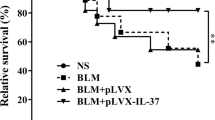
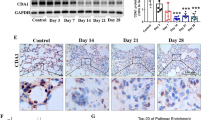
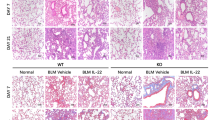
Abstract
Pulmonary fibrosis is a kind of pulmonary disorder with chronic inflammation and excessive collagen deposition, and its etiology is not clear. Interleukin (IL)-38 is a new member of IL-1 family cytokines, but its role in pulmonary fibrosis has not been elucidated. In this study, a lentivirus expressing IL-38 was injected into the nasal cavity of mice with bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. We found that IL-38 overexpression reduced the body weight loss and improved the survival of mice induced by bleomycin. Furthermore, IL-38 expression attenuated the pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis damage induced by bleomycin, decreased the production of pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic cytokines such as IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17A, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and tumor necrosis factor-α, but increased the release of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) in the lungs of bleomycin-challenged mice. Our data suggest that IL-38 may inhibit bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through its anti-inflammatory effect and regulation of IL-1β/IL-1Ra balance, and IL-38 may be a new strategy for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson IY (1976) Pulmonary toxicity of bleomycin. Environ Health Perspect 16:119–126
Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V (1988) Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol 41:467–470
Atamas SP, White B (2003) Cytokine regulation of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:537–550
Barlo NP, van Moorsel CH, Korthagen NM, Heron M, Rijkers GT, Ruven HJ, van den Bosch JM, Grutters JC (2011) Genetic variability in the IL1RN gene and the balance between interleukin (IL)-1 receptor agonist and IL-1beta in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Exp Immunol 166:346–351
Bensen JT, Dawson PA, Mychaleckyj JC, Bowden DW (2001) Identification of a novel human cytokine gene in the interleukin gene cluster on chromosome 2q12-14. J Interf Cytokine Res 21:899–904
Beyaert R, Cuenda A, Vanden Berghe W, Plaisance S, Lee JC, Haegeman G, Cohen P, Fiers W (1996) The p38/RK mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway regulates interleukin-6 synthesis response to tumor necrosis factor. EMBO J 15:1914–1923
Boutet MA, Najm A, Bart G, Brion R, Touchais S, Trichet V, Layrolle P, Gabay C, Palmer G, Blanchard F, Le Goff B (2017) IL-38 overexpression induces anti-inflammatory effects in mice arthritis models and in human macrophages in vitro. Ann Rheum Dis 76:1304–1312
Car BD, Meloni F, Luisetti M, Semenzato G, Gialdroni-Grassi G, Walz A (1994) Elevated IL-8 and MCP-1 in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149:655–659
Chen Y, Li C, Weng D, Song L, Tang W, Dai W, Yu Y, Liu F, Zhao M, Lu C, Chen J (2014) Neutralization of interleukin-17A delays progression of silica-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 275:62–72
Chu M, Tam LS, Zhu J, Jiao D, Liu H, Cai Z, Dong J, Kai Lam CW, Wong CK (2017) In vivo anti-inflammatory activities of novel cytokine IL-38 in Murphy Roths Large (MRL)/lpr mice. Immunobiology 222:483–493
Claussen CA, Long EC (1999) Nucleic acid recognition by metal complexes of bleomycin. Chem Rev 99:2797–2816
Dinarello CA, van der Meer JW (2013) Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in humans. Semin Immunol 25:469–484
Gao Q, Li Y, Pan X, Yuan X, Peng X, Li M (2016) Lentivirus expressing soluble ST2 alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 30:188–193
Garraud T, Harel M, Boutet MA, Le Goff B, Blanchard F (2018) The enigmatic role of IL-38 in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 39:26–35
Gasse P, Mary C, Guenon I, Noulin N, Charron S, Schnyder-Candrian S, Schnyder B, Akira S, Quesniaux VF, Lagente V, Ryffel B, Couillin I (2007) IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling and the inflammasome are essential in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest 117:3786–3799
Ge Y, Huang M, Wu Y, Dong N, Yao YM (2020) Interleukin-38 protects against sepsis by augmenting immunosuppressive activity of CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells. J Cell Mol Med 24:2027–2039
Gross TJ, Hunninghake GW (2001) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 345:517–525
Han Y, Mora J, Huard A, da Silva P, Wiechmann S, Putyrski M, Schuster C, Elwakeel E, Lang G, Scholz A, Scholz T, Schmid T, de Bruin N, Billuart P, Sala C, Burkhardt H, Parnham MJ, Ernst A, Brune B, Weigert A (2019) IL-38 ameliorates skin inflammation and limits IL-17 production from gammadelta T cells. Cell Rep 27(835–846):e835
