Abstract
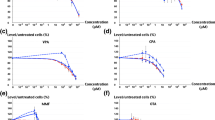
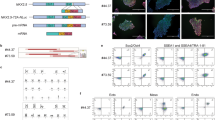
The first in vitro tests for developmental toxicity made use of rodent cells. Newer teratology tests, e.g. developed during the ESNATS project, use human cells and measure mechanistic endpoints (such as transcriptome changes). However, the toxicological implications of mechanistic parameters are hard to judge, without functional/morphological endpoints. To address this issue, we developed a new version of the human stem cell-based test STOP-tox(UKN). For this purpose, the capacity of the cells to self-organize to neural rosettes was assessed as functional endpoint: pluripotent stem cells were allowed to differentiate into neuroepithelial cells for 6 days in the presence or absence of toxicants. Then, both transcriptome changes were measured (standard STOP-tox(UKN)) and cells were allowed to form rosettes. After optimization of staining methods, an imaging algorithm for rosette quantification was implemented and used for an automated rosette formation assay (RoFA). Neural tube toxicants (like valproic acid), which are known to disturb human development at stages when rosette-forming cells are present, were used as positive controls. Established toxicants led to distinctly different tissue organization and differentiation stages. RoFA outcome and transcript changes largely correlated concerning (1) the concentration-dependence, (2) the time dependence, and (3) the set of positive hits identified amongst 24 potential toxicants. Using such comparative data, a prediction model for the RoFA was developed. The comparative analysis was also used to identify gene dysregulations that are particularly predictive for disturbed rosette formation. This ‘RoFA predictor gene set’ may be used for a simplified and less costly setup of the STOP-tox(UKN) assay.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AOP:
-
Adverse outcome pathway
- BMC25:
-
Benchmark concentration leading to 25% decrease compared to control
- BPA:
-
Bisphenol A
- BR:
-
Borderline range
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CsA:
-
Cyclosporin A
- DMSO:
-
Dimethylsulfoxide
- DNT:
-
Developmental neurotoxicity
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- HDACi:
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor
- IFNbeta:
-
Interferon beta
- KE:
-
Key events
- KNDP:
-
Key neurodevelopmental processes
- mEST:
-
Mouse embryonic stem cell test
- NAM:
-
New approach methods
- NCAM:
-
Neural cell adhesion molecule
- NDD:
-
Neurodevelopmental distance
- NEP:
-
Neuroepithelial precursor
- OECD:
-
Organization for economic co-operation and development
- PCMB:
-
P-chloromercuribenzoic acid
- PMA:
-
Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate
- PSC:
-
Pluripotent stem cells
- RA:
-
Retinoic acid
- REACH:
-
Registration, evaluation, authorisation and restriction of chemicals (EC 1907/2006)
- RoFA:
-
Rosette formation assay
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- STOP-tox(UKN) :
-
Stem cell-based teratogenic omics prediction-UKN toxicity assay (Shinde et al. 2016a), previously named:
- UKN1:
-
University of Konstanz (1) assay (Krug et al. 2013b)
- T:
-
Threshold
- TSA:
-
Trichostatin A
- U(T):
-
Uncertainty of threshold
- VPA:
-
Valproic acid
- Wnta:
-
Wnt activators
References
Aschner M, Ceccatelli S, Daneshian M, Fritsche E, Hasiwa N, Hartung T, Hogberg HT, Leist M, Li A, Mundi WR et al (2017) Reference compounds for alternative test methods to indicate developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) potential of chemicals: example lists and criteria for their selection and use. Altex 34:49–74
Baker N, Boobis A, Burgoon L, Carney E, Currie R, Fritsche E, Knudsen T, Laffont M, Piersma AH, Poole A et al (2018) Building a developmental toxicity ontology. Birth Defects Res 110:502–518
Bal-Price A, Fritsche E (2018) Editorial: developmental neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:1–2
