Abstract
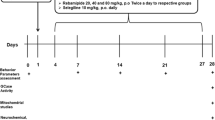
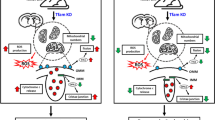
Disease-modifying agents are unmet medical need for Parkinson’s disease (PD). Drugs are under clinical trial to halt its progression, such as ambroxol due to its glucocerebrosidase (GCase)-stimulating activity. However, the neurorestorative effect of ambroxol is not yet investigated in any of the well-established PD models in vivo. Ambroxol was administered as 400 mg/kg orally twice a day from D-28 to D-70 after the unilateral intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in male rats. Behavioral parameters were observed every week, and at last, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), dopamine transporter (DAT), glucocerbrosidase (GCase) enzymatic and mitochondrial complex-I activity, α-synuclein levels, and Nissl’s staining were performed. Behavioral functions were progressively recovered. Ambroxol restored TH and DAT levels on D-71 as the markers of dopaminergic cell and extracellular DA concentration respectively, indicating the recovery of dopaminergic system. Factors involved in PD pathogenesis such as GCase enzymatic and mitochondrial complex-I activity were restored, and α-synuclein pathology was decreased by ambroxol. GCase deficiency is involved in mitochondrial impairment and formation of oligomeric α-synuclein aggregates which negatively affect mitochondrial function. Nissl bodies were also normalized. Therefore, both the GCase-stimulating and α-synuclein pathology-diminishing effects of ambroxol may be responsible for increment in mitochondrial function and restoration of dopaminergic system. These may act as significant mechanisms for disease-modifying potential of ambroxol. The current study provides the preclinical evidence to support the neurorestorative potential of ambroxol in 6-OHDA-induced hemiparkinson’s rat model and indicates its possible use as disease-modifying agent in PD.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allbutt HN, Henderson JM (2007) Use of the narrow beam test in the rat, 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci Methods 159:195–202
Bendikov-Bar I, Ron I, Filocamo M, Horowitz M (2011) Characterization of the ERAD process of the L444P mutant glucocerebrosidase variant. Blood Cells Mol Dis 46:4–10
Berger K, Przedborski S, Cadet JL (1991) Retrograde degeneration of nigrostriatal neurons induced by intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine injection in rats. Brain Res Bull 26:301–307
Berman SB, Hastings TG (1999) Dopamine oxidation alters mitochondrial respiration and induces permeability transition in brain mitochondria. J Neurochem 73:1127–1137
Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F (1973) Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci 20:415–455
Bhardwaj HC, Arunachalam M, Kumar SH, Navis S (2016) Neuroprotective and anti-nociceptive potential of ambroxol in oxaliplatin induced peripheral neuropathic pain in rats. Biol Med 8:1–7
Bianchi G, Landi M, Garattini S (1986) Disposition of apomorphine in rat brain areas: relationship to stereotypy. Eur J Pharmacol 131:229–236
Bonini NM, Giasson BI (2005) Snaring the function of α-synuclein. Cell 123:359–361
Bronstein PM (1972) Open-field behavior of the rat as a function of age: cross-sectional and longitudinal investigations. J Comp Physiol Psychol 80:335–341
Budi A, Heru S, Ahmad RA, Yusuf A (2012) Increase of oxidative stress and accumulation of α-Synuclein in Wistar rat's midbrain treated with rotenone. ITB J 44(A):317–332
Byrne JH, Heidelberger R, Waxham MN (2014) From molecules to networks: an introduction to cellular and molecular neuroscience. Academic Press, Cambridge
Chandra S, Fornai F, Kwon H-B, Yazdani U, Atasoy D, Liu X, Hammer RE, Battaglia G, German DC, Castillo PE, Südhof TC (2004) Double-knockout mice for α- and β-synucleins: effect on synaptic functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:14966–14971
Cleeter MW, Chau K-Y, Gluck C, Mehta A, Hughes DA, Duchen M, Wood NW, Hardy J, Cooper JM, Schapira AH (2013) Glucocerebrosidase inhibition causes mitochondrial dysfunction and free radical damage. Neurochem Int 62:1–7