Huang C, Li Y, Fan X, Ma Y, Zhang M, Wang W (2014) IL-17A promotes pulmonary inflammation in rats with pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 30:366–370
Hubner RH, Gitter W, El Mokhtari NE, Mathiak M, Both M, Bolte H, Freitag-Wolf S, Bewig B (2008) Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. Biotechniques 44(507–511):514–507
Izumo T, Kondo M, Nagai A (2009) Effects of a leukotriene B4 receptor antagonist on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J 34:1444–1451
Kolb M, Margetts PJ, Anthony DC, Pitossi F, Gauldie J (2001) Transient expression of IL-1beta induces acute lung injury and chronic repair leading to pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 107:1529–1536
Li Y, Gao Q, Xu K, Peng X, Yuan X, Jiang W, Li M (2018) Interleukin-37 attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice. Inflammation 41:1772–1779
Lin H, Ho AS, Haley-Vicente D, Zhang J, Bernal-Fussell J, Pace AM, Hansen D, Schweighofer K, Mize NK, Ford JE (2001) Cloning and characterization of IL-1HY2, a novel interleukin-1 family member. J Biol Chem 276:20597–20602
Luo Y, Laning J, Hayashi M, Hancock PR, Rollins B, Dorf ME (1994) Serologic analysis of the mouse beta chemokine JE/monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. J Immunol 153:3708–3716
Maron-Gutierrez T, Castiglione RC, Xisto DG, Oliveira MG, Cruz FF, Pecanha R, Carreira-Junior H, Ornellas DS, Moraes MO, Takiya CM, Rocco PR, Morales MM (2011) Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell therapy attenuates silica-induced lung fibrosis. Eur Respir J 37:1217–1225
Matsuoka M, Kawayama T, Tominaga M, Kaieda S, Tokunaga Y, Kaku Y, Imaoka H, Kinoshita T, Okamoto M, Akiba J, Hoshino T (2019) Attenuated airway eosinophilic inflammations in IL-38 knockout mouse model. Kurume Med J 65:37–46
Mercurio L, Morelli M, Scarponi C, Eisenmesser EZ, Doti N, Pagnanelli G, Gubinelli E, Mazzanti C, Cavani A, Ruvo M, Dinarello CA, Albanesi C, Madonna S (2018) IL-38 has an anti-inflammatory action in psoriasis and its expression correlates with disease severity and therapeutic response to anti-IL-17A treatment. Cell Death Dis 9:1104
Mi S, Li Z, Yang HZ, Liu H, Wang JP, Ma YG, Wang XX, Liu HZ, Sun W, Hu ZW (2011) Blocking IL-17A promotes the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis via TGF-beta1-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Immunol 187:3003–3014
Moore BB, Hogaboam CM (2008) Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L152–L160
Moore BB, Paine R 3rd, Christensen PJ, Moore TA, Sitterding S, Ngan R, Wilke CA, Kuziel WA, Toews GB (2001) Protection from pulmonary fibrosis in the absence of CCR2 signaling. J Immunol 167:4368–4377
Nakao A, Fujii M, Matsumura R, Kumano K, Saito Y, Miyazono K, Iwamoto I (1999) Transient gene transfer and expression of Smad7 prevents bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest 104:5–11
O'Donoghue RJ, Knight DA, Richards CD, Prele CM, Lau HL, Jarnicki AG, Jones J, Bozinovski S, Vlahos R, Thiem S, McKenzie BS, Wang B, Stumbles P, Laurent GJ, McAnulty RJ, Rose-John S, Zhu HJ, Anderson GP, Ernst MR, Mutsaers SE (2012) Genetic partitioning of interleukin-6 signalling in mice dissociates Stat3 from Smad3-mediated lung fibrosis. EMBO Mol Med 4:939–951
O'Reilly S, Ciechomska M, Cant R, Hugle T, van Laar JM (2012) Interleukin-6, its role in fibrosing conditions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 23:99–107
Ortiz LA, Lasky J, Lungarella G, Cavarra E, Martorana P, Banks WA, Peschon JJ, Schmidts HL, Brody AR, Friedman M (1999) Upregulation of the p75 but not the p55 TNF-alpha receptor mRNA after silica and bleomycin exposure and protection from lung injury in double receptor knockout mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 20:825–833
Pan X, Xu K, Li Y, Wang X, Peng X, Li M, Li Y (2019) Interleukin-35 expression protects against cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 110:727–732
Phan SH, Kunkel SL (1992) Lung cytokine production in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res 18:29–43
Piguet PF, Vesin C (1994) Treatment by human recombinant soluble TNF receptor of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin or silica in mice. Eur Respir J 7:515–518
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Kapanci Y, Vassalli P (1989) Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin plays a key role in bleomycin-induced pneumopathy and fibrosis. J Exp Med 170:655–663