Bal-Price A, Crofton KM, Leist M, Allen S, Arand M, Buetler T, Delrue N, FitzGerald RE, Hartung T, Heinonen T et al (2015) International STakeholder NETwork (ISTNET): creating a developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing road map for regulatory purposes. Arch Toxicol 89:269–287
Bal-Price A, Hogberg HT, Crofton KM, Daneshian M, FitzGerald RE, Fritsche E, Heinonen T, Hougaard Bennekou S, Klima S, Piersma AH et al (2018a) Recommendation on test readiness criteria for new approach methods in toxicology: exemplified for developmental neurotoxicity. Altex 35:306–352
Bal-Price A, Pistollato F, Sachana M, Bopp SK, Munn S, Worth A (2018b) Strategies to improve the regulatory assessment of developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) using in vitro methods. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:7–18
Balmer NV, Weng MK, Zimmer B, Ivanova VN, Chambers SM, Nikolaeva E, Jagtap S, Sachinidis A, Hescheler J, Waldmann T et al (2012) Epigenetic changes and disturbed neural development in a human embryonic stem cell-based model relating to the fetal valproate syndrome. Hum Mol Genet 21:4104–4114
Balmer NV, Klima S, Rempel E, Ivanova VN, Kolde R, Weng MK, Meganathan K, Henry M, Sachinidis A, Berthold MR et al (2014) From transient transcriptome responses to disturbed neurodevelopment: role of histone acetylation and methylation as epigenetic switch between reversible and irreversible drug effects. Arch Toxicol 88:1451–1468
Barenys M, Gassmann K, Baksmeier C, Heinz S, Reverte I, Schmuck M, Temme T, Bendt F, Zschauer TC, Rockel TD et al (2017) Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) inhibits adhesion and migration of neural progenitor cells in vitro. Arch Toxicol 91:827–837
Baumann J, Barenys M, Gassmann K, Fritsche E (2014) Comparative human and rat "neurosphere assay" for developmental neurotoxicity testing. Curr Protoc Toxicol 59:11–24
Baumann J, Gassmann K, Masjosthusmann S, DeBoer D, Bendt F, Giersiefer S, Fritsche E (2016) Comparative human and rat neurospheres reveal species differences in chemical effects on neurodevelopmental key events. Arch Toxicol 90:1415–1427
Beccari L, Moris N, Girgin M, Turner DA, Baillie-Johnson P, Cossy AC, Lutolf MP, Duboule D, Arias AM (2018) Multi-axial self-organization properties of mouse embryonic stem cells into gastruloids. Nature 562:272–276
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 57:289–300
Berthold MR, Cebron N, Dill F, Gabriel TR, Kötter T, Meinl T, Ohl P, Sieb C, Thiel K, Wiswedel B (2007) KNIME: The konstanz information miner. In: Preisach C, Burkhardt H, Schmidt-Thieme L, Decker R (eds) Data analysis, machine learning and applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 319–326
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Campbell CT, Sampathkumar SG, Yarema KJ (2007) Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering: perspectives, applications, and future directions. Mol Biosyst 3:187–194
Chambers SM, Fasano CA, Papapetrou EP, Tomishima M, Sadelain M, Studer L (2009) Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat Biotechnol 27:275–280
Chambers SM, Mica Y, Studer L, Tomishima MJ (2011) Converting human pluripotent stem cells to neural tissue and neurons to model neurodegeneration. Methods Mol Biol 793:87–97
Colleoni S, Galli C, Gaspar JA, Meganathan K, Jagtap S, Hescheler J, Sachinidis A, Lazzari G (2011) Development of a neural teratogenicity test based on human embryonic stem cells: response to retinoic acid exposure. Toxicol Sci 124:370–377
Conti L, Cattaneo E (2010) Neural stem cell systems: physiological players or in vitro entities? Nat Rev Neurosci 11:176–187
Corvi R, Vilardell M, Aubrecht J, Piersma A (2016) Validation of transcriptomics-based in vitro methods. Adv Exp Med Biol 856:243–257
Delp J, Gutbier S, Klima S, Hoelting L, Pinto-Gil K, Hsieh JH, Aichem M, Klein K, Schreiber F, Tice RR et al (2018) A high-throughput approach to identify specific neurotoxicants/developmental toxicants in human neuronal cell function assays. Altex 35:235–253
