Abstract
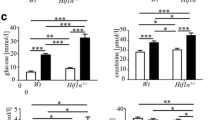
Early renal morphological alterations including glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial expansion occur in diabetic kidney disease and correlate with various clinical manifestations of diabetes. The present study was designed to investigate the influence of pharmacological modulation of HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha) protein levels, on these glomerular changes in rodent model of type 1 diabetes. Male wistar rats were made diabetic (Streptozotocin 45 mg/kg; i.p.) and afterwards treated with HIF activator cobalt chloride for 4 weeks. Renal function was assessed by serum creatinine, albumin, proteinuria levels, oxidative stress: reduced glutathione levels and catalase activity, and renal tissue HIF-1α protein levels were determined by ELISA assay. Histological analysis of kidney sections was done by haematoxylin and eosin (glomeruli diameter), periodic acid Schiff (mesangial expansion and glomerulosclerosis) and sirius red (fibrosis, tubular dilation) staining. Diabetes rats displayed reduced serum albumin levels, marked proteinuria, lower kidney reduced glutathione content, glomerular hypertrophy, glomerulosclerosis, mesangial expansion, tubular dilation and renal fibrosis. Cobalt chloride treatment normalised renal HIF-1α protein levels, reduced development of proteinuria and tubulo-interstitial fibrosis, but the glomerular morphological alterations such as glomerulosclerosis, mesangial expansion, increased glomerular diameter and tubular vacoulations were not abrogated in diabetic kidneys. Glomerular morphological abnormalities might precede the development of proteinuria and renal fibrosis in experimental model of type 1 diabetes. Pharmacological modulation of renal HIF-1α protein levels does not influence glomerular and tubular dilatory changes in diabetic kidney disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsaad KO, Herzenberg AM (2007) Distinguishing diabetic nephropathy from other causes of glomerulosclerosis: an update. J Clin Pathol 60:18–26
Anderson S, Meyer TW, Rennke HG Brenner BM (1985) Control of glomerular hypertension limits glomerular injury in rats with reduced renal mass. J Clin Invest 76:612–619
Anderson S, Rennke HG, Brenner BM (1986) Therapeutic advantage of converting enzyme inhibitors in arresting progressive renal disease associated with systemic hypertension in the rat. J Clin Invest 77:1993–2000
Barrera-Chimal J, Pérez-Villalva R, Rodríguez-Romo R, Reyna J, Uribe N, Gamba G, Bobadilla NA (2013) Spironolactone prevents chronic kidney disease caused by ischemic acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 83(1):93–103
Bell ET (1953) Renal vascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2:376–389
Bohle A, Mackensen-Haen S, Wehrmann M (1996) Significance of postglomerular capillaries in the pathogenesis of chronic renal failure. Kidney Blood Press Res 19:191–195
Boyne AF, Ellman GL (1972) A methodology for analysis of tissue sulfhydryl components. Anal Biochem 46(2):639–653
Brenner BM, Meyer TW, Hostetter TH (1982) Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med 307:652–659
Brito P, Fioretto P, Drummund K, Kim Y, Steffes MW, Basgen JM, Sisson-Ross S, Mauer M (1998) Proximal tubular basement membrane width in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 53:754–761
Caramori ML, Kim Y, Huang C, Fish AJ, Rich SS, Miller ME, Russell G, Mauer M (2002) Cellular basis of diabetic nephropathy: 1. Study design and renal structural–functional relationships in patients with long-standing type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 51:506–513
Chance B, Sies H, Boveris A (1979) Hydroperoxide metabolism in mammalian organs. Physiol Rev 59(3):527–605
Cheng HF, Wang CJ, Moeckel GW, Zhang MZ, Mckanna JA, Harris RC (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor blocks expression of mediators of renal injury in a model of diabetes and hypertension1. Kidney Int 62(3):929–939
Cummins EP, Taylor CT (2005) Hypoxia-responsive transcription factors. Pflugers Arch 450:363–371
De Vriese AS, Tilton RG, Elger M, Stephan CC, Kriz W, Lameire NH (2001) Antibodies against vascular endothelial growth factor improve early renal dysfunction in experimental diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:993–1000
