Abstract
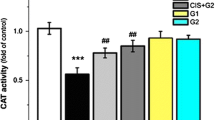
The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) use on cisplatin (CP)-induced nephrotoxicty. Twenty-eight rats were randomly divided into four groups. The rats in the control group were injected a single dose of 1 ml/kg saline intra-peritoneally (IP) during 10 days. The rats in the ATRA group were injected a single dose of ATRA during 10 days. The rats in the ATRA+CP group were injected a single dose of CP on the fourth day of the 10 days of ATRA treatment. The rats in the CP group were injected a single dose of CP on the fourth day of 10 days without administering a treatment. After treatment, the groups were compared with regard to total antioxidant status (TAS), total oxidant status (TOS), and oxidative stress index (OSI) levels in renal tissue and renal histopathology. The serum creatinine and urea values were statistically significantly higher in the CP group compared to the other groups. The serum creatinine and urea values were statistically significantly lower in the ATRA+CP group when compared to the CP group. Although the TOS and OSI levels were found to be lower in the ATRA+CP group compared to the CP group, the difference was not statistically significant. Administration of ATRA together with CP was observed to reduce the histopathologic destruction in the kidney and lead to mild tubular degeneration, vacuolization, and necrosis (57.1% grade 1; 28.6% grade2, and 14.3% grade 3 necrosis). The results of the present study have revealed that ATRA administration ameliorates CP-induced nephrotoxicity; however, further studies are required to identify this issue before clinical application.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aburto A, Barria A, Cardenas A, Carpio D, Figueroa CD, Burgos ME, Ardiles L (2014) Pre-stimulation of the kallikrein system in cisplatin-induced acute renal injury: an approach to renoprotection. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280(2):216–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.07.023
Alibakhshi T, Khodayar MJ, Khorsandi L, Rashno M, Zeidooni L (2018) Protective effects of zingerone on oxidative stress and inflammation in cisplatin-induced rat nephrotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother 105:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.085
Arany I, Safirstein RL (2003) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol 23(5):460–464
Bouhadjari N, Gabato W, Calabrese D, Msika S, Keita H (2016) Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy with cisplatin: amifostine prevents acute severe renal impairment. Eur J Surg Oncol 42(2):219–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2015.07.016
Cekmen M, Ilbey YO, Ozbek E, Simsek A, Somay A, Ersoz C (2009) Curcumin prevents oxidative renal damage induced by acetaminophen in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 47(7):1480–1484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.03.034
Crona DJ, Faso A, Nishijima TF, McGraw KA, Galsky MD, Milowsky MI (2017) A systematic review of strategies to prevent cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Oncologist 22(5):609–619. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0319
Elsayed AM, Abdelghany TM, Akool el S, Abdel-Aziz AA, Abdel-Bakky MS (2016) All-trans retinoic acid potentiates cisplatin-induced kidney injury in rats: impact of retinoic acid signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 389(3):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1193-3
Erel O (2004) A novel automated method to measure total antioxidant response against potent free radical reactions. Clin Biochem 37(2):112–119
Erel O (2005) A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem 38(12):1103–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2005.08.008
Ewees MG, Abdelghany TM, Abdel-Aziz AA, Abdel-Bakky MS (2015) All-trans retinoic acid mitigates methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats; relevance of retinoic acid signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388(9):931–938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1130-5
Ezaki T, Nishiumi S, Azuma T, Yoshida M (2017) Metabolomics for the early detection of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Res (Camb) 6(6):843–853. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tx00171a
Gomez-Sierra T, Eugenio-Perez D, Sanchez-Chinchillas A, Pedraza-Chaverri J (2018) Role of food-derived antioxidants against cisplatin induced-nephrotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 120:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.07.018
Gudas LJ (2012) Emerging roles for retinoids in regeneration and differentiation in normal and disease states. Biochim Biophys Acta 1821(1):213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.08.002
Han SY, So GA, Jee YH, Han KH, Kang YS, Kim HK, Kang SW, Han DS, Han JY, Cha DR (2004) Effect of retinoic acid in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Immunol Cell Biol 82(6):568–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1711.2004.01287.x
Ilbey YO, Ozbek E, Cekmen M, Somay A, Ozcan L, Otunctemur A, Simsek A, Mete F (2009) Melatonin prevents acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int Urol Nephrol 41(3):695–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9503-z
Jung K, An JM, Eom DW, Kang KS, Kim SN (2017) Preventive effect of fermented black ginseng against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J Ginseng Res 41(2):188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2016.03.001
Kavukcu S, Turkmen MA, Soylu A (2001) Could the effective mechanisms of retinoids on nephrogenesis be also operative on the amelioration of injury in acquired renal lesions? Pediatr Nephrol 16(8):689–690
Kim CS, Park JS, Ahn CW, Kim KR (2015) All-trans retinoic acid has a potential therapeutic role for diabetic nephropathy. Yonsei Med J 56(6):1597–1603. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1597
Lelievre-Pegorier M, Vilar J, Ferrier ML, Moreau E, Freund N, Gilbert T, Merlet-Benichou C (1998) Mild vitamin A deficiency leads to inborn nephron deficit in the rat. Kidney Int 54(5):1455–1462. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00151.x
Moreb JS, Ucar-Bilyeu DA, Khan A (2017) Use of retinoic acid/aldehyde dehydrogenase pathway as potential targeted therapy against cancer stem cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 79(2):295–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3213-5
Moulder JE, Fish BL, Regner KR, Cohen EP, Raife TJ (2002) Retinoic acid exacerbates experimental radiation nephropathy. Radiat Res 157(2):199–203
Nematbakhsh M, Ashrafi F, Pezeshki Z, Fatahi Z, Kianpoor F, Sanei MH, Talebi A (2012) A histopathological study of nephrotoxicity, hepatoxicity or testicular toxicity: which one is the first observation as side effect of Cisplatin-induced toxicity in animal model? J Nephropathol 1(3):190–193. https://doi.org/10.5812/nephropathol.8122
Oseto S, Moriyama T, Kawada N, Nagatoya K, Takeji M, Ando A, Yamamoto T, Imai E, Hori M (2003) Therapeutic effect of all-trans retinoic acid on rats with anti-GBM antibody glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 64(4):1241–1252. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00219.x
Ozbek E, Ilbey YO, Simsek A, Cekmen M, Mete F, Somay A (2010) Rosiglitazone, peroxisome proliferator receptor-gamma agonist, ameliorates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int Urol Nephrol 42(3):579–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-009-9645-7
Penniston KL, Tanumihardjo SA (2006) The acute and chronic toxic effects of vitamin A. Am J Clin Nutr 83(2):191–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/83.2.191
Saifi MA, Sangomla S, Khurana A, Godugu C (2018) Protective effect of nanoceria on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by amelioration of oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory mechanisms. Biol Trace Elem Res 1:1–12
Tang XH, Gudas LJ (2011) Retinoids, retinoic acid receptors, and cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 6:345–364. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130303
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank to Pelin Teke Kisa, Serdar Bayrak, and Ozgur Cakmak for their contribution to the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CY and EEY conceived and designed research. CY, FDA, and SE conducted experiments. EK, VU, and MU contributed new reagents or analytical tools. CY and OC analyzed data. YOI, BB, and ZK made supervision. CY wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
All procedures were performed in accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Research Council after approval had been obtained from the Dokuz Eylül University local ethical committee of animal experiments.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yucel, C., Erdogan Yucel, E., Arslan, F.D. et al. All-trans retinoic acid prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 392, 159–164 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-01603-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-01603-0