Dhara SK, Stice SL (2008) Neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem 105:633–640
Dhara SK, Hasneen K, Machacek DW, Boyd NL, Rao RR, Stice SL (2008) Human neural progenitor cells derived from embryonic stem cells in feeder-free cultures. Differentiation 76:454–464
Dreser N, Zimmer B, Dietz C, Sugis E, Pallocca G, Nyffeler J, Meisig J, Bluthgen N, Berthold MR, Waldmann T et al (2015) Grouping of histone deacetylase inhibitors and other toxicants disturbing neural crest migration by transcriptional profiling. Neurotoxicology 50:56–70
Elkabetz Y, Panagiotakos G, Al Shamy G, Socci ND, Tabar V, Studer L (2008) Human ES cell-derived neural rosettes reveal a functionally distinct early neural stem cell stage. Genes Dev 22:152–165
Fenech M (2000) The in vitro micronucleus technique. Mutat Res 455:81–95
Fenech M, Morley AA (1985) Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat Res 147:29–36
Frank CL, Brown JP, Wallace K, Mundy WR, Shafer TJ (2017) From the cover: developmental neurotoxicants disrupt activity in cortical networks on microelectrode arrays: results of screening 86 compounds during neural network formation. Toxicol Sci 160:121–135
Frank CL, Brown JP, Wallace K, Wambaugh JF, Shah I, Shafer TJ (2018) Defining toxicological tipping points in neuronal network development. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:81–93
Fritsche E, Crofton KM, Hernandez AF, Hougaard Bennekou S, Leist M, Bal-Price A, Reaves E, Wilks MF, Terron A, Solecki R et al (2017) OECD/EFSA workshop on developmental neurotoxicity (DNT): The use of non-animal test methods for regulatory purposes. Altex 34:311–315
Fritsche E, Barenys M, Klose J, Masjosthusmann S, Nimtz L, Schmuck M, Wuttke S, Tigges J (2018a) Development of the concept for stem cell-based developmental neurotoxicity evaluation. Toxicol Sci 165:14–20
Fritsche E, Grandjean P, Crofton KM, Aschner M, Goldberg A, Heinonen T, Hessel EVS, Hogberg HT, Bennekou SH, Lein PJ et al (2018b) Consensus statement on the need for innovation, transition and implementation of developmental neurotoxicity (DNT) testing for regulatory purposes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:3–6
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2006) Developmental neurotoxicity of industrial chemicals. Lancet 368:2167–2178
Grandjean P, Landrigan PJ (2014) Neurodevelopmental toxicity: still more questions than answers–authors' response. Lancet Neurol 13:648–649
Grinberg M, Stober RM, Edlund K, Rempel E, Godoy P, Reif R, Widera A, Madjar K, Schmidt-Heck W, Marchan R et al (2014) Toxicogenomics directory of chemically exposed human hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 88:2261–2287
Harbron C, Chang KM, South MC (2007) RefPlus: an R package extending the RMA algorithm. Bioinformatics 23:2493–2494
Harrill JA, Freudenrich T, Wallace K, Ball K, Shafer TJ, Mundy WR (2018) Testing for developmental neurotoxicity using a battery of in vitro assays for key cellular events in neurodevelopment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:24–39
Hartung T, Hoffmann S, Stephens M (2013) Mechanistic validation. Altex 30:119–130
Hermsen SA, Pronk TE, van den Brandhof EJ, van der Ven LT, Piersma AH (2013) Transcriptomic analysis in the developing zebrafish embryo after compound exposure: individual gene expression and pathway regulation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 272:161–171
Hoelting L, Klima S, Karreman C, Grinberg M, Meisig J, Henry M, Rotshteyn T, Rahnenfuhrer J, Bluthgen N, Sachinidis A et al (2016) Stem cell-derived immature human dorsal root ganglia neurons to identify peripheral neurotoxicants. Stem Cells Transl Med 5:476–487
Hunt PR, Olejnik N, Bailey KD, Vaught CA, Sprando RL (2018) C. elegans development and activity test detects mammalian developmental neurotoxins. Food Chem Toxicol 121:583–592
