Abstract
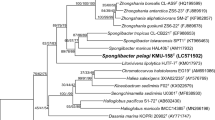
A study based on a polyphasic taxonomic approach was carried out to identify and classify a novel marine alphaproteobacterium, designated as KMU-140T, isolated from coastal seawater collected at Jeju Island, Republic of Korea. Cells of strain KMU-140T were spherical, Gram-stain-negative, reddish-orange colored, strictly aerobic, catalase- and oxidase-positive, non-motile, and chemoorganoheterotrophic. The novel isolate was able to grow at NaCl concentrations of 0–5%, pH 6.0–9.5, and 10–45 °C. A phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence showed that strain KMU-140T belongs to the family Erythrobacteraceae and was most closely related to Erythrobacter longus OCh101T (98.7%). Strain KMU-140T contained ubiquinone-10 (Q-10) as the only respiratory quinone and C18:1 ω7c, iso-C18:0, and C16:0 as the main (> 10%) cellular fatty acids. Strain KMU-140T produced carotenoid compounds that rendered the cell biomass a reddish-orange color. The assembled draft genome size of strain KMU-140T was 3.04 Mbp with G + C content of 60.6 mol%. The average nucleotide identity (ANI), digital DNA–DNA hybridization (dDDH), and average amino acid identity (AAI) values of KMU-140T and the species of the genus Erythrobacter were found to be 76.6–78.4%, 14.0–18.7%, and 69.6–77.8%, respectively. Phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, an unidentified phospholipid, and two unidentified lipids were identified as major polar lipids. On the basis of the polyphasic taxonomic features presented, the strain is considered to represent a novel species of the genus Erythrobacter for which the name Erythrobacter rubeus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain of E. rubeus sp. nov. is KMU-140T (= KCCM 90479T = NBRC 115159T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All other data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Atlas RM (1993) Handbook of microbiological media. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420039726
Britton G, Liaaen-Jensen S, Pfander H (2004) Carotenoids handbook. Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760410001727849
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu XW, De Meyer S, Trujillo ME (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002516
Collins MD, Jones D (1981) A note on the separation of natural mixtures of bacterial ubiquinones using reverse-phase partition thin-layer chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography. J Appl Bacteriol 51:129–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00916.x
Colwell RR (1970) Polyphasic taxonomy of the genus Vibrio: numerical taxonomy of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and related Vibrio species. J Bacteriol 104:410–433. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.104.1.410-433.1970
Fang C, Wu YH, Sun C, Wang H, Cheng H, Meng FX, Wang CS, Xu XW (2019) Erythrobacter zhengii sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from deep-sea sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003136
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408678
Fitch WM (1971) Towards defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416. https://doi.org/10.2307/2412116
Fraser PD, Bramley PM (2004) The biosynthesis and nutritional uses of carotenoids. Prog Lipid Res 43:228–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2003.10.002
Fuerst JA, Hawkins JA, Holmes A, Sly LI, Moore CJ, Stackebrandt E (1993) Porphyrobacter neustonensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic bacteriochlorophyll-synthesizing budding bacterium from fresh water. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-43-1-125
Galasso C, Corinaldesi C, Sansone C (2017) Carotenoids from marine organisms: biological functions and industrial applications. Antioxidants (basel) 23(6):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox6040096
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through the comparative studies of sequence evolution. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Komagata K, Suzuki K (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70410-0
Konstantinidis KT, Tiedje JM (2005) Genomic insights that advance the species definition for prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2567–2572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409727102
Kristyanto S, Lee SD, Kim J (2017) Porphyrobacter algicida sp. nov., an algalytic bacterium isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4526–4533. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002324
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Lee KB, Liu CT, Anzai Y, Kim H, Aono T, Oyaizu H (2005) The hierarchical system of the ‘Alphaproteobacteria’: description of Hyphomonadaceae fam. nov., Xanthobacteraceae fam. nov. and Erythrobacteraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1907–1919. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63663-0
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Klenk HP, Göker M (2014) Taxonomic use of DNA G+C content and DNA–DNA hybridization in the genomic age. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:352–356. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.056994-0