Deckert T, Kofoed-Enevoldsen A, Vidal P, Nørgaard K, Andreasen HB, Feldt-Rasmussen B (1993) Size-and charge selectivity of glomerular filtration in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with and without albuminuria. Diabetologia 36:244–251
Drummond K, Mauer M (2002) The early natural history of nephropathy in type 1 diabetes: II. Early renal structural changes in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 51:1580–1587
Falk RJ, JL S, Mauer SM, Michael AF (1983) Polyantigenic expansion of basement membrane constituents in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 32:34
Fine L, Orphanides C, Norman JT (1998) Progressive renal disease: the chronic hypoxia hypothesis. Kidney Int 53:S74–S78
Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Mauer M (1994) Glomerular structure in nonproteinuric IDDM patients with various levels of albuminuria. Diabetes 43:1358–1364
Friederich-Persson M, Thörn E, Hansell P, Nangaku M, Levin M, Palm F (2013) Kidney hypoxia, attributable to increased oxygen consumption, induces nephropathy independently of hyperglycemia and oxidative stress. Hypertension 62:914–919
Gilbert RE, Cooper ME (1999) The tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: more than an aftermath of glomerular injury? Kidney Int 56:1627–1637
Gwinner W, Deters-Evers U, Brandes RP, Kubat B, Koch KM, Pape M, Olbricht CJ (1998) Antioxidant-oxidant balance in the glomerulus and proximal tubule of the rat kidney. J Physiol 509(2):599–606
Harris RD, Steffes MW, Bilous RW, Sutherland DE, Mauer SM (1991) Global glomerular sclerosis and glomerular arteriolar hyalinosis in insulin-dependent diabetes. Kidney Int 40:107–114
Hostetter TH, Olson JL, Rennke HG Venkatachalam MA, Brenner BM (1981) Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Phys 241:F85–F93
Hwang I, Lee J, Huh JY, Park J, Lee HB, Ho YS, Ha H (2012) Catalase deficiency accelerates diabetic renal injury through peroxisomal dysfunction. Diabetes 61(3):728–738
Kang DH, Kanellis J, Hugo C, Truong L, Anderson S, Kerjaschki D, Schreiner GF, Johnson RJ (2002) Role of microvascular endothelium in progressive renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:806–816
Kim Y, Kleppel MM, Butkowski R, Mauer SM, Wieslander J, Michael AF (1991) Differential expression of basement membrane collagen chains in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Pathol 138:413
Lane PH, Steffes MW, Mauer SM (1992) Glomerular structure in IDDM women with low glomerular filtration rate and normal urinary albumin excretion. Diabetes 41:581–586
Lane PH, Steffes MW, Fioretto P, Mauer SM (1993) Renal interstitial expansion in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 43:661–667
Lassila M, Fukami K, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Semple T, Carmeliet P, Cooper ME, Kitching AR (2007) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 production is pathogenetic in experimental murine diabetic renal disease. Diabetologia 50(6):1315–1326
Lemley KV, Blouch K, Abdullah I, Boothroyd DB, Bennett PH, Myers BD, Nelson RG (2000) Glomerular permselectivity at the onset of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:2095–2105
Liu Y (2004) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal fibrogenesis: pathologic significance, molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1–12
Mauer SM, Steffes MW, Ellis EN, Sutherland DE, Brown DM, Goetz FC (1984) Structural functional relationships in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest 74:1143–1155
Mauer M, Fioretto P, Woredekal Y (2001) Friedman E 2001 diabetic nephropathy. In: Schrier RW (ed) Disease of the kidney and urinary tract. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 2083–2127
Michiels C (2004) Physiological and pathological responses to hypoxia. Am J Pathol 164(6):1875–1882
Mole DR, Ratcliffe PJ (2008) Cellular oxygen sensing in health and disease. Pediatr Nephrol 23:681–694
Nordquist L, Friederich-Persson M, Fasching A, Liss P, Shoji K, Nangaku M, Hansell P, Palm F (2015) Activation of hypoxia-inducible factors prevents diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:328–338
Ohtomo S, Nangaku M, Izuhara Y, Takizawa S, Strihou C, Miyata T (2008) Cobalt ameliorates renal injury in an obese, hypertensive type 2 diabetes rat model. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1166–1172
Osterby R (1992) Glomerular structural changes in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: causes, consequences, and prevention. Diabetologia 35:803–812
