Abstract
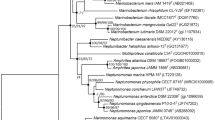
A Gram-negative, aerobic, non-motile, and rod-shaped bacterial strain, designated BSSL-BM10T, was isolated from sand of a dune that was collected from the Yellow Sea, Republic of Korea. It was subjected to a polyphasic taxonomic study. 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis showed that strain BSSL-BM10T fell phylogenetically within the radiation comprising type strains of Devosia species. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain BSSL-BM10T shared sequence similarities of 98.2% with the type strain of D. naphthalenivorans and 93.5–97.7% with type strains of other Devosia species. ANI and dDDH values between strain BSSL-BM10T and type strains of 18 Devosia species were 71.0–78.4% and 18.8–21.5%, respectively. The DNA G + C content of strain BSSL-BM10T was 60.9% based on its genomic sequence data. Strain BSSL-BM10T contained Q-10 as the predominant ubiquinone and 11-methyl C18:1 ω7c, C18:1 ω7c, summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c), and C16:0 as its major fatty acids. Major polar lipids of strain BSSL-BM10T were phosphatidylglycerol and two unidentified glycolipids. Strain BSSL-BM10T showed distinguishable phenotypic properties with its phylogenetic and genetic distinctiveness separated from recognized Devosia species. Based on data presented in this study, strain BSSL-BM10T should be placed in the genus Devosia. The name Devosia litorisediminis sp. nov. is proposed for strain BSSL-BM10T (= KACC 21633T = NBRC 115152T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- dDDH:
-
Digital DNA–DNA hybridization
- GC:
-
Gas chromatograph
References
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kuliko AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Phan S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Barrow GI, Feltham RKA (1993) Cowan and Steel’s Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria In: G. I. Barrow, R. K. A. Feltham Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511527104
Bautista VV, Monsalud RG, Yokota A (2010) Devosia yakushimensis sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:627–632. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.011254-0
Bruns A, Rohde M, Berthe-Corti L (2001) Muricauda ruestringensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultatively anaerobic, appendaged bacterium from German North Sea intertidal sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1997–2006. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-6-1997
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu XW, De Meyer SD, Trujillo ME (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002516
Embley TM, Wait R (1994) Structural lipids of eubacteria. In: Goodfellow M, O’Donnell AG (eds) Modern Microbial Methods. Chemical Methods in Prokaryotic Systematics. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp 121–161
Galatis H, Martin K, Kämpfer P, Glaeser SP (2013) Devosia epidermidihirudinis sp. nov. isolated from the surface of a medical leech. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:1165–1171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9895-3
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA–DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0
Hördt A, López MG, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Schleuning M, Weinhold LM, Tindall BJ, Gronow S, Kyrpides NC, Woyke T, Göker M (2020) Analysis of 1000+ type-strain genomes substantially improves taxonomic classification of Alphaproteobacteria. Front Microbiol 11:468. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00468
Jia YY, Sun C, Pan J, Zhang WY, Zhang XQ, Huo YY, Zhu XF, Wu M (2014) Devosia pacifica sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2637–2641. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.059626-0
Kämpfer P, Steiof M, Dott W (1991) Microbiological characterization of a fuel-oil contaminated site including numerical identification of heterotrophic water and soil bacteria. Microb Ecol 21:227–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539156
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.059774-0
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70410-0
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005) Genomic insights that advance the species definition for prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2567–2572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409727102
Kumar M, Verma M, Lal R (2008) Devosia chinhatensis sp. nov., isolated from a hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) dump site in India. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:861–865. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65574-0
Lányí B (1987) Classical and rapid identification methods for medically important bacteria. Methods Microbiol 19:1–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70407-0
Lee I, Chalita M, Ha SM, Na SI, Yoon SH, Chun J (2017) ContEst16S: an algorithm that identifies contaminated prokaryotic genomes using 16S RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2053–2057. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001872
Lefort V, Desper R, Gascuel O (2015) FastME 2.0: A comprehensive, accurate, and fast distance-based phylogeny inference program. Mol Biol Evol 32:2798–2800. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msv150
Lin D, Huang Y, Chen Y, Zhu S, Yang J, Chen J (2020) Devosia indica sp. nov., isolated from surface seawater in the Indian Ocean. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:340–345. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003759
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinforma 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Nakagawa Y, Sakane T, Yokota A (1996) Transfer of “Pseudomonas riboflavina” (Foster 1944), a gram-negative, motile rod with long-chain 3-hydroxy fatty acids, to Devosia riboflavina gen. nov., sp. nov., nom. rev. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-46-1-16
Park S, Won SM, Kim H, Park DS, Yoon JH (2014) Aestuariivita boseongensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2969–2974. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.062406-0
Park S, Jung YT, Kim S, Yoon JH (2016) Devosia confluentis sp. nov., isolated from the junction between the ocean and a freshwater lake, and reclassification of two Vasilyevaea species as Devosia enhydra comb. nov. and Devosia mishustinii comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:3935–3941. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001291
Parte AC (2018) LPSN-List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (bacterio.net), 20 years on. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1825–1829. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002786
Quan XT, Siddiqi MZ, Liu QZ, Lee SM, Im WT (2020) Devosia ginsengisoli sp. nov., isolated from ginseng cultivation soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:1489–1495. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003843
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Glöckner FO, Peplies J (2015) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32(6):929–931. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv681
Romanenko LA, Tanaka N, Svetashev VI (2013) Devosia submarina sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea surface sediments. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3079–3085. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.046607-0
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Inc, MIDI Technical Note 101. Newark, DE
Yoon JH, Lee ST, Kim SB, Kim WY, Goodfellow M, Park YH (1997) Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified 16S ribosomal DNA for rapid identification of Saccharomonospora strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:111–114. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-47-1-111
Yoon JH, Kim H, Kim IG, Kang KH, Park YH (2003) Erythrobacter flavus sp. nov., a slight halophile from the East Sea in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1169–1174. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02510-0
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Park S, Oh TK (2007) Devosia insulae sp. nov., isolated from soil, and emended description of the genus Devosia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1310–1314. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65028-0
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Zhang DC, Redzic M, Liu HC, Zhou YG, Schinner F, Margesin R (2012) Devosia psychrophila sp. nov. and Devosia glacialis sp. nov., from alpine glacier cryoconite, and an emended description of the genus Devosia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:710–715. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.023937-0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the project on survey of indigenous species of Korea of the National Institute of Biological Resources (NIBR) under the Ministry of Environment (MOE) and "Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ014442)" of Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Funding
National Institute of Biological Resources, project on survey of indigenous species of Korea, Jung-Hoon Yoon, Rural Development Administration, PJ014442, Jung-Hoon Yoon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Seo, M.J., Kim, W. et al. Devosia litorisediminis sp. nov., isolated from a sand dune. Arch Microbiol 204, 623 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03181-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03181-5