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinines and polar lipids. J Microbiol Meth 2:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Nurk S, Bankevich A, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Korobeynikov A, Lapidus A, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin A, Sirotkin A, Sirotkin Y, Stepanauskas R, Clingenpeel SR, Woyke T, McLean JS, Lasken R, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2013) Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J Comput Biol 20:714–737. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2013.0084
Park S, Chen S, Yoon JH (2020) Erythrobacter insulae sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:1470–1477. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003824
Power DA, Johnson JA (2009) Difco™ and BBL™ manual: manual of microbiological culture media, 2nd edn. Becton Dickinson and Company, Sparks, pp 359–360 (ISBN 0-9727207-1-5)
Rainey FA, Silva J, Nobre MF, Silva MT, da Costa MS (2003) Porphyrobacter cryptus sp. nov., a novel slightly thermophilic, aerobic, bacteriochlorophyll a-containing species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:35–41. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02308-0
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2014) Bypassing cultivation to identify bacterial species. Microbe 9:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbe.9.111.1
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Shiba T, Simidu U (1982) Erythrobacter longus gen. nov., sp. nov., an aerobic bacterium which contains bacteriochlorophyll a. Int J Syst Bacteriol 32:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-32-2-211
Shindo K, Misawa N (2014) New and rare carotenoids isolated from marine bacteria and their antioxidant activities. Mar Drugs 24(12):1690–1698. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12031690
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44:6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569
Ten LN, Im WT, Kim MK, Kang MS, Lee ST (2004) Development of a plate technique for screening of polysaccharide-degrading microorganisms by using a mixture of insoluble chromogenic substrates. J Microbiol Methods 56:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2003.11.008
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Tonon LAC, Moreira APB, Thompson F (2014) The family Erythrobacteraceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria, 4th edn. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-30197-1_376
Xu M, Xin Y, Yu Y, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Liu H, Tian J, Li Y (2010) Erythrobacter nanhaisediminis sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment of the South China Sea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2215–2220. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.014027-0
Xu L, Sun C, Fang C, Oren A, Xu XW (2020) Genomic-based taxonomic classification of the family Erythrobacteraceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:4470–4495. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004293
Yoon BJ, Lee DH, Oh DC (2013) Erythrobacter jejuensis sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1421–1426. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.038349-0
Yoon J, Lee KC, Lee JS (2016) Cribrihabitans pelagius sp. nov., a marine alphaproteobacterium isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:3195–3200. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001171
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA and whole genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Yoon J, Yasumoto-Hirose M, Kasai H (2021) Identification and classification of Croceivirga thetidis sp. nov., a marine Flavobacteriaceae isolated from the hard coral Acropora. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 114:1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01611-w
Yurkov V, Stackebrandt E, Holmes A, Fuerst JA, Hugenholtz P, Golecki J, Gad’on N, Gorlenko VM, Kompantseva EI, Drews G (1994) Phylogenetic positions of novel aerobic, bacteriochlorophyll a-containing bacteria and description of Roseococcus thiosulfatophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., Erythromicrobium ramosum gen. nov., sp. nov., and Erythrobacter litoralis sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:427–434. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-44-3-427
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: JY. Performed the experiments: JY, EYL. Analyzed the data: JY, EYL, SJN. Wrote the paper: JY, SJN.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
203_2021_2736_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 1 A two-dimensional thin-layer chromatogram showing the total polar lipid compositions of KMU-140T and the reference strain. Total polar lipids were detected by spraying the plate with molybdatophosphoric acid. PE: phosphatidylethanolamine, PC: phosphatidylcholine, PG: phosphatidylglycerol, PL: unidentified phospholipid, L: unidentified lipid (PDF 92 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, J., Lee, EY. & Nam, SJ. Erythrobacter rubeus sp. nov., a carotenoid-producing alphaproteobacterium isolated from coastal seawater. Arch Microbiol 204, 125 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02736-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02736-2