Abstract
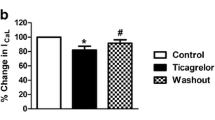
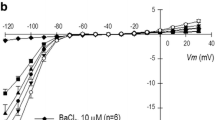
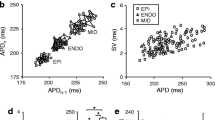
We examined the inhibitory effect of amiodarone, a class III anti-arrhythmic agent, on voltage-dependent K+ (Kv) currents in freshly isolated rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells, using a whole-cell patch clamp technique. Amiodarone inhibited Kv currents in a concentration-dependent manner, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 3.9 ± 1.44 μM and a Hill coefficient of 0.45 ± 0.14. Amiodarone did not have a significant effect on the steady-state activation of Kv channels, but shifted the inactivation current toward a more negative potential. Application of consecutive pulses progressively augmented the amiodarone-induced Kv channel inhibition. Another class III anti-arrhythmic agent, dofetilide, did not inhibit the Kv current or change the inhibitory effect of amiodarone on Kv channels. Therefore, these results strongly suggest that amiodarone inhibits Kv currents in a concentration- and state-dependent manner.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archer SL, London B, Hampl V, et al. (2001) Impairment of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in mice lacking the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.5. FASEB J 15:1801–1803
Carlsson B, Singh BN, Temciuc M, et al. (2002) Synthesis and preliminary characterization of a novel antiarrhythmic compound (KB130015) with an improved toxicity profile compared with amiodarone. J Med Chem 45:623–630
Clapp LH, Gurney AM (1992) ATP-sensitive K+ channels regulate resting potential of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Phys 262:916–920
Cox RH, Folander K, Swanson R (2001) Differential expression of voltage-gated K+ channel genes in arteries from spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats. Hypertension 37:1315–1322
Förstermann U, Pollock JS, Schmidt HH, et al. (1991) Calmodulin-dependent endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase activity is present in the particulate and cytosolic fractions of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:1788–1792
Gessner G, Heller R, Hoshi T, et al. (2007) The amiodarone derivative 2-methyl-3-(3,5-diiodo-4-carboxymethoxybenzyl) benzofuran (KB130015) opens large- conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels and relaxes vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 555:185–193
Grossman M, Dobrev D, Kirch W (1998) Amiodarone causes endothelium-dependent vasodilation in human hand vein in vivo. Clin Pharmacol Ther 64:302–311
Hara Y, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H (1980) Actions of 4-aminopyridine on vascular smooth muscle tissues of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol 68:99–106
Heijman J, Dobrev D (2013) Pleiotropic actions of amiodarone: still puzzling after half a century. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 386:571–574
Holmes DS, Sun ZQ, Porter LM, et al. (2000) Amiodarone inhibits cardiac ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 11:1152–1158
Hondeghem LM, Snyders DJ (1990) Class III antiarrhythmic agents have a lot of potential but a long way to go. Reduced effectiveness and dangers of reverse use dependence. Circulation 81:686–690
Hong DH, Yang D, Choi IW, et al. (2012) The T-type Ca2+ channel inhibitor mibefradil inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Sci 120:196–205
Hong DH, Choi IW, Son YK, et al. (2013) The effect of P13 kinase inhibitor LY294002 on voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 92:916–922
Hong DH, Son YK, Li H, et al. (2014) The calmodulin inhibitor and antipsychotic drug trifluoperazine inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443:321–425
Kauthale RR, Dadarkar SS, Husain R, et al. (2015) Assessment of temperature-induced hERG channel blockade variation by drugs. J Appl Toxicol 35:799–805
Kiehn J, Thomas D, Karle CA, et al. (1999) Inhibitory effects of the class III antiarrhythmic drug amiodarone on cloned HERG potassium channels. Naunyn Schmiedeber’s Arch Pharmacol 359:212–219
Ko EA, Han J, Jung ID, et al. (2008) Physiological roles of K+ channels in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Smooth Muscle Res 44:65–81
Ko EA, Park WS, Son YK, et al. (2009) The effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein on voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Vasc Pharmacol 50:51–56
Ko EA, Park WS, Son YK, et al. (2010) Calcium channel inhibitor, verapamil, inhibits the voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary smooth muscle cells. Biol Pharm Bull 33:47–52