Østerby R, Andersen AR, Gundersen HJ (1984) Quantitative studies of glomerular ultrastructure in type 1 diabetics with incipient nephropathy. Diab Nephropath 3:95
Palm F, Cederberg J, Hansell P, Liss P, Carlsson PO (2003) Reactive oxygen species cause diabetes-induced decrease in renal oxygen tension. Diabetologia 46(8):1153–1160
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123(11):1939–1951
Risdon RA, Sloper JC, De Wardener HE (1968) Relationship between renal function and histological changes found in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Lancet 2:363–366
Rodríguez-Iturbe B, Johnson RR, Herrera-Acosta J (2005) Tubulointerstitial damage and progression of renal failure. Kidney Int 68:S82–S86
Rodríguez-Romo R, Benítez K, Barrera-Chimal J, Pérez-Villalva R, Gómez A, Aguilar-León D, Rangel- Santiago JF, Huerta S, Gamba G, Uribe N, Bobadilla NA (2016) AT1 receptor antagonism before ischemia prevents the transition of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 89(2):363–373
Rosenberger C, Khamaisi M, Abassi Z, Shilo V, Weksler-Zangen S, Goldfarb M, Shina A, Zibertrest F, Eckardt KU, Rosen S, Heyman SN (2008) Adaptation to hypoxia in the diabetic rat kidney. Kidney Int 73:34–42
Saker F, Ybarra J, Leahy P, Hanson RW, Kalhan SC, Ismail-Beigi F (1998) Glycemia-lowering effect of cobalt chloride in the diabetic rat: role of decreased gluconeogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 274(6):E984–E991
Scandling JD, Myers BD (1992) Glomerular size-selectivity and microalbuminuria in early diabetic glomerular disease. Kidney Int 41:840–846
Schacterle GR, Pollack RL (1973) A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem 51(2):654–655
Smithies O (2003) Why the kidney glomerulus does not clog: a gel permeation/diffusion hypothesis of renal function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4108–4113
Tanaka T, Matsumoto M, Inagi R, Miyata T, Kojima I, Ohse T, Fujita T, Nangaku M (2005) Induction of protective genes by cobalt ameliorates tubulointerstitial injury in the progressive Thy1 nephritis. Kidney Int 68(6):2714–2725
Warnecke C, Griethe W, Weidemann A, Jurgensen JS, Willam C, Bachmann S, Ivashchenko Y, Wagner I, Frei U, Wiesener M, Eckardt KU (2003) Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway and stimulation of angiogenesis by application of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. FASEB J 17:1186–1188
Wiesener MS, Jurgensen JS, Rosenberger C, Scholze CK, Horstrup JH, Warnecke C, Mandriota S, Bechmann I, Frei UA, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Bachmann S, Maxwell PH, Eckardt KU (2003) Widespread hypoxia-inducible expression of HIF-2 alpha in distinct cell populations of different organs. FASEB J 17:271–273
Zerbini G, Bonfanti R, Meschi F, Bognetti E, Paesano PL, Gianolli L, Querques M, Maestroni A, G C, Del Maschio A, Fazio F (2006) Persistent renal hypertrophy and faster decline of glomerular filtration rate precede the development of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 55(9):2620–2625
Zheng M, Ye S, Zhai Z, Chen Y, Li X, Yang G, Fan A, Wang Y (2009) Rosiglitazone protects diabetic rats against kidney disease through the suppression of renal monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression. J Diabetes Complicat 23:124–129
Acknowledgements
Gaaminepreet Singh received Basic Science Research fellowship from University Grant Commission, New Delhi, India during Ph.D study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GS designed research and conducted experiments. PK helped in analysing data and manuscript drafting. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experimental procedures on rats were approved by institutional animal ethics committee of Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research, Punjabi University, Patiala (Punjab), India.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of institutional animal ethics committee of Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research, Punjabi University, Patiala (Punjab), India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G., Krishan, P. Cobalt treatment does not prevent glomerular morphological alterations in type 1 diabetic rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 391, 933–944 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1511-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1511-7