Jagtap S, Meganathan K, Gaspar J, Wagh V, Winkler J, Hescheler J, Sachinidis A (2011) Cytosine arabinoside induces ectoderm and inhibits mesoderm expression in human embryonic stem cells during multilineage differentiation. Br J Pharmacol 162:1743–1756
Johansson H, Lindstedt M, Albrekt AS, Borrebaeck CA (2011) A genomic biomarker signature can predict skin sensitizers using a cell-based in vitro alternative to animal tests. BMC Genom 12:399
Johansson H, Albrekt AS, Borrebaeck CA, Lindstedt M (2013) The GARD assay for assessment of chemical skin sensitizers. Toxicol In Vitro 27:1163–1169
Krebs A, Nyffeler J, Rahnenfuhrer J, Leist M (2018) Normalization of data for viability and relative cell function curves. Altex 35:268–271
Krug AK, Balmer NV, Matt F, Schonenberger F, Merhof D, Leist M (2013a) Evaluation of a human neurite growth assay as specific screen for developmental neurotoxicants. Arch Toxicol 87:2215–2231
Krug AK, Kolde R, Gaspar JA, Rempel E, Balmer NV, Meganathan K, Vojnits K, Baquie M, Waldmann T, Ensenat-Waser R et al (2013b) Human embryonic stem cell-derived test systems for developmental neurotoxicity: a transcriptomics approach. Arch Toxicol 87:123–143
Lancaster MA, Corsini NS, Wolfinger S, Gustafson EH, Phillips AW, Burkard TR, Otani T, Livesey FJ, Knoblich JA (2017) Guided self-organization and cortical plate formation in human brain organoids. Nat Biotechnol 35:659–666
Legler J, van den Brink CE, Brouwer A, Murk AJ, van der Saag PT, Vethaak AD, van der Burg B (1999) Development of a stably transfected estrogen receptor-mediated luciferase reporter gene assay in the human T47D breast cancer cell line. Toxicol Sci 48:55–66
Leist M, Ayrton AD, Ioannides C (1992) A cytosolic oxygenase activity involved in the bioactivation of 2-aminofluorene. Toxicology 71:7–20
Leist M, Hasiwa N, Daneshian M, Hartung T (2012a) Validation and quality control of replacement alternatives—current status and future challenges. Toxicol Res 1:8–22
Leist M, Lidbury BA, Yang C, Hayden PJ, Kelm JM, Ringeissen S, Detroyer A, Meunier JR, Rathman JF, Jackson GR Jr et al (2012b) Novel technologies and an overall strategy to allow hazard assessment and risk prediction of chemicals, cosmetics, and drugs with animal-free methods. Altex 29:373–388
Leist M, Hasiwa N, Rovida C, Daneshian M, Basketter D, Kimber I, Clewell H, Gocht T, Goldberg A, Busquet F et al (2014) Consensus report on the future of animal-free systemic toxicity testing. Altex 31:341–356
Leist M, Ghallab A, Graepel R, Marchan R, Hassan R, Bennekou SH, Limonciel A, Vinken M, Schildknecht S, Waldmann T et al (2017) Adverse outcome pathways: opportunities, limitations and open questions. Arch Toxicol 91:3477–3505
Leontaridou M, Urbisch D, Kolle SN, Ott K, Mulliner DS, Gabbert S, Landsiedel R (2017) The borderline range of toxicological methods: quantification and implications for evaluating precision. Altex 34:525–538
Leontaridou M, Gabbert S, Landsiedel R (2019) The impact of precision uncertainty on predictive accuracy metrics of non-animal testing methods. Altex 36:435–446
Li H, Bai J, Zhong G, Lin H, He C, Dai R, Du H, Huang L (2019) Improved defined approaches for predicting skin sensitization hazard and potency in humans. Altex 36:363–372
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
London L, Beseler C, Bouchard MF, Bellinger DC, Colosio C, Grandjean P, Harari R, Kootbodien T, Kromhout H, Little F et al (2012) Neurobehavioral and neurodevelopmental effects of pesticide exposures. Neurotoxicology 33:887–896
Mundy WR, Robinette B, Radio NM, Freudenrich TM (2008) Protein biomarkers associated with growth and synaptogenesis in a cell culture model of neuronal development. Toxicology 249:220–229
Murko C, Lagger S, Steiner M, Seiser C, Schoefer C, Pusch O (2013) Histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A induces neural tube defects and promotes neural crest specification in the chicken neural tube. Differentiation 85:55–66
New DA (1978) Whole-embryo culture and the study of mammalian embryos during organogenesis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 53:81–122