Coronel-Oliveros CM, Pacheco-Calderón R (2018) Prenatal exposure to ketamine in rats: implications on animal models of schizophrenia. Dev Psychobiol 60:30–42
Coulombe K, Saint-Pierre M, Cisbani G, St-Amour I, Gibrat C, Giguère-Rancourt A, Calon F, Cicchetti F (2016) Partial neurorescue effects of DHA following a 6-OHDA lesion of the mouse dopaminergic system. J Nutr Biochem 30:133–142
Counihan TJ, Penney JB (1998) Regional dopamine transporter gene expression in the substantia nigra from control and Parkinson’s disease brains. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 65:164–169
Dauer W, Przedborski S (2003) Parkinson's disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 39:889–909
Dehay B, Martinez-Vicente M, Caldwell GA, Caldwell KA, Yue Z, Cookson MR, Klein C, Vila M, Bezard E (2013) Lysosomal impairment in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 28:725–732
Di Maio R, Barrett PJ, Hoffman EK, Barrett CW, Zharikov A, Borah A, Hu X, McCoy J, Chu CT, Burton EA (2016) α-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson’s disease. Sci Transl Med 8:342ra378
Domesick VB, Stinus L, Paskevich PA (1983) The cytology of dopaminergic and nondopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area of the rat: a light- and electron-microscopic study. Neuroscience 8:743–765
Dum RP, Strick PL (2002) Motor areas in the frontal lobe of the primate. Physiol Behav 77:677–682
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Emson PC, Koob GF (1978) The origin and distribution of dopamine-containing afferents to the rat frontal cortex. Brain Res 142:249–267
Erickson AH, Ginns E, Barranger J (1985) Biosynthesis of the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase. J Biol Chem 260:14319–14324
Fernandez A, De La Vega AG, Torres-Aleman I (1998) Insulin-like growth factor I restores motor coordination in a rat model of cerebellar ataxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:1253–1258
Fortin DL, Nemani VM, Voglmaier SM, Anthony MD, Ryan TA, Edwards RH (2005) Neural activity controls the synaptic accumulation of α-synuclein. J Neurosci 25:10913–10921
Francardo V, Schmitz Y, Sulzer D, Cenci MA (2017) Neuroprotection and neurorestoration as experimental therapeutics for Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol 298(Pt B):137–147
Gainetdinov RR, Jones SR, Fumagalli F, Wightman RM, Caron MG (1998) Re-evaluation of the role of the dopamine transporter in dopamine system homeostasis1. Brain Res Rev 26:148–153
Geed M, Garabadu D, Ahmad A, Krishnamurthy S (2014) Silibinin pretreatment attenuates biochemical and behavioral changes induced by intrastriatal MPP+ injection in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 117:92–103
Gegg ME, Burke D, Heales SJ, Cooper JM, Hardy J, Wood NW, Schapira AH (2012) Glucocerebrosidase deficiency in substantia nigra of parkinson disease brains. Ann Neurol 72:455–463
Greenamyre JT, Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Panov AV (2001) Complex I and Parkinson's disease. IUBMB Life 52:135–141
Gu X-S, Wang F, Zhang C-Y, Mao C-J, Yang J, Yang Y-P, Liu S, Hu L-F, Liu C-F (2016) Neuroprotective effects of paeoniflorin on 6-OHDA-lesioned rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 41:2923–2936
Haavik J, Toska K (1998) Tyrosine hydroxylase and Parkinson's disease. Mol Neurobiol 16:285–309
Hambright WS, Fonseca RS, Chen L, Na R, Ran Q (2017) Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol 12:8–17
Hamel SC, Pelphrey A (2009) Chapter 4 - PRESCHOOL YEARS. In: Carey WB, Crocker AC, Coleman WL, Elias ER, Feldman HM (eds) Developmental-behavioral pediatrics, 4th edn. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 39–49
Ismail S, Mohamad M, Syazarina S, Nafisah W (2014) Hand grips strength effect on motor function in human brain using fMRI: a pilot study. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, Bristol, p 012005
Jones SR, Gainetdinov RR, Jaber M, Giros B, Wightman RM, Caron MG (1998) Profound neuronal plasticity in response to inactivation of the dopamine transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:4029–4034
