med 11:806–817. https://doi.org/10.21037/apm-21-3286
Wang N, Zhang X, Ma Z, Niu J, Ma S, Wenjie W, Chen J (2020a) Combination of tanshinone IIA and astragaloside IV attenuate atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability in ApoE(-/-) mice by activating PI3K/AKT signaling and suppressing TRL4/NF-κB signaling. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie 123:109729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109729
Wang Q, Zhao Y, Zang B (2020b) Anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis effects of growth arrest-specific protein 6 in acute liver injury induced by LPS/D-GalN in mice. Acta Cir Bras 35:9. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0102-865020200020000004
Wolthuis E, Vlaar A, Choi G, Roelofs J, Juffermans N, Schultz M (2009) Mechanical ventilation using non-injurious ventilation settings causes lung injury in the absence of pre-existing lung injury in healthy mice. Critical care (London, England) 13:R1. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc7688
Wu RQ, Meng BZ, Corredig M, Griffiths MW (2022) Efficient capturing and sensitive detection of hepatitis A virus from solid foods (green onion, strawberry, and mussel) using protamine-coated iron oxide (Fe3O4) magnetic nanoparticles and real-time RT-PCR. Food Microbiol 102:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2021.103921
Xu Z, Li K, Pan T, Liu J, Li B, Li C, Wang S, Diao Y, Liu X (2019) Lonicerin, an anti-algE flavonoid against Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence screened from Shuanghuanglian formula by molecule docking based strategy. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.111909
Yang H, Zhang H, Wang C, Pang L (2021) An analysis of the clinical features of children with early congenital Syphilis and Syphilitic Hepatitis. BMC Pediatr 21:498. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-021-02932-5
Funding
This work was supported financially by National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC1712304), National Natural Science Foundations of China under Grant (81860684), Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (GJJ190689), and Key projects of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20212ACB206007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.W.X.—isolation and purification. Q.W. and Z.W.X.—identify the structure. Z.W.X and Y.S.C.—acute liver injury evaluation and animal experiment. J.H.W. and L.Y.S. processed the data. Z.W.X—writing original draft preparation. S.L.Y.—writing review and editing. Y.L.F. and Q.W.—supervision. All data were generated in-house and no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Protection of animals
Animal experiments were conducted according to the regulations of the Institute Animal Ethics Committee (approval number: SCXK (Xiang) 2019-0004).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, Z., Cui, Y., Wu, J. et al. Luteolin-7-O-rutinoside from Pteris cretica L. var. nervosa attenuates LPS/D-gal-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/AMPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 1283–1295 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02266-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02266-8