Nyffeler J, Dolde X, Krebs A, Pinto-Gil K, Pastor M, Behl M, Waldmann T, Leist M (2017a) Combination of multiple neural crest migration assays to identify environmental toxicants from a proof-of-concept chemical library. Arch Toxicol 91:3613–3632
Nyffeler J, Karreman C, Leisner H, Kim YJ, Lee G, Waldmann T, Leist M (2017b) Design of a high-throughput human neural crest cell migration assay to indicate potential developmental toxicants. Altex 34:75–94
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9:62–66
Pallocca G, Grinberg M, Henry M, Frickey T, Hengstler JG, Waldmann T, Sachinidis A, Rahnenfuhrer J, Leist M (2016) Identification of transcriptome signatures and biomarkers specific for potential developmental toxicants inhibiting human neural crest cell migration. Arch Toxicol 90:159–180
Piersma AH, Genschow E, Verhoef A, Spanjersberg MQ, Brown NA, Brady M, Burns A, Clemann N, Seiler A, Spielmann H (2004) Validation of the postimplantation rat whole-embryo culture test in the international ECVAM validation study on three in vitro embryotoxicity tests. Altern Lab Anim 32:275–307
Piersma AH, Bosgra S, van Duursen MB, Hermsen SA, Jonker LR, Kroese ED, van der Linden SC, Man H, Roelofs MJ, Schulpen SH et al (2013) Evaluation of an alternative in vitro test battery for detecting reproductive toxicants. Reprod Toxicol 38:53–64
Radio NM, Breier JM, Shafer TJ, Mundy WR (2008) Assessment of chemical effects on neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells using high content screening. Toxicol Sci 105:106–118
Rempel E, Hoelting L, Waldmann T, Balmer NV, Schildknecht S, Grinberg M, Das Gaspar JA, Shinde V, Stober R, Marchan R et al (2015) A transcriptome-based classifier to identify developmental toxicants by stem cell testing: design, validation and optimization for histone deacetylase inhibitors. Arch Toxicol 89:1599–1618
Schmidt BZ, Lehmann M, Gutbier S, Nembo E, Noel S, Smirnova L, Forsby A, Hescheler J, Avci HX, Hartung T et al (2017) In vitro acute and developmental neurotoxicity screening: an overview of cellular platforms and high-throughput technical possibilities. Arch Toxicol 91:1–33
Scholz S, Fischer S, Gundel U, Kuster E, Luckenbach T, Voelker D (2008) The zebrafish embryo model in environmental risk assessment–applications beyond acute toxicity testing. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 15:394–404
Seiler AE, Spielmann H (2011) The validated embryonic stem cell test to predict embryotoxicity in vitro. Nat Protoc 6:961–978
Shinde V, Klima S, Sureshkumar PS, Meganathan K, Jagtap S, Rempel E, Rahnenfuhrer J, Hengstler JG, Waldmann T, Hescheler J et al (2015) Human pluripotent stem cell based developmental toxicity assays for chemical safety screening and systems biology data generation. J Vis Exp 100:e52333
Shinde V, Hoelting L, Srinivasan SP, Meisig J, Meganathan K, Jagtap S, Grinberg M, Liebing J, Bluethgen N, Rahnenfuhrer J et al (2016a) Definition of transcriptome-based indices for quantitative characterization of chemically disturbed stem cell development: introduction of the STOP-Tox and STOP-Tox tests. Arch Toxicol 91:839–864
Shinde V, Perumal Srinivasan S, Henry M, Rotshteyn T, Hescheler J, Rahnenfuhrer J, Grinberg M, Meisig J, Bluthgen N, Waldmann T et al (2016b) Comparison of a teratogenic transcriptome-based predictive test based on human embryonic versus inducible pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 7:190
Sletten EM, Bertozzi CR (2009) Bioorthogonal chemistry: fishing for selectivity in a sea of functionality. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48:6974–6998
Smirnova L, Hogberg HT, Leist M, Hartung T (2014) Developmental neurotoxicity—challenges in the 21st century and in vitro opportunities. Altex 31:129–156
Spate AK, Busskamp H, Niederwieser A, Schart VF, Marx A, Wittmann V (2014) Rapid labeling of metabolically engineered cell-surface glycoconjugates with a carbamate-linked cyclopropene reporter. Bioconjug Chem 25:147–154