Rudloff I, Godsell J, Nold-Petry CA, Harris J, Hoi A, Morand EF, Nold MF (2015) Brief report: Interleukin-38 exerts antiinflammatory functions and is associated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 67:3219–3225
Saito F, Tasaka S, Inoue K, Miyamoto K, Nakano Y, Ogawa Y, Yamada W, Shiraishi Y, Hasegawa N, Fujishima S, Takano H, Ishizaka A (2008) Role of interleukin-6 in bleomycin-induced lung inflammatory changes in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 38:566–571
Sheppard D (2006) Transforming growth factor beta: a central modulator of pulmonary and airway inflammation and fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:413–417
Sleijfer S (2001) Bleomycin-induced pneumonitis. Chest 120:617–624
Suga M, Iyonaga K, Ichiyasu H, Saita N, Yamasaki H, Ando M (1999) Clinical significance of MCP-1 levels in BALF and serum in patients with interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J 14:376–382
Sun X, Hou T, Cheung E, Iu TN, Tam VW, Chu IM, Tsang MS, Chan PK, Lam CW, Wong CK (2019) Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the novel cytokine interleukin-38 in allergic asthma. Cell Mol Immunol
Tan HL, Rosenthal M (2013) IL-17 in lung disease: friend or foe? Thorax 68:788–790
Todd NW, Luzina IG, Atamas SP (2012) Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5:11
Tominaga M, Okamoto M, Kawayama T, Matsuoka M, Kaieda S, Sakazaki Y, Kinoshita T, Mori D, Inoue A, Hoshino T (2017) Overexpression of IL-38 protein in anticancer drug-induced lung injury and acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Investig 55:293–299
van de Veerdonk FL, Stoeckman AK, Wu G, Boeckermann AN, Azam T, Netea MG, Joosten LA, van der Meer JW, Hao R, Kalabokis V, Dinarello CA (2012) IL-38 binds to the IL-36 receptor and has biological effects on immune cells similar to IL-36 receptor antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:3001–3005
Wang Q, Wang Y, Hyde DM, Gotwals PJ, Koteliansky VE, Ryan ST, Giri SN (1999) Reduction of bleomycin induced lung fibrosis by transforming growth factor beta soluble receptor in hamsters. Thorax 54:805–812
Wilson MS, Wynn TA (2009) Pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis, etiology and regulation. Mucosal Immunol 2:103–121
Wilson MS, Madala SK, Ramalingam TR, Gochuico BR, Rosas IO, Cheever AW, Wynn TA (2010) Bleomycin and IL-1beta-mediated pulmonary fibrosis is IL-17A dependent. J Exp Med 207:535–552
Xie C, Yan W, Quan R, Chen C, Tu L, Hou X, Fu Y (2020) Interleukin-38 is elevated in inflammatory bowel diseases and suppresses intestinal inflammation. Cytokine 127:154963
Xu F, Lin S, Yan X, Wang C, Tu H, Yin Y, Cao J (2018) Interleukin 38 protects against lethal sepsis. J Infect Dis 218:1175–1184
Xu K, Sun J, Chen S, Li Y, Peng X, Li M, Li Y (2019) Hydrodynamic delivery of IL-38 gene alleviates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 508:198–202
Yuan X, Li Y, Pan X, Peng X, Song G, Jiang W, Gao Q, Li M (2016) IL-38 alleviates concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 40:452–457
Zhang Y, Lee TC, Guillemin B, Yu MC, Rom WN (1993) Enhanced IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha release and messenger RNA expression in macrophages from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis or after asbestos exposure. J Immunol 150:4188–4196
Zhu Y, Liu Y, Zhou W, Xiang R, Jiang L, Huang K, Xiao Y, Guo Z, Gao J (2010) A prostacyclin analogue, iloprost, protects from bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Respir Res 11:34
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970735), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY17H010001, LY18H010003), and sponsored by K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhiwei Xu and Xianli Yuan contributed equally to this work. Z.X. and X.Y. performed the molecular biological and animal studies, and wrote the manuscript; Q.G. performed the biochemical analysis and ELISA; Y.L. and M.L. conceived the study, performed the data analysis, and revised the manuscript; and all authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript. All data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal procedures were in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (8th edition, NIH) and approved by The Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Ningbo University School of Medicine.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Yuan, X., Gao, Q. et al. Interleukin-38 overexpression prevents bleomycin-induced mouse pulmonary fibrosis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 391–399 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01920-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01920-3