Joshua M, Adler A, Bergman H (2009) The dynamics of dopamine in control of motor behavior. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19:615–620
Kakkar AK, Singh H, Medhi B (2018) Old wines in new bottles: repurposing opportunities for Parkinson's disease. Eur J Pharmacol 830:115–127
Kheradmand A, Nayebi AM, Jorjani M, Haddadi R (2016) Effect of WR-1065 on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced catalepsy and IL-6 level in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 19:490–496
Kumar A, Sharma N, Gupta A, Kalonia H, Mishra J (2012) Neuroprotective potential of atorvastatin and simvastatin (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induced Parkinson-like symptoms. Brain Res 1471:13–22
Lamprea M, Cardenas F, Silveira R, Walsh T, Morato S (2003) Effects of septal cholinergic lesion on rat exploratory behavior in an open-field. Braz J Med Biol Res 36:233–238
Lang AE, Espay AJ (2018) Disease modification in Parkinson's disease: current approaches, challenges, and future considerations. Mov Disord 33:660–677
Lesage S, Brice A (2009) Parkinson's disease: from monogenic forms to genetic susceptibility factors. Hum Mol Genet 18:R48–R59
Li L-y, Zhao X-l, Fei X-f, Gu Z-l, Qin Z-h, Liang Z-q (2008) Bilobalide inhibits 6-OHDA-induced activation of NF-κB and loss of dopaminergic neurons in rat substantia nigra. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:539–547
Li X, Dong C, Hoffmann M, Garen CR, Cortez LM, Petersen NO, Woodside MT (2019) Early stages of aggregation of engineered α-synuclein monomers and oligomers in solution. Sci Rep 9:1734
Lindholm P, Voutilainen MH, Laurén J, Peränen J, Leppänen V-M, Andressoo J-O, Lindahl M, Janhunen S, Kalkkinen N, Timmusk T (2007) Novel neurotrophic factor CDNF protects and rescues midbrain dopamine neurons in vivo. Nature 448:73
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Maegawa GH, Tropak MB, Buttner JD, Rigat BA, Fuller M, Pandit D, Tang L, Kornhaber GJ, Hamuro Y, Clarke JT (2009) Identification and characterization of ambroxol as an enzyme enhancement agent for Gaucher disease. J Biol Chem 284:23502–23516
Malerba M, Ragnoli B (2008) Ambroxol in the 21st century: pharmacological and clinical update. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4:1119–1129
Maor G, Cabasso O, Krivoruk O, Rodriguez J, Steller H, Segal D, Horowitz M (2016) The contribution of mutant GBA to the development of Parkinson disease in Drosophila. Hum Mol Genet 25:2712–2727
Mazzulli JR, Xu Y-H, Sun Y, Knight AL, McLean PJ, Caldwell GA, Sidransky E, Grabowski GA, Krainc D (2011) Gaucher disease glucocerebrosidase and α-synuclein form a bidirectional pathogenic loop in synucleinopathies. Cell 146:37–52
McMahon B, Aflaki E, Sidransky E (2016) Chaperoning glucocerebrosidase: a therapeutic strategy for both Gaucher disease and Parkinsonism. Neural Regen Res 11:1760–1761
Meyer OA, Tilson H, Byrd W, Riley M (1979) A method for the routine assessment of fore-and hindlimb grip strength of rats and mice. Neurobehav Toxicol 1:233–236
Migdalska-Richards A, Daly L, Bezard E, Schapira AH (2016) Ambroxol effects in glucocerebrosidase and α-synuclein transgenic mice. Ann Neurol 80:766–775
Mishra A, Krishnamurthy S (2019) Rebamipide mitigates impairments in mitochondrial function and bioenergetics with α-synuclein pathology in 6-OHDA-induced Hemiparkinson’s model in rats. Neurotox Res 35:542–562
Mishra A, Chandravanshi LP, Trigun SK, Krishnamurthy S (2018) Ambroxol modulates 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced temporal reduction in glucocerebrosidase (GCase) enzymatic activity and Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Biochem Pharmacol 155:479–493
Moore DJ, West AB, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2005) Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:57–87
Müller T (2012) Drug therapy in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Transl Neurodegener 1:10
