Abstract
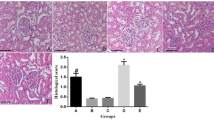
Combined antioxidants effect for prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) remains unclear. This study assessed the potential protective effects of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) alone or combined with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) or atorvastatin against CIN in diabetic rats. Animals were randomly divided into five groups, including control and four disease groups with CIN and diabetes. Group 2 included diabetic rats with CIN. Groups 3–5 included diabetic rats that received CoQ10, CoQ10 and NAC, or CoQ10 and atorvastatin, respectively, before CIN induction. Serum, urine, and tissue were collected to evaluate renal protective effects of tested agents. Renal biomarkers, oxidative stress, and histopathological alterations were investigated. Rats with CIN showed significant renal impairment as revealed by the deleterious effects on kidney function and histology. While induction of CIN did not affect the renal levels of catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, pretreatment of animals with CoQ10/NAC showed significant increase in GPx and catalase levels versus controls. Lastly, pretreatment with CoQ10/atorvastatin showed regenerative effect on distal tubules with mild kidney histology alterations relative to CIN rats. The combined use of CoQ10/atorvastatin could be a potential strategy to prevent CIN. However, future studies are warranted to test different combinations for longer prophylactic periods.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKI:
-
acute kidney injury
- CIN:
-
contrast-induced nephropathy
- CoQ10:
-
coenzyme Q10
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- IP:
-
intraperitoneal
- L-NAME:
-
NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester
- NAC:
-
N-acetyl cysteine
- STZ:
-
streptozotocin
- TBARS:
-
thiobarbituric acid reactive substances.
References
Acosta MJ, Vazquez Fonseca L, Desbats MA, Cerqua C, Zordan R, Trevisson E, Salviati L (2016) Coenzyme Q biosynthesis in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1857(8):1079–1085
Andreucci M, Faga T, Pisani A, Sabbatini M, Michael A (2014a) Acute kidney injury by radiographic contrast media: pathogenesis and prevention. Biomed Res Int 2014:362725
Andreucci M, Faga T, Pisani A, Sabbatini M, Russo D, Michael A (2014b) Prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy through a knowledge of its pathogenesis and risk factors. ScientificWorldJournal 2014:823169
Au TH, Bruckner A, Mohiuddin SM, Hilleman DE (2014) The prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy. Ann Pharmacother 48(10):1332–1342
Bhagavan HN, Chopra RK (2006) Coenzyme Q10: absorption, tissue uptake, metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Free Radic Res 40(5):445–453
Bhagavan HN, Chopra RK (2007) Plasma coenzyme Q10 response to oral ingestion of coenzyme Q10 formulations. Mitochondrion 7(Suppl):S78–S88
Briasoulis A, Pala M, Telila T, Merid O, Akintoye E, Vogiatzi G, Oikonomou E, Tousoulis D (2017) Statins and contrast-induced nephropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Pharm Des
Chen F, Liu F, Lu J, Yang X, Xiao B, Jin Y, Zhang J (2018a) Coenzyme Q10 combined with trimetazidine in the prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with coronary heart disease complicated with renal dysfunction undergoing elective cardiac catheterization: a randomized control study and in vivo study. Eur J Med Res 23(1):23
Chen PP, Xu HL, Ting Y, ZhuGe DL, Jin BH, Zhu QY, Shen BX, Wang LF, Lu CT, Zhao YZ, Li XK (2018b) CoQ10-loaded liposomes combined with UTMD prevented early nephropathy of diabetic rats. Oncotarget 9(14):11767–11782
Farmer JA (2000) Pleiotropic effects of statins. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2(3):208–217
Gong X, Duan Y, Zheng J, Wang Y, Wang G, Norgren S, Hei TK (2016) Nephroprotective Effects of N-Acetylcysteine amide against contrast-induced nephropathy through upregulating thioredoxin-1, inhibiting ASK1/p38MAPK pathway, and suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:8715185
Hong YA, Bae SY, Ahn SY, Kim J, Kwon YJ, Jung WY, Ko GJ (2017) Resveratrol ameliorates contrast induced nephropathy through the activation of SIRT1-PGC-1alpha-Foxo1 signaling in mice. Kidney Blood Press Res 42(4):641–653
Indo HP, Yen HC, Nakanishi I, Matsumoto K, Tamura M, Nagano Y, Matsui H, Gusev O, Cornette R, Okuda T, Minamiyama Y, Ichikawa H, Suenaga S, Oki M, Sato T, Ozawa T, Clair DK, Majima HJ (2015) A mitochondrial superoxide theory for oxidative stress diseases and aging. J Clin Biochem Nutr 56(1):1–7