Kobayashi S, Reien Y, Ogura T, et al. (2001) Inhibitory effect of bepridil on hKv1.5 channel current: comparison with amiodarone and E-4031. Eur J Pharmacol 430:149–157
Kodama I, Kamiya K, Toyama J (1999) Amiodarone: ionic and cellular mechanisms of action of the most promising class III agent. Am J Cardiol 84:20–28
Li H, Choi IW, Hong DH, et al. (2015a) W-7 inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels independent of calmodulin activity in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol 750:14–19
Li H, Hong DH, Kim HS, et al. (2015b) The calmodulin inhibitor CGS 9343B inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 285:207–213
Liu Y, Terata K, Rusch NJ, et al. (2001) High glucose impairs voltage-gated K+ channel current in rat small coronary arteries. Circ Res 89:146–152
Nelson MT, Quayle JM (1995) Physiological roles and properties of potassium channels in arterial smooth muscle. Am J Phys 268:799–822
Nishida A, Takizawa T, Matsumoto A, et al. (2011) Inhibition of ATP-sensitive K+ channels and L-type Ca2+ channels by amiodarone elicits contradictory effect on insulin secretion in MIN6 cells. J Pharmacol Sci 116:73–80
Okabe K, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H (1987) Features of 4-aminopyridine sensitive outward current observed in single smooth muscle cells from the rabbit pulmonary artery. Pflügers Arch 409:561–568
Park WS, Son YK, Han J, et al. (2005a) Stauroporine inhibits voltage-dependent K+ current through a PKC-independent mechanism in isolated coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 45:260–269
Park WS, Son YK, Ko EA, et al. (2005b) The protein kinase C inhibitor, bisindolylmaleimide (I), inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels in coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 77:512–527
Park WS, Son YK, Ko EA, et al. (2010a) A carbohydrate fraction, AIP1, from Artemisia iwayomogi reduces the action potential duration by activation of rapidly activating delayed rectifier K channels in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 14:119–125
Park WS, Ko JH, Ko EA, et al. (2010b) The guanylyl cyclase activator YC-1 directly inhibits the voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Sci 112:64–72
Park MH, Son YK, Hong DH, et al. (2013) The Ca2+ channel inhibitor efonidipine decreases voltage-dependent K+ channel activity in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Vasc Pharmacol 59:90–95
Quayle JM, McCarron JG, Brayden JE, et al. (1993) Inward rectifier K+ currents in smooth muscle cells from rat resistance-sized cerebral arteries. Am J Phys 265:1363–1370
Snyders DJ, Yeola SW (1995) Determinants of antiarrhythmic drug action. Electrostatic and hydrophobic components of block of the human cardiac hKv 1.5 channel. Circ Res 77:575–583
Son YK, Park WS, Kim SJ, et al. (2006) Direct inhibition of a PKA inhibitor, H-89 on Kv channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:931–937
Son YK, Hong DH, Li H, et al. (2014) The Ca2+ channel inhibitor NNC 55-0396 inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Sci 19:312–319
Standen NB, Quayle JM (1998) K+ channel modulation in arterial smooth muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 164:549–557
Turker I, Yu CC, Chang PC, et al. (2013) Amiodarone inhibits apamin-sensitive potassium currents. PLoS One 8:e70450
Xu C, Lu Y, Tang G, et al. (1999) Expression of voltage-dependent K+ channel genes in mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells. Am J Phys 277:1055–1063
Yuan XJ (1995) Voltage-gated K+ currents regulate resting membrane potential and [Ca2+]i in pulmonary arterial myocytes. Circ Res 77:370–378
Yuan XJ, Wang J, Juhaszova M, et al. (1998) Molecular basis and function of voltage-gated K+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Phys 274:621–635
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Education: 2014-R1A1A4A01003840) (Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning: 2012-M3A9C7050184, 2015-R1A4A1038666).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures performed in studies involving animals were approved by the Committee for Animal Experiments of Kangwon National University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Kim, H.S., Kim, H.W. et al. The class III anti-arrhythmic agent, amiodarone, inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389, 713–721 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1232-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1232-8