Nutt JG, Carter JH, Sexton GJ (2004) The dopamine transporter: importance in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 55:766–773
Osellame LD, Rahim AA, Hargreaves IP, Gegg ME, Richard-Londt A, Brandner S, Waddington SN, Schapira AH, Duchen MR (2013) Mitochondria and quality control defects in a mouse model of Gaucher disease—links to Parkinson’s disease. Cell Metab 17:941–953
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Perez-Pardo P, de Jong EM, Broersen LM, van Wijk N, Attali A, Garssen J, Kraneveld AD (2017) Promising effects of neurorestorative diets on motor, cognitive, and gastrointestinal dysfunction after symptom development in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Front Aging Neurosci 9:57
Pires AO, Teixeira FG, Mendes-Pinheiro B, Serra SC, Sousa N, Salgado AJ (2017) Old and new challenges in Parkinson's disease therapeutics. Prog Neurobiol 156:69–89
Pradhan SD, Brewer BR, Carvell GE, Sparto PJ, Delitto A, Matsuoka Y (2010) Assessment of fine motor control in individuals with Parkinson's disease using force tracking with a secondary cognitive task. J Neurol Phys Ther 34:32–40
Pringsheim T, Jette N, Frolkis A, Steeves TD (2014) The prevalence of Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov Disord 29:1583–1590
Qian Y, Lei G, Castellanos FX, Forssberg H, Heijtz RD (2010) Deficits in fine motor skills in a genetic animal model of ADHD. Behav Brain Funct 6:51–51
Reidling JC, Relaño-Ginés A, Holley SM, Ochaba J, Moore C, Fury B, Lau A, Tran AH, Yeung S, Salamati D (2018) Human neural stem cell transplantation rescues functional deficits in R6/2 and Q140 Huntington's disease mice. Stem Cell Reports 10:58–72
Robinson TE, Whishaw IQ (1988) Normalization of extracellular dopamine in striatum following recovery from a partial unilateral 6-OHDA lesion of the substantia nigra: a microdialysis study in freely moving rats. Brain Res 450:209–224
Rocha EM, Smith GA, Park E, Cao H, Brown E, Hallett P, Isacson O (2015a) Progressive decline of glucocerebrosidase in aging and Parkinson's disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2:433–438
Rocha EM, Smith GA, Park E, Cao H, Graham A-R, Brown E, McLean JR, Hayes MA, Beagan J, Izen SC (2015b) Sustained systemic glucocerebrosidase inhibition induces brain α-synuclein aggregation, microglia and complement C1q activation in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 23:550–564
Rozas G, Guerra M, Labandeira-Garcıa J (1997) An automated rotarod method for quantitative drug-free evaluation of overall motor deficits in rat models of parkinsonism. Brain Res Protocol 2:75–84
Sanberg PR, Bunsey MD, Giordano M, Norman AB (1988) The catalepsy test: its ups and downs. Behav Neurosci 102:748–759
Sauer H, Oertel W (1994) Progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons following intrastriatal terminal lesions with 6-hydroxydopamine: a combined retrograde tracing and immunocytochemical study in the rat. Neuroscience 59:401–415
Schapira AHV (2015) Glucocerebrosidase and Parkinson disease: recent advances. Mol Cell Neurosci 66:37–42
Schapira A, Cooper J, Dexter D, Clark J, Jenner P, Marsden C (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 54:823–827
Sedaghat R, Roghani M, Khalili M (2014) Neuroprotective effect of thymoquinone, the nigella sativa bioactive compound, in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced hemi-parkinsonian rat model. Iran J Pharm Res: IJPR 13:227–234
Seibenhener ML, Wooten MC (2015) Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE, Cambridge, pp e52434–e52434
Shapiro BL, Feigal RJ, Lam L (1979) Mitrochondrial NADH dehydrogenase in cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:2979–2983
Shimada S, Kitayama S, Walther D, Uhl G (1992) Dopamine transporter mRNA: dense expression in ventral midbrain neurons. Mol Brain Res 13:359–362
Silveira C, MacKinley J, Coleman K, Li Z, Finger E, Bartha R, Morrow S, Wells J, Borrie M, Tirona R (2019) Ambroxol as a novel disease-modifying treatment for Parkinson’s disease dementia: protocol for a single-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. BMC Neurol 19:20