Stiegler NV, Krug AK, Matt F, Leist M (2011) Assessment of chemical-induced impairment of human neurite outgrowth by multiparametric live cell imaging in high-density cultures. Toxicol Sci 121:73–87
Terron A, Bennekou SH (2018) Towards a regulatory use of alternative developmental neurotoxicity testing (DNT). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 354:19–23
Tonk EC, Robinson JF, Verhoef A, Theunissen PT, Pennings JL, Piersma AH (2013) Valproic acid-induced gene expression responses in rat whole embryo culture and comparison across in vitro developmental and non-developmental models. Reprod Toxicol 41:57–66
Tonk EC, Pennings JL, Piersma AH (2015) An adverse outcome pathway framework for neural tube and axial defects mediated by modulation of retinoic acid homeostasis. Reprod Toxicol 55:104–113
van der Burg B, van der Linden S, Man H, Winter R, Jonker L, van Vugt‐Lussenburg B, Brouwe A (2013) A panel of quantitative calux® reporter gene assays for reliable high-throughput toxicity screening of chemicals and complex mixtures. In High‐throughput screening methods in toxicity testing, pp 519–532
van der Linden SC, von Bergh AR, van Vught-Lussenburg BM, Jonker LR, Teunis M, Krul CA, van der Burg B (2014) Development of a panel of high-throughput reporter-gene assays to detect genotoxicity and oxidative stress. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 760:23–32
van Thriel C, Westerink RH, Beste C, Bale AS, Lein PJ, Leist M (2012) Translating neurobehavioural endpoints of developmental neurotoxicity tests into in vitro assays and readouts. Neurotoxicology 33:911–924
van Vliet E, Kuhnl J, Goebel C, Martinozzi-Teissier S, Alepee N, Ashikaga T, Blomeke B, Del Bufalo A, Cluzel M, Corsini E et al (2018) State-of-the-art and new options to assess T cell activation by skin sensitizers: cosmetics Europe workshop. Altex 35:179–192
Waldmann T, Rempel E, Balmer NV, Konig A, Kolde R, Gaspar JA, Henry M, Hescheler J, Sachinidis A, Rahnenfuhrer J et al (2014) Design principles of concentration-dependent transcriptome deviations in drug-exposed differentiating stem cells. Chem Res Toxicol 27:408–420
Waldmann T, Grinberg M, Konig A, Rempel E, Schildknecht S, Henry M, Holzer AK, Dreser N, Shinde V, Sachinidis A et al (2017) Stem cell transcriptome responses and corresponding biomarkers that indicate the transition from adaptive responses to cytotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol 30:905–922
Walmsley RM (2008) GADD45a-GFP GreenScreen HC genotoxicity screening assay. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4:827–835
Weigt S, Huebler N, Braunbeck T, von Landenberg F, Broschard TH (2010) Zebrafish teratogenicity test with metabolic activation (mDarT): effects of phase I activation of acetaminophen on zebrafish Danio rerio embryos. Toxicology 275:36–49
Weng MK, Zimmer B, Poltl D, Broeg MP, Ivanova V, Gaspar JA, Sachinidis A, Wullner U, Waldmann T, Leist M (2012) Extensive transcriptional regulation of chromatin modifiers during human neurodevelopment. PLoS ONE 7:e36708
Zhang X, Huang CT, Chen J, Pankratz MT, Xi J, Li J, Yang Y, Lavaute TM, Li XJ, Ayala M et al (2010) Pax6 is a human neuroectoderm cell fate determinant. Cell Stem Cell 7:90–100
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Land BW, the Doerenkamp-Zbinden foundation, the DFG (RTG1331, KoRS-CB) and the Projects from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme EU-ToxRisk (Grant agreement No 681002) and ENDpoiNTs (Grant agreement No 825759). We are grateful to H. Leisner and D. Fischer and the staff of the bioimaging center (BIC) for invaluable experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dreser, N., Madjar, K., Holzer, AK. et al. Development of a neural rosette formation assay (RoFA) to identify neurodevelopmental toxicants and to characterize their transcriptome disturbances. Arch Toxicol 94, 151–171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02612-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02612-5