Katsiki N, Athyros VG, Karagiannis A, Mikhailidis DP (2015) Contrast-induced nephropathy: an all or none phenomenon? Angiology 66(6):508–513
Mamoulakis C, Tsarouhas K, Fragkiadoulaki I, Heretis I, Wilks MF, Spandidos DA, Tsitsimpikou C, Tsatsakis A (2017) Contrast-induced nephropathy: basic concepts, pathophysiological implications and prevention strategies. Pharmacol Ther 180:99–112
Mayyas F, Alzoubi KH (2018) Cardiac effects of cigarette tobacco smoking in rat model of diabetes. Life Sci 211:279–285
Mikhailidis DP, Athyros VG (2014) Acute kidney injury: short-term statin therapy for prevention of contrast-induced AKI. Nat Rev Nephrol 10(1):8–9
Mokhtari V, Afsharian P, Shahhoseini M, Kalantar SM, Moini A (2017) A review on various uses of n-acetyl cysteine. Cell J 19(1):11–17
Nusair SD, Ahmad MI (2019) Toxicity of Vipera palaestinae venom and antagonistic effects of methanolic leaf extract of Eryngium creticum lam. Toxicon 166:1–8
Ozturk O, Eroglu HA, Ustebay S, Kuzucu M, Adali Y (2018) An experimental study on the preventive effects of n-acetyl cysteine and ozone treatment against contrast-induced nephropathy. Acta Cir Bras 33(6):508–517
Rababa’h AM, Hijjawi TB, Alzoubi KH, Al Demour S, Ababneh MA (2018) The nephroprotective effect of N-Aacetyl-L-cysteine and atorvastatin against imipenem induced nephrotoxicity. Curr Mol Pharmacol 11(2):155–161
Rahman MM, Haque HS, Banerjee SK, Ahsan SA, Rahman MF, Mahmood M, Salman M, Azam MG (2010) Contrast induced nephropathy in diabetic and non-diabetic patients during coronary angiogram and angioplasty. Mymensingh Med J 19(3):372–376
Sadat U, Usman A, Gillard JH, Boyle JR (2013) Does ascorbic acid protect against contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary angiography: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 62(23):2167–2175
Seeliger E, Sendeski M, Rihal CS, Persson PB (2012) Contrast-induced kidney injury: mechanisms, risk factors, and prevention. Eur Heart J 33(16):2007–2015
Su J, Zou W, Cai W, Chen X, Wang F, Li S, Ma W, Cao Y (2014) Atorvastatin ameliorates contrast medium-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis in diabetic rats via suppression of Rho-kinase pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 723:15–22
Svensson M, Malm C, Tonkonogi M, Ekblom B, Sjödin B, Sahlin K (1999) Effect of Q10 supplementation on tissue Q10 levels and adenine nucleotide catabolism during high-intensity exercise. Int J Sport Nutr 9(2):166–180
Toso A, Maioli M, Leoncini M, Gallopin M, Tedeschi D, Micheletti C, Manzone C, Amato M, Bellandi F (2010) Usefulness of atorvastatin (80 mg) in prevention of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with chronic renal disease. Am J Cardiol 105(3):288–292
Zealley I, Wang H, Donnan PT, Bell S (2018) Exposure to contrast media in the perioperative period confers no additional risk of acute kidney injury in surgical patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33(10):1751–1756
Funding
This work was funded by a grant from the Deanship of Research, Jordan University of Science and Technology (Grant number: 380/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OYA: Idea generation and conceptualization, experimental design, methodology, data processing, analysis and interpretation, manuscript writing. SDN: Experimental design, methodology, data processing and interpretation, manuscript writing. TE: Methodology, data interpretation, manuscript writing. KHA: Experimental design, data interpretation, manuscript writing. AO: Experimental work and data processing. MS: Experimental work and data processing. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript and all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical standards
The Animal Care and Use Committee of JUST approved the study protocol (protocol approval number 16/3/3/320). The study was conducted in accordance with the standards of Guide for the US National research Council’s and Laboratory.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(XLSX 12 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshogran, O.Y., Nusair, S.D., El-Elimat, T. et al. Evaluation of coenzyme Q10 combined with or without N-acetyl cysteine or atorvastatin for preventing contrast-induced kidney injury in diabetic rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 1403–1410 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02070-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02070-w