Son G, Han J (2018) Roles of mitochondria in neuronal development. BMB Rep 51:549
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M (1998) α-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:6469–6473
Stern Y, Mayeux R, Rosen J, Ilson J (1983) Perceptual motor dysfunction in Parkinson's disease: a deficit in sequential and predictive voluntary movement. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:145–151
Stojkovska I, Krainc D, Mazzulli JR (2018) Molecular mechanisms of α-synuclein and GBA1 in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Tissue Res 373:51–60
Takeshita H, Yamamoto K, Nozato S, Inagaki T, Tsuchimochi H, Shirai M, Yamamoto R, Imaizumi Y, Hongyo K, Yokoyama S (2017) Modified forelimb grip strength test detects aging-associated physiological decline in skeletal muscle function in male mice. Sci Rep 7:42323
Ungerstedt U (1971) Postsynaptic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta Physiol 82:69–93
Van Den Buuse M, Veldhuis HD, De Boer S, Versteeg DH, De Jong W (1986) Central 6-OHDA affects both open-field exploratory behaviour and the development of hypertension in SHR. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:15–21
Voutilainen MH, De Lorenzo F, Stepanova P, Bäck S, Yu L-Y, Lindholm P, Pörsti E, Saarma M, Männistö PT, Tuominen RK (2017) Evidence for an additive neurorestorative effect of simultaneously administered CDNF and GDNF in hemiparkinsonian rats: implications for different mechanism of action. eNeuro 4(ENEURO):0117–0116 2017
Walther S, Strik W (2012) Motor symptoms and schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 66:77–92
Whishaw IQ, Tomie J-A, Ladowsky RL (1990) Red nucleus lesions do not affect limb preference or use, but exacerbate the effects of motor cortex lesions on grasping in the rat. Behav Brain Res 40:131–144
Yap TL, Gruschus JM, Velayati A, Westbroek W, Goldin E, Moaven N, Sidransky E, Lee JC (2011) α-Synuclein interacts with glucocerebrosidase providing a molecular link between Parkinson and Gaucher diseases. J Biol Chem 286:28080–28088
Yuan H, Sarre S, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (2004) Neuroprotective and neurotrophic effect of apomorphine in the striatal 6-OHDA-lesion rat model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res 1026:95–107
Zaitone SA, Abo-Elmatty DM, Shaalan AA (2012) Acetyl-L-carnitine and α-lipoic acid affect rotenone-induced damage in nigral dopaminergic neurons of rat brain, implication for Parkinson's disease therapy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100:347–360
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Merril Pharma Pvt. Ltd., Roorkee for providing ambroxol hydrochloride (active pharmaceutical ingredient) as a gift sample. This work was supported by the teaching assistantship to Akanksha Mishra from Indian Institute of Technology (Banaras Hindu University), Varanasi-221005, U.P., India.
Funding
The research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The conception and design of study was done by AM and SK. AM acquired the data, which was analyzed and interpreted by AM and SK. AM and SK drafted the article and revised it for important intellectual content. SK approved the final version to be submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All the experimental protocols were approved by institutional animal ethical committee, Banaras Hindu University (Dean/2016/CAEC/33).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the experiments were performed in line with the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of Laboratory animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978). All the experimental protocols were approved by Institutional animal ethical committee, Banaras Hindu University (Dean/2016/CAEC/33). This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, A., Krishnamurthy, S. Neurorestorative effects of sub-chronic administration of ambroxol in rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 429–444 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